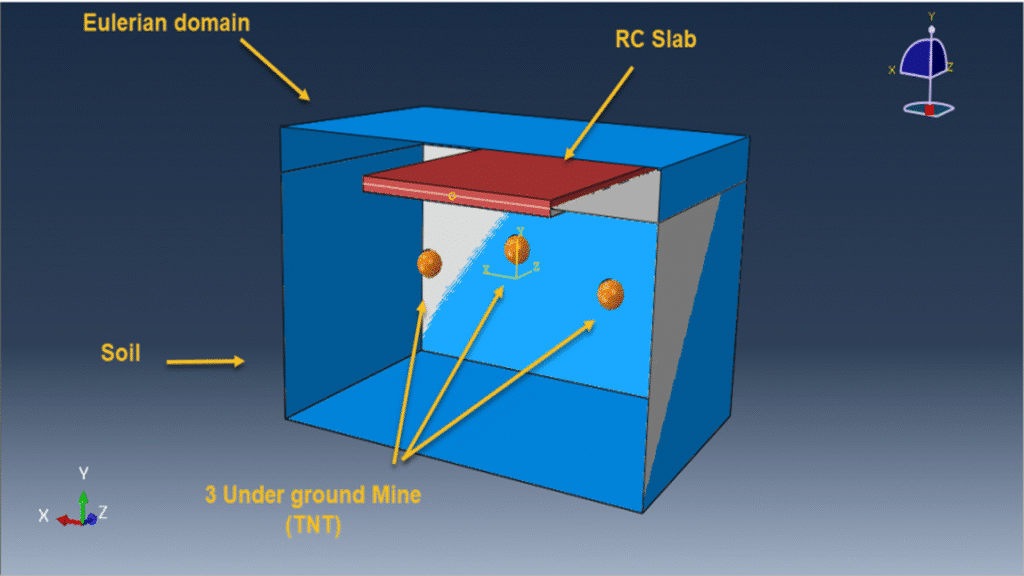
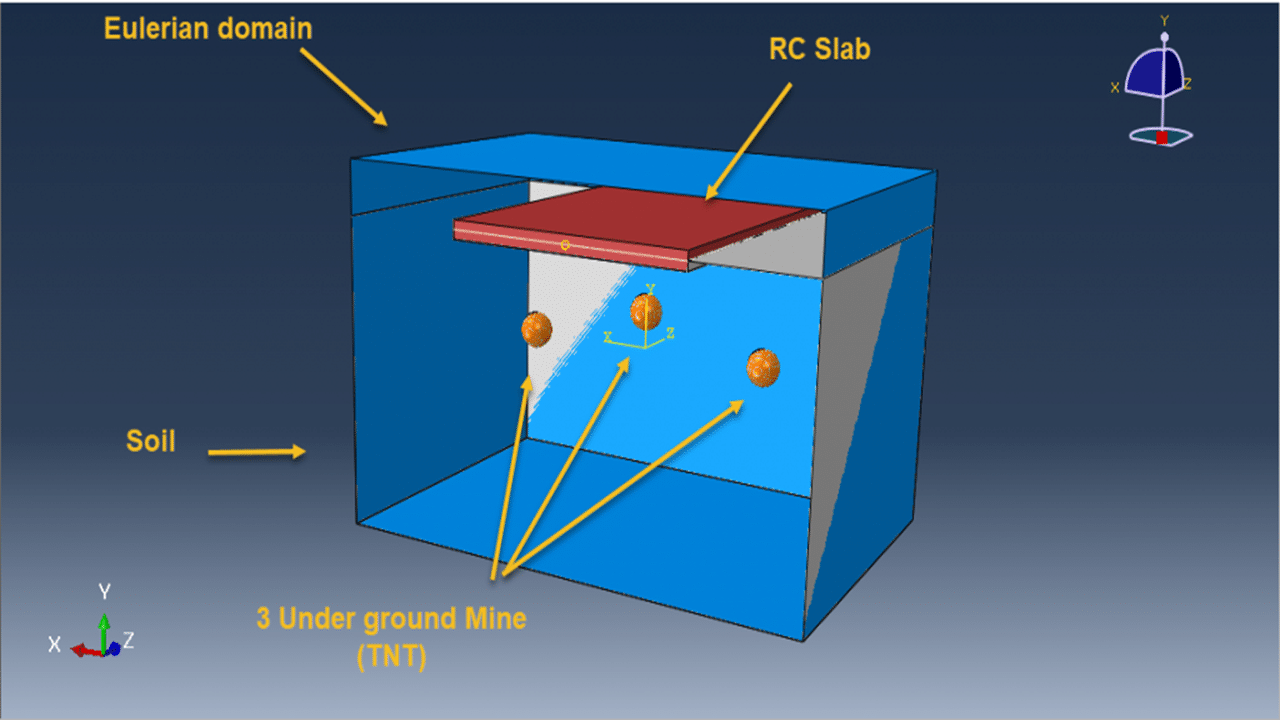
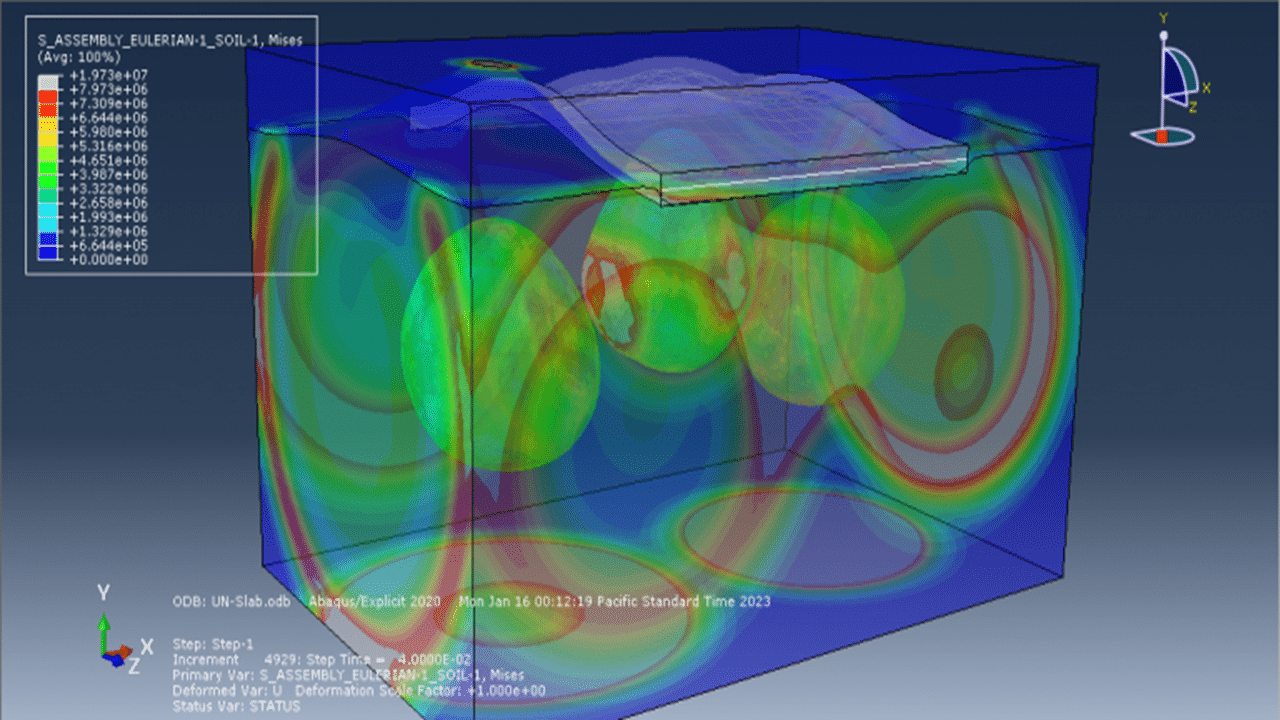
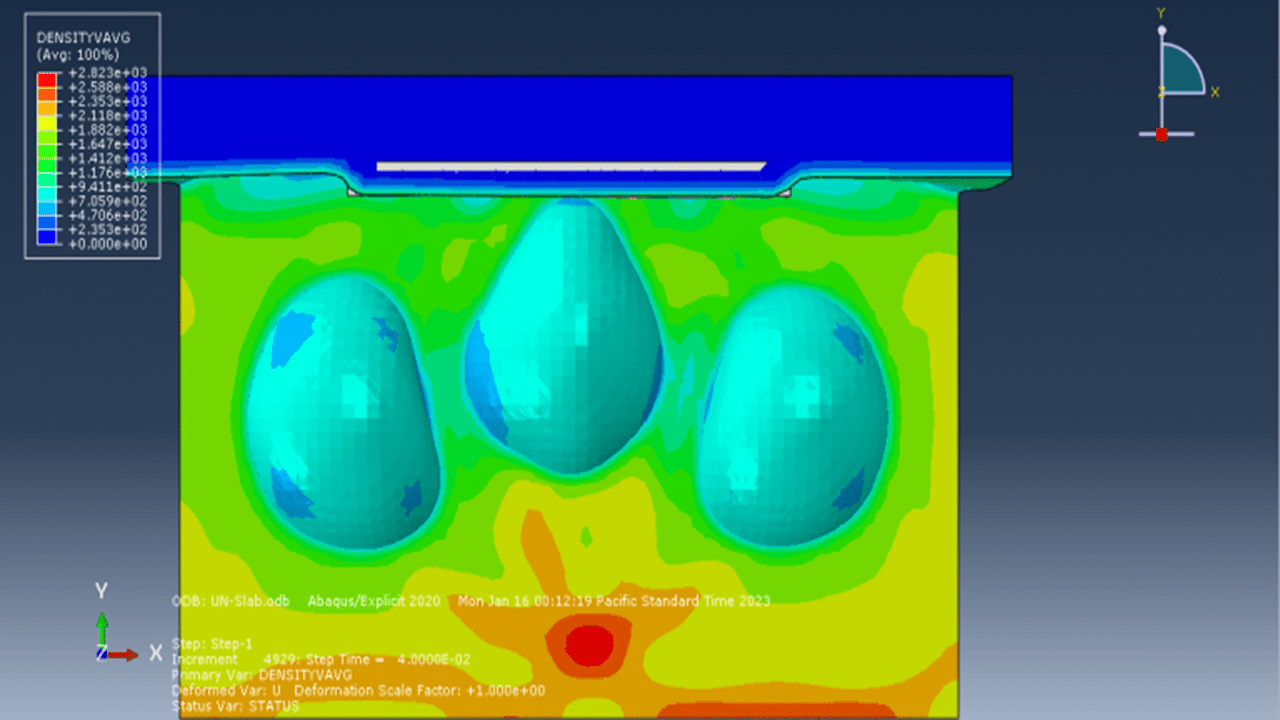
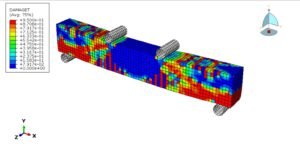
In this tutorial, a sequential CEL explosion in the depth of soil beneath a reinforced concrete (RC) slab is simulated in Abaqus. The RC slab is modeled as a 3D solid part with embedded wire reinforcements. The soil and TNT charges are modeled as 3D solid parts, while the surrounding domain is represented with a 3D Eulerian part.
