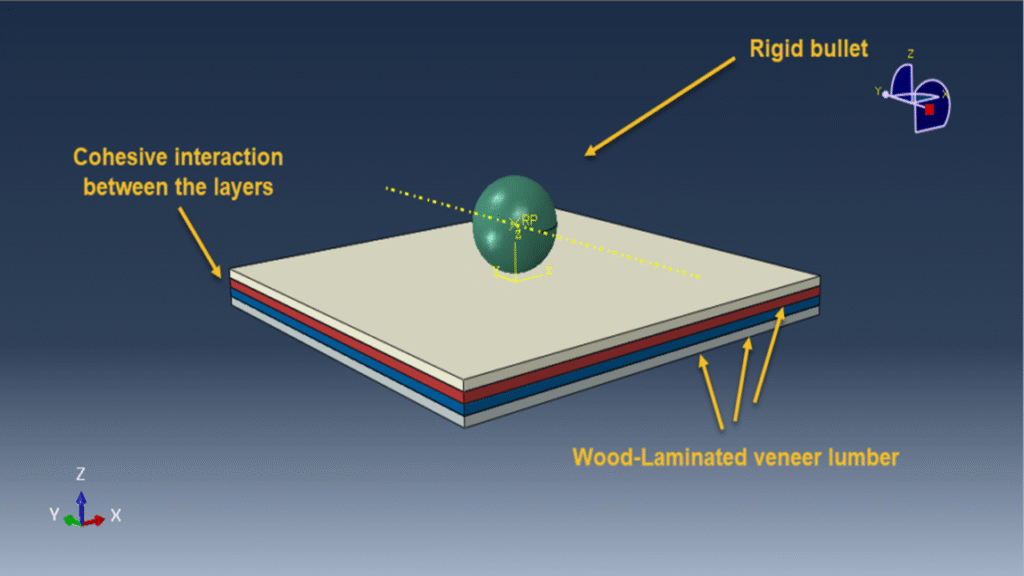
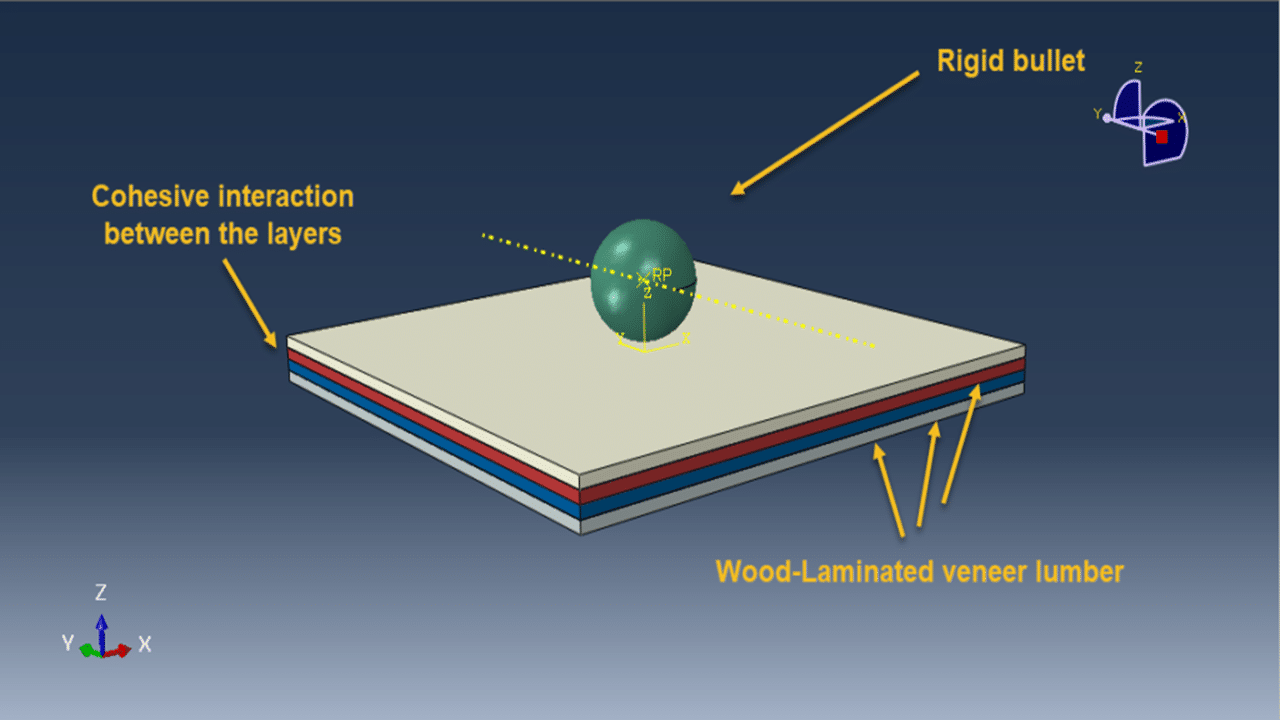
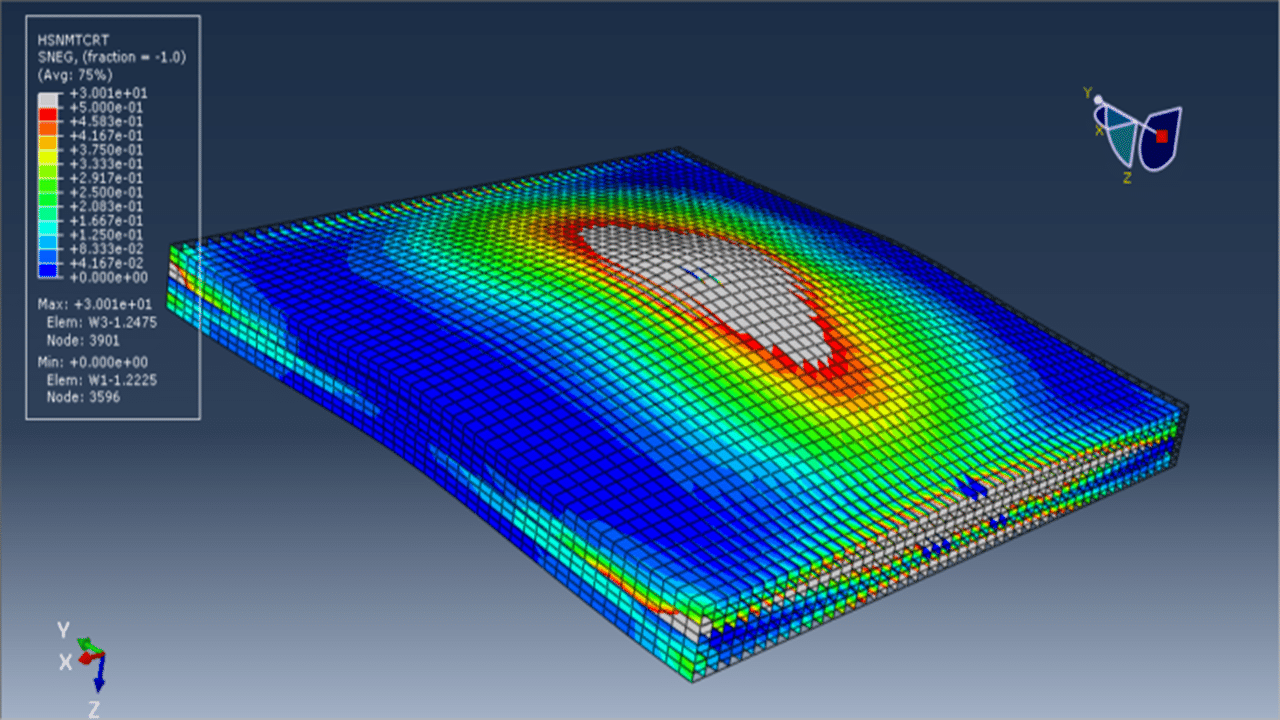
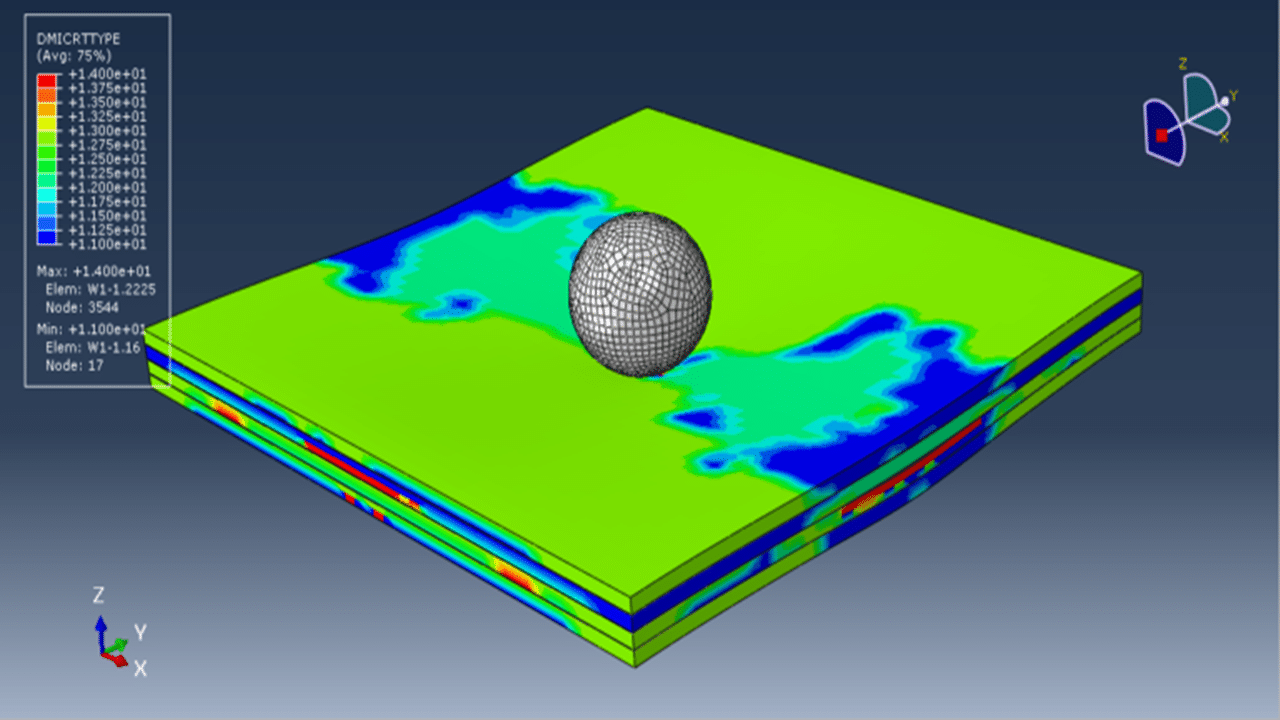
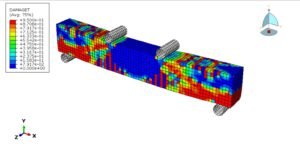
In this tutorial, the simulation of low-energy impact on a multilayered wood panel in Abaqus for damage investigation has been performed. A rigid impactor, modeled as a