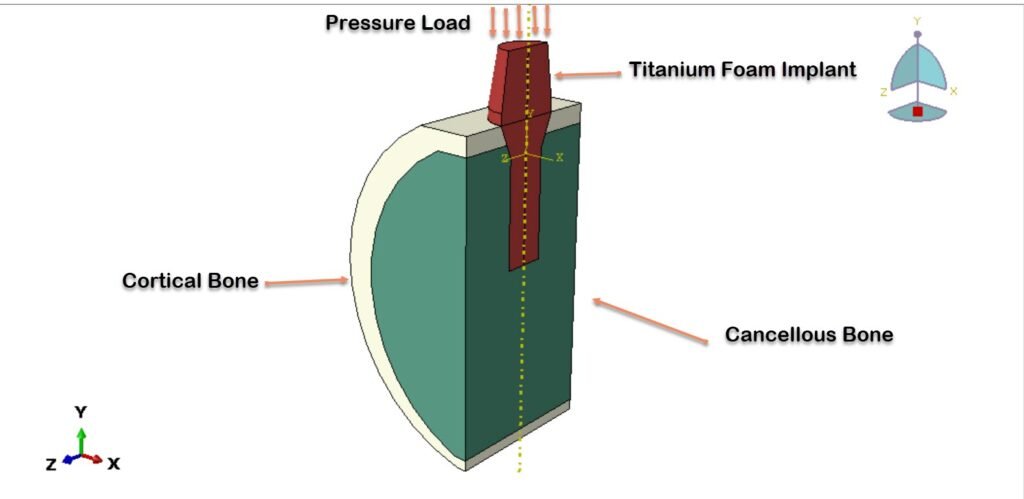
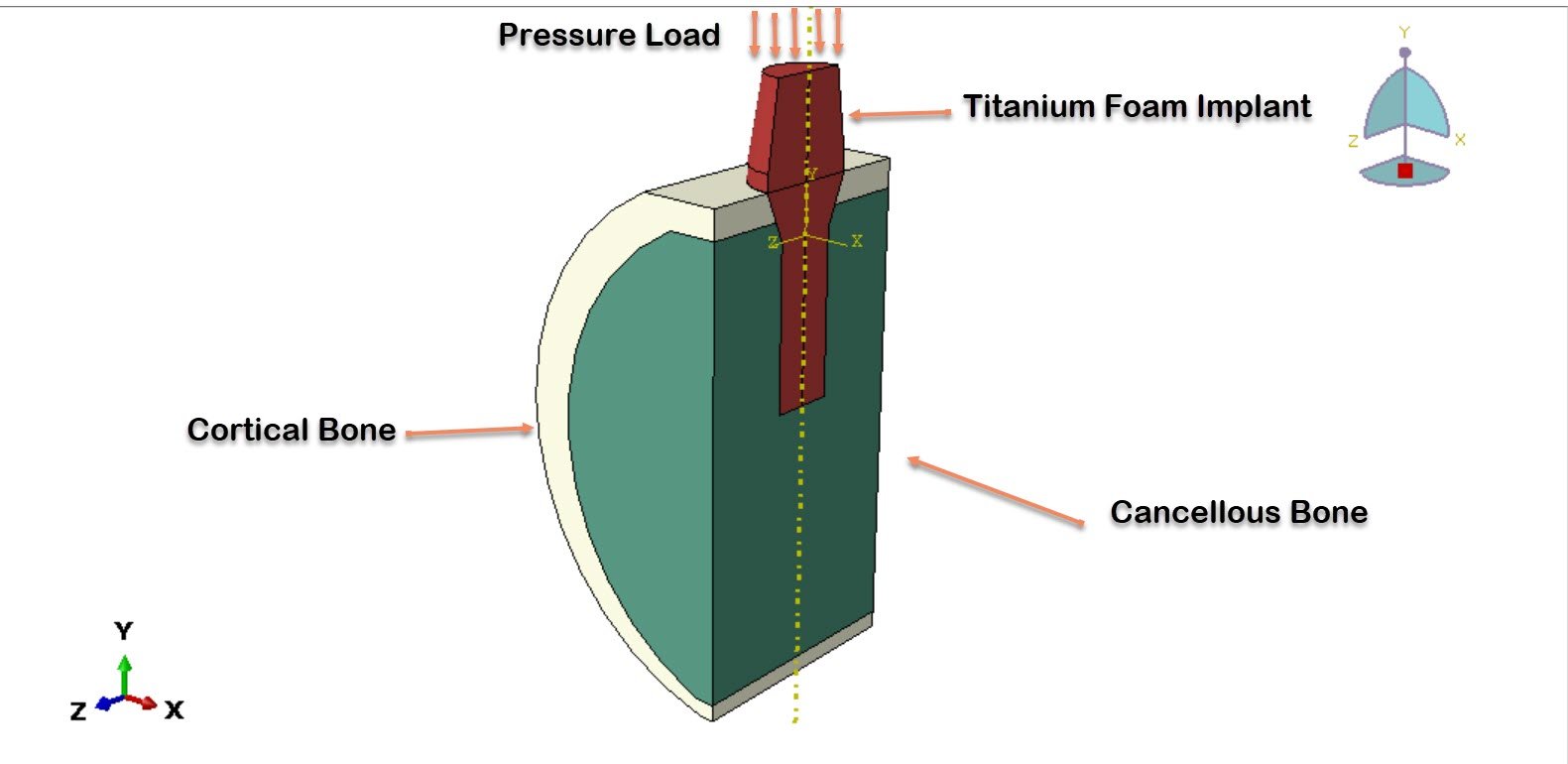
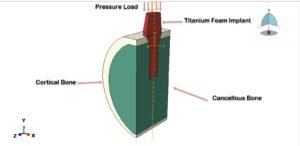
Dental implants are widely used to restore missing teeth and to re-establish oral function and aesthetics. The long-term success of an implant depends primarily on effective load transfer between the implant and surrounding bone, as well as on the quality of