This simulation focuses on modeling underground detonations—common in mining, seismic studies, and military testing. To simulate these effects accurately, Concrete Damaged Plasticity (CDP) is used for the RC slab, accounting for both cracking and crushing. Steel reinforcement is modeled with an elastic-plastic material model. The JWL equation of state defines the explosive behavior of TNT. The Mohr-Coulomb plasticity model is applied for soil to capture its pressure-dependent failure.
Three TNT charges are placed at different locations and set to detonate sequentially using delay times. A dynamic explicit step with general contact is used. Proper Eulerian boundary conditions and volume fraction methods define explosive regions. A fine mesh is essential for capturing the wave propagation and structural response accurately.
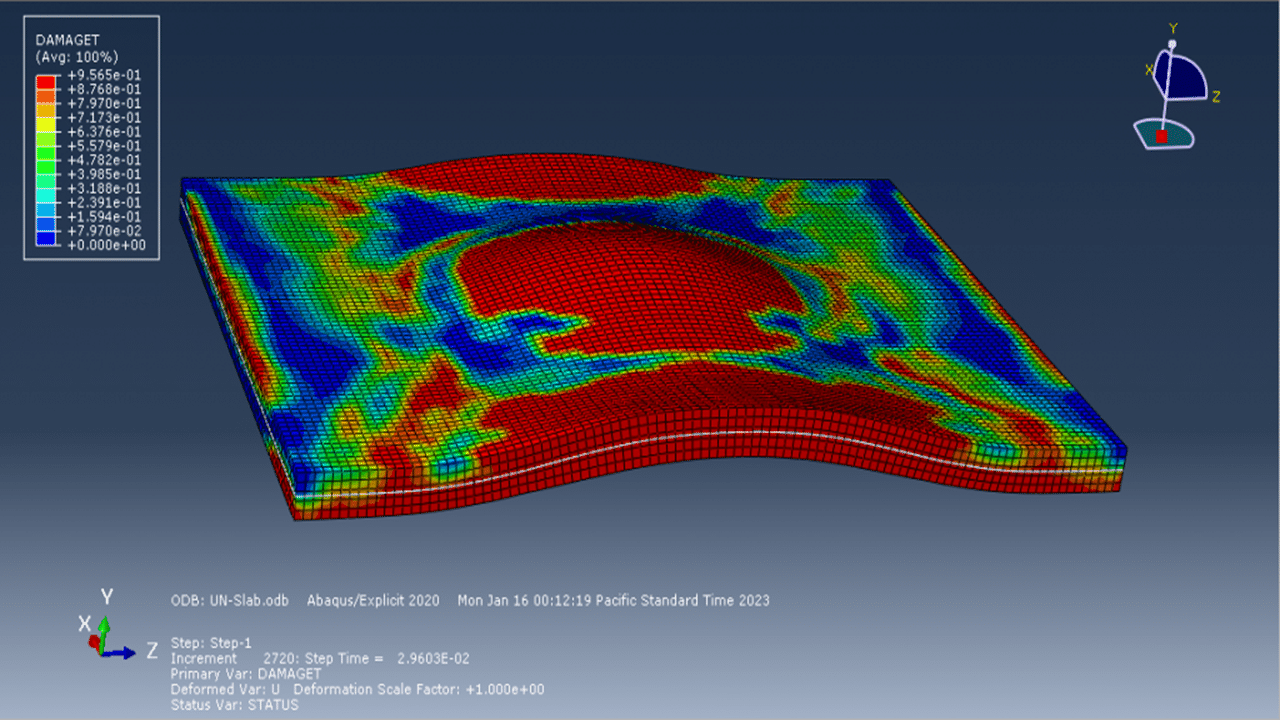
