Introduction to Water and Air Simulation and Analysis in Abaqus
1. Overview
Abaqus is a powerful finite element analysis (FEA) software that allows simulation of solid mechanics, fluid interactions, and coupled physical phenomena. While it is primarily a structural analysis tool, Abaqus also provides capabilities to model fluid-like behavior, such as water and air, through specialized methods. These simulations are crucial in engineering fields such as offshore structures, civil engineering (dams, breakwaters), aerospace (aerodynamic loading), and automotive (airbag deployment, water sloshing in fuel tanks).
This package includes the SPH, CEL, Acoustic, and Lagrangian models for water and air. Through 22 practical tutorials, you’ll learn all about the matter in Abaqus.
2. Water and Air analysis in Abaqus
a. Air (Compressible Gas)
- Modeled as a compressible fluid using the Eulerian approach.
- Applications:
- Airbag inflation.
- Blast wave propagation.
- Aerodynamic pressure loading.
- Typically uses:
- Eulerian analysis (Abaqus/Explicit).
- Acoustic analysis (for sound propagation in air).
b. Water (Incompressible or Slightly Compressible Fluid)
- Water is nearly incompressible and often modeled as such.
- Available modeling techniques in Abaqus:
- Acoustic Elements – for pressure wave propagation in water (e.g., sonar, underwater blast).
- Eulerian Formulation – to simulate free-surface water flow, sloshing, and impact on structures.
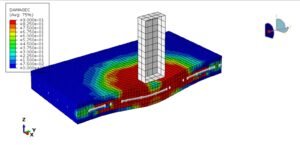
- Coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian (CEL) – combines fluid motion (Eulerian) with structural response (Lagrangian). Ideal for water–structure interaction problems.
- Hydrostatic Pressure Loading – simplified representation of static water pressure on structures like dams and tanks.
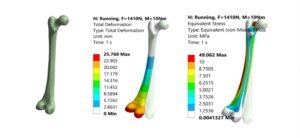
3. Coupled Fluid–Structure Interaction (FSI)
- Abaqus can couple fluids (water/air) with solids using:
- CEL method → for strong interactions like sloshing, impact, or blast.
- Acoustic–structural coupling → for sound waves in fluids interacting with structures.
- Example applications:
- Ship hull impact with water waves.
- Underwater explosion effects on submarines.
- Wind (air) loading on flexible membranes.
4. Common Applications
- Water
- Wave loading on offshore platforms.
- Sloshing in tanks (marine, automotive).
- Underwater blast or shock wave propagation.
- Hydraulic pressure on dams or gates.
- Air
- Airbag deployment (gas expansion and interaction with fabric).
- Blast wave simulation in air.
- Aeroacoustics (sound radiation, noise studies).
5. Limitations
- Abaqus is not a full Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) tool.
- Air and water simulations are simplified compared to specialized CFD solvers (like Fluent, OpenFOAM, or STAR-CCM+).
- Best suited for fluid–structure interaction problems where structural response is equally important.
In short:
Abaqus provides robust tools to simulate the effects of water and air on structures using methods such as acoustic elements, Eulerian formulations, and CEL techniques. It is extreme for FSI problems where traditional CFD codes may not easily capture the structural response.