osseointegration. Conventional solid titanium implants possess high strength and excellent biocompatibility; however, their elastic modulus is significantly higher than that of natural bone. This mismatch in stiffness may lead to stress shielding, bone resorption, and eventual implant failure.
To overcome these limitations, porous titanium foam implants have gained attention in dental biomechanics. Titanium foam exhibits a reduced elastic modulus closer to that of cancellous bone, along with an interconnected pore structure that promotes bone ingrowth and vascularization. The crushable and energy-absorbing characteristics of titanium foam also make it suitable for dissipating occlusal loads, potentially improving implant stability and longevity.
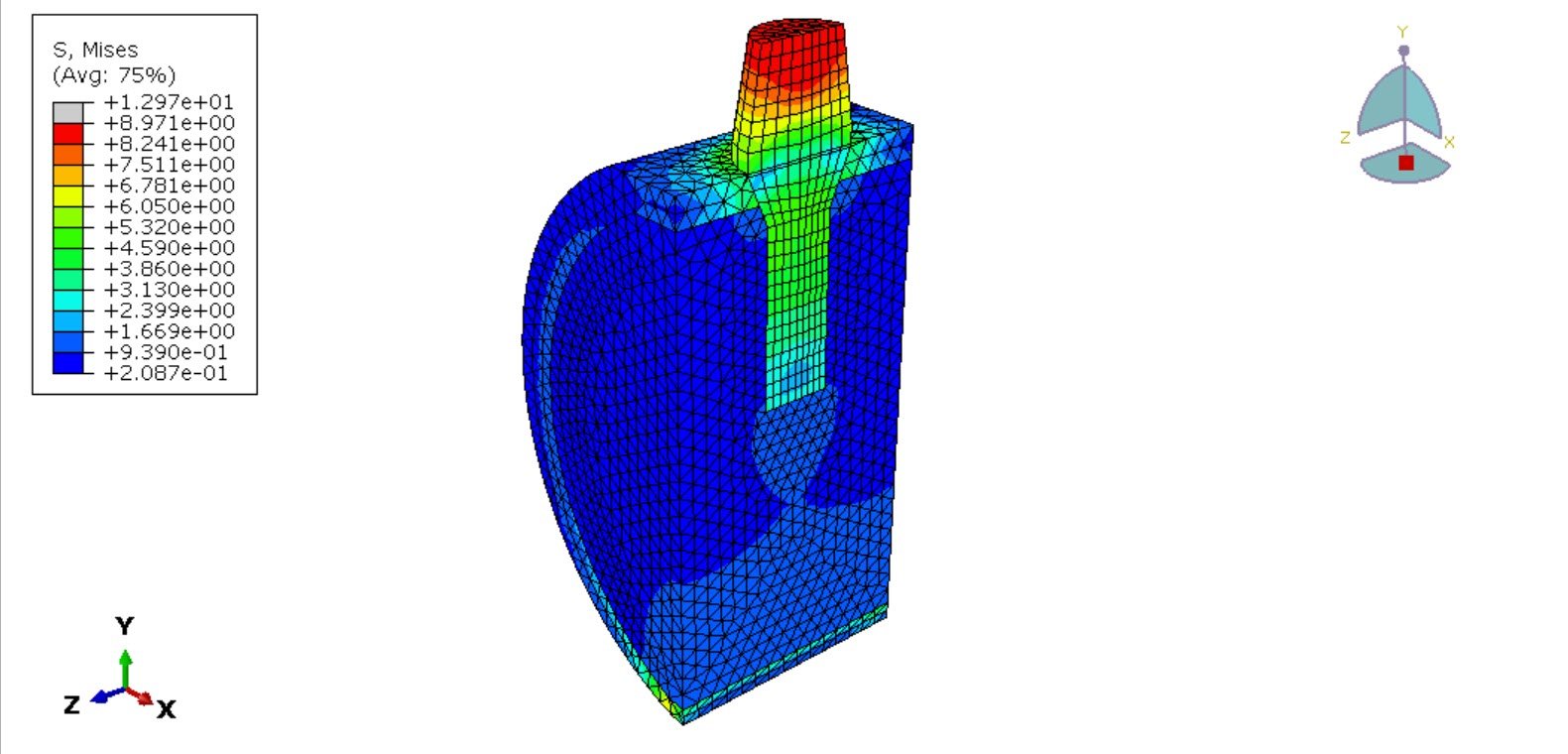