three-dimensional shell part with a defined mass, strikes the wood panel. Each layer of the wood panel is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part, with cohesive interactions defined between layers to simulate interlaminar bonding and failure.
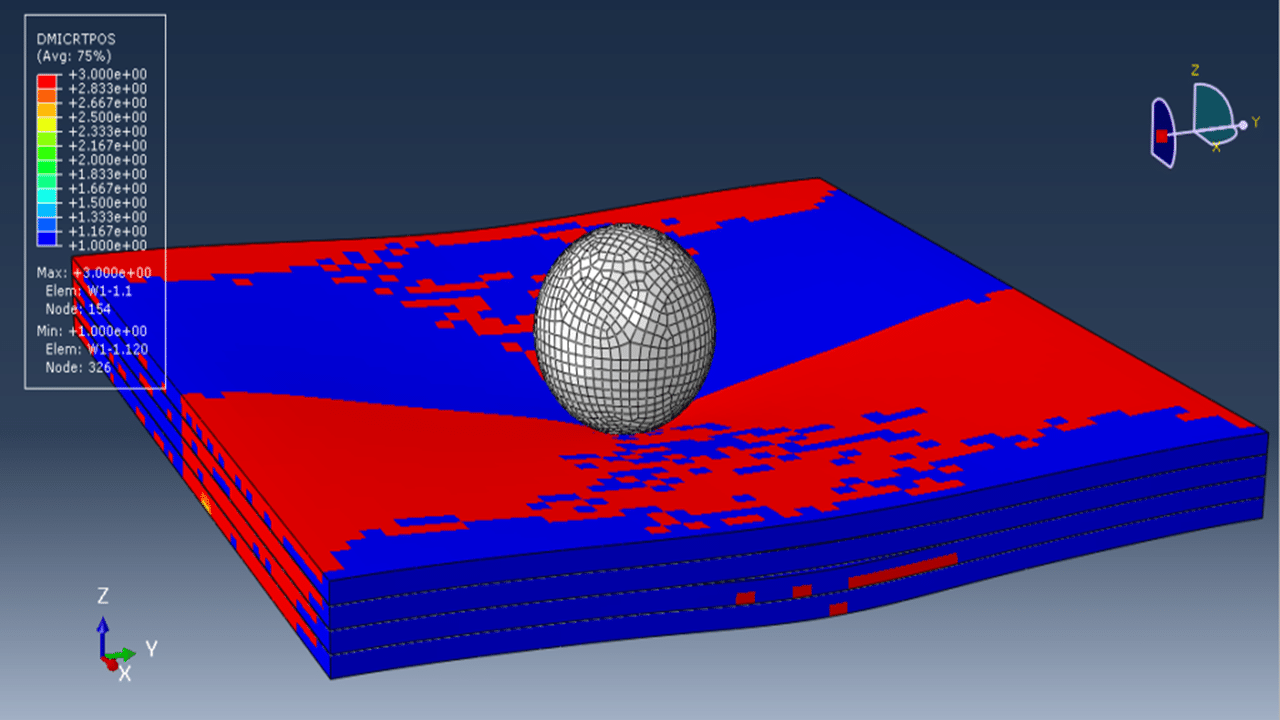
To accurately capture material degradation under impact, the Hashin damage criteria are employed, which are suitable for fiber-reinforced composites and adapted here for wood behavior. These criteria address four primary damage modes: fiber tension, fiber compression, matrix tension, and matrix compression. For the material behavior of wood, an elastic model is used along with plasticity defined via Hill’s yield criterion, enabling the modeling of anisotropic yielding.
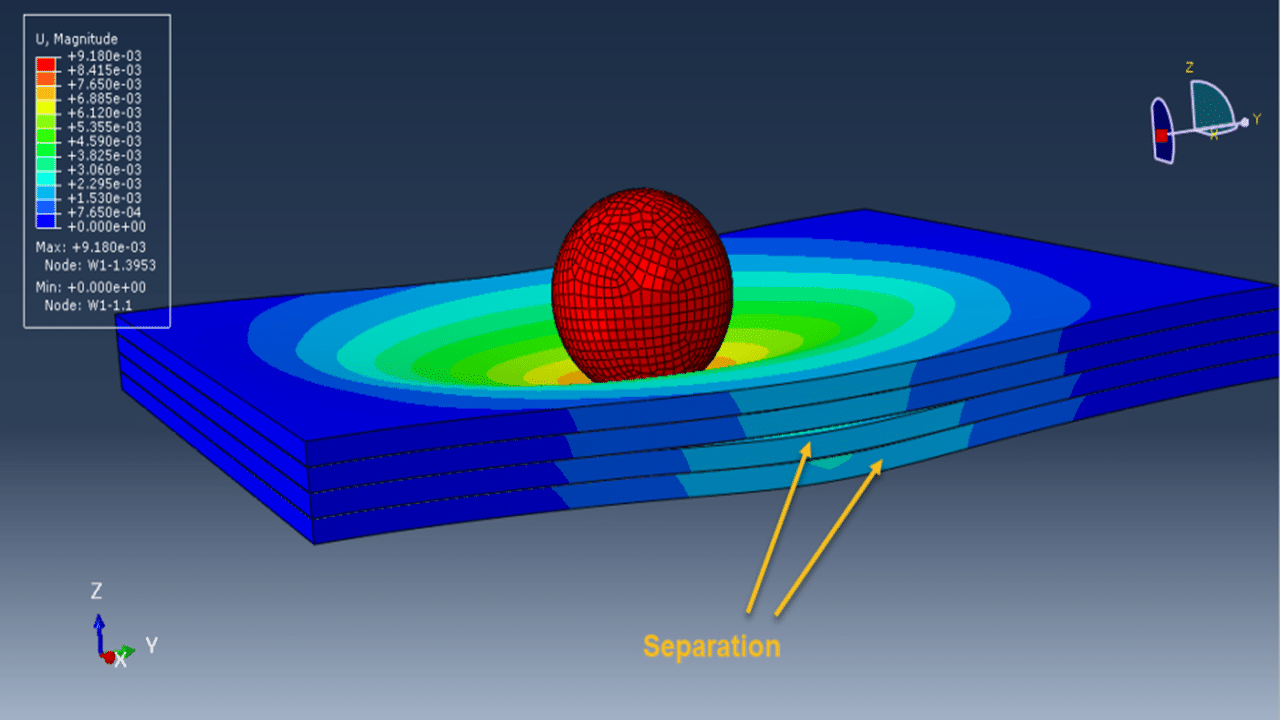
The simulation is carried out using a dynamic explicit step with general contact capability. Cohesive behavior is defined between layers through appropriate stiffness, damage initiation, and evolution properties to simulate delamination or interlayer failure. The rigid impactor is given an initial velocity, and fixed boundary conditions are applied to the sides of the wood panel. A refined mesh is used to ensure accurate stress and damage predictions.
After the simulation, detailed results such as stress, strain, damage and failure modes are available for interpretation and analysis.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?