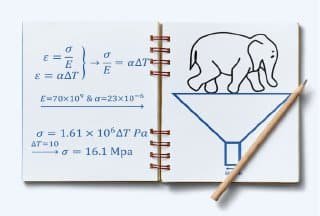
Confession Time: I sometimes totally underestimate thermal expansion it looks so innocent on paper! 🤓 Let’s break it down: We’ve all seen that classic formula strain = ΔT × α, where α (alpha) is the material’s “how much do I expand when heated?” number. For aluminum, α is 23e-6 /°C which looks ridiculously tiny, like a decimal point took a vacation! At first glance, you’d think, “Pfft, 0.000023 per degree? That’s nothing!”
Now, let’s mix the drama! If we combine this with our thermal strain equation (strain = ΔT × α), things get spicy:
ΔT * 23e-6 * 70e9 = Stress.
Simplifying this, we find:
Stress = 1.61e6 * ΔT.
Here’s the fun part: Just a 10°C temperature jump can create a whopping 16.1 MPa of stress! To wrap your head around that, imagine diving 160 meters deep underwater—that’s the kind of pressure we’re talking about. Or picture this: if you heated up a tiny aluminum cube (say, 5cm x 5cm), you’d need an entire elephant standing on it to stop it from expanding.
Wait, why is heating stuff up so… powerful? Let’s zoom in on the atomic dance party! When things get hotter, atoms get super energetic—they start jiggling around more and need extra space to party. But if you lock them in place (like clamping a material down), they’re basically shouting, “Let us move!” Think of it like holding back a crowd of hyper toddlers after a sugar rush—there’s going to be a lot of pushing. That collective atomic frustration? That’s what creates massive forces!
So here’s the big idea: Thermal expansion packs a punch because trillions of tiny atoms are all trying to stretch their legs at once. When you stop them, their teamwork adds up to huge stresses. And that’s why I cheekily named this section… well, you get it now. 😉