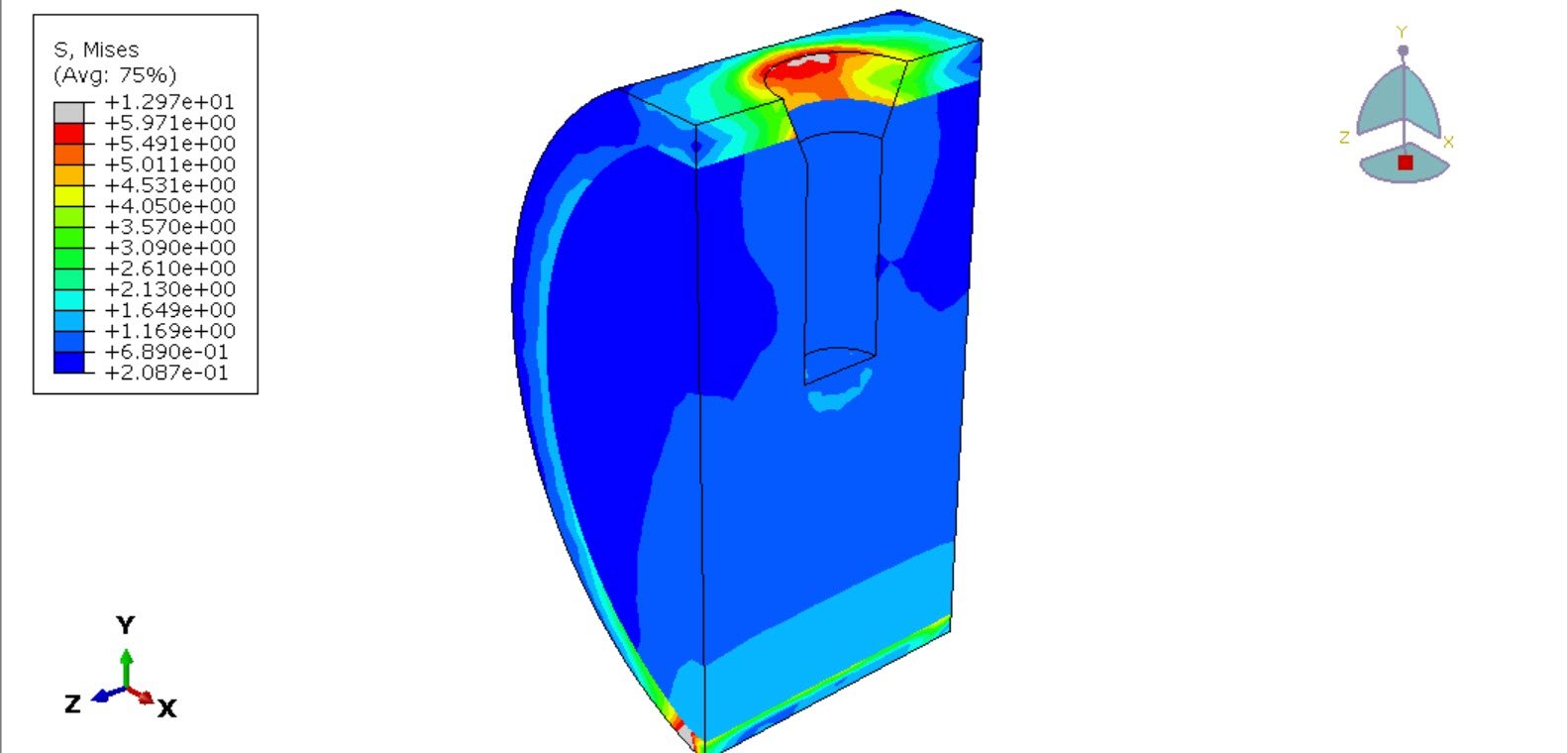
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) has become an essential tool for evaluating the biomechanical behavior of dental implants under physiological loading conditions. It enables detailed investigation of stress distribution, deformation patterns, and implant–bone interactions that are difficult to measure experimentally.
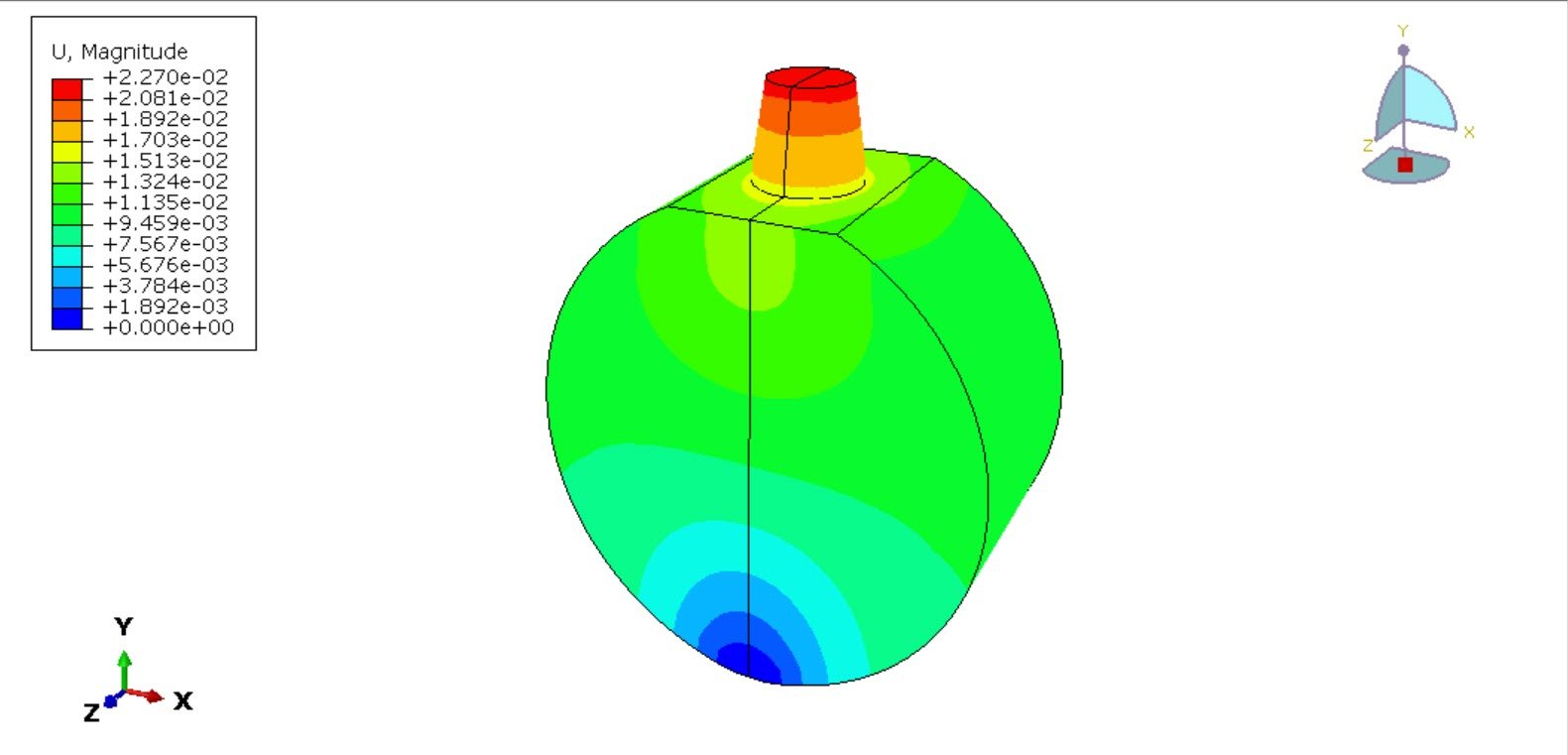
In this study, a three-dimensional finite element model was developed in Abaqus to analyze the mechanical response of a titanium foam dental implant. The jawbone was modeled as two distinct regions: cortical bone and cancellous bone. Both bone types were assumed to behave as homogeneous, isotropic, and linearly elastic materials based on commonly reported biomechanical properties.
