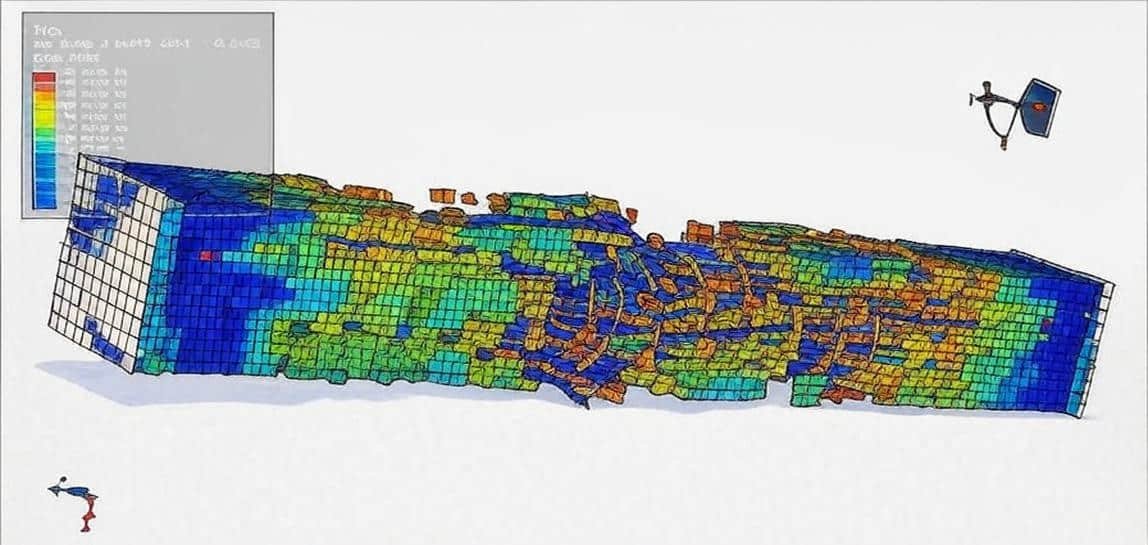
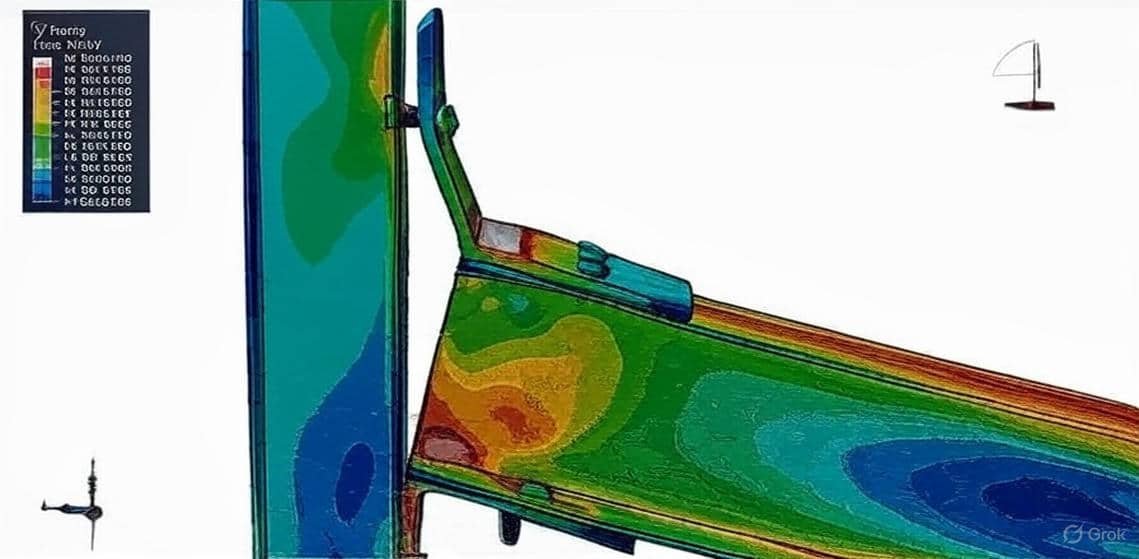
Columns are essential structural elements that primarily carry axial loads and may also resist bending, shear, and torsion. The performance of columns directly affects the safety, stability, and durability of buildings, bridges, and other civil engineering structures. Among the most common types are steel columns and reinforced concrete (RC) columns, each with distinct characteristics and design considerations.
This package includes 25 tutorials covering everything you need to master modeling and simulation
Steel columns are widely used in high-rise buildings and industrial structures due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, ductility, and ease of fabrication. Their analysis often involves:
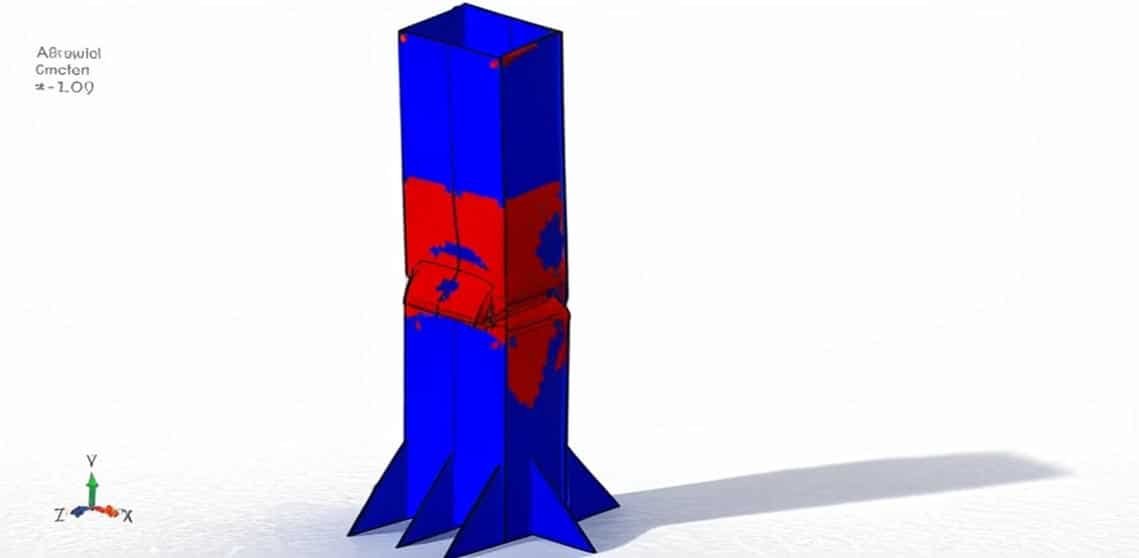
Simulation of steel columns typically includes finite element analysis (FEA) to study stress distribution, local and global buckling, and post-buckling behavior.
Concrete columns, usually reinforced with steel bars, are preferred for their compressive strength, fire resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Their analysis is more complex than steel because of the nonlinear, brittle behavior of concrete and the composite interaction with reinforcement. Key considerations include:
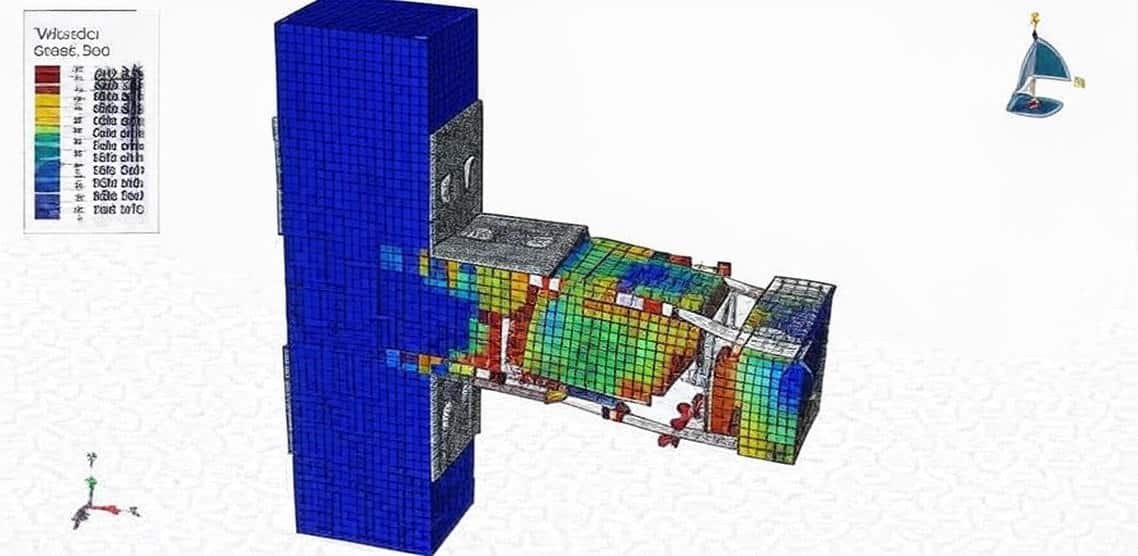
Simulations of concrete columns in software like Abaqus often rely on Concrete Damaged Plasticity (CDP) models or other advanced constitutive laws to capture material degradation, cracking, and failure modes.
Finite element simulations (e.g., in Abaqus, ANSYS, SAP2000) provide powerful insights by:
By combining analytical methods (codes and hand calculations) with simulations, engineers can achieve safer, more economical, and reliable designs for steel and concrete columns.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?