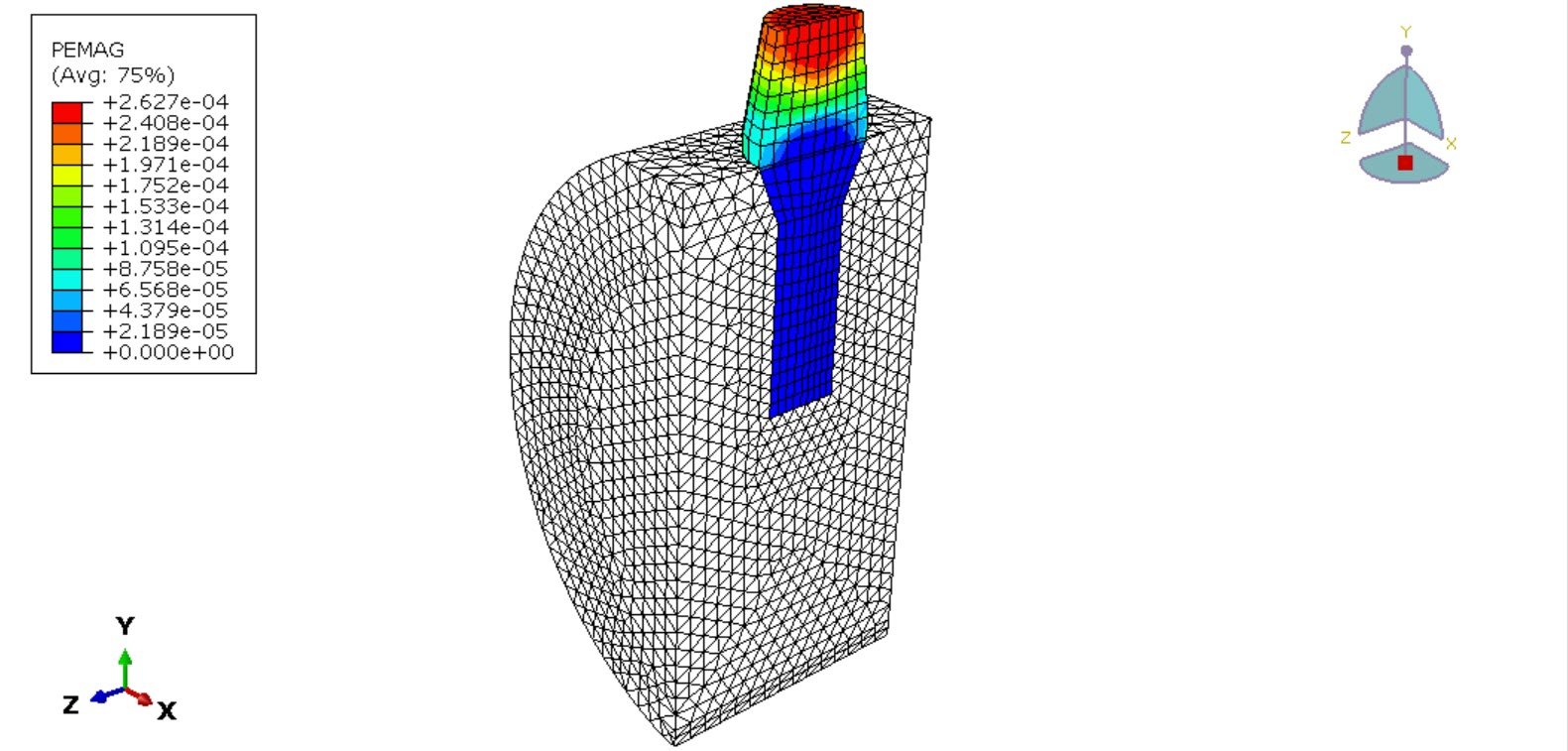
The implant was modeled using a crushable foam constitutive model with isotropic hardening to capture the nonlinear compressive behavior of porous titanium. This material formulation allows simulation of pore collapse and progressive densification under load, which are critical to understanding the implant’s load-bearing performance.
A general static analysis step was employed to simulate quasi-static loading conditions representative of masticatory forces. Boundary conditions were applied to constrain the bone model appropriately, and a compressive pressure load was applied to the top surface of the implant to represent occlusal loading.
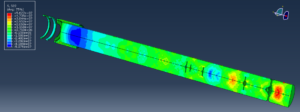
The objective of this analysis is to evaluate stress distribution within the implant and surrounding bone, assess deformation and energy absorption characteristics of the titanium foam structure, and determine the biomechanical suitability of porous implants for dental applications. Insights from this study may contribute to improved implant design aimed at minimizing stress shielding and enhancing osseointegration.


Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€84,00 €41,00
Abaqus
€86,00 €43,00
Abaqus
€88,00 €49,00
Abaqus
€86,00 €42,00
Abaqus
€86,00 €42,00
Abaqus
€78,00 €41,00
Abaqus
€100,00 €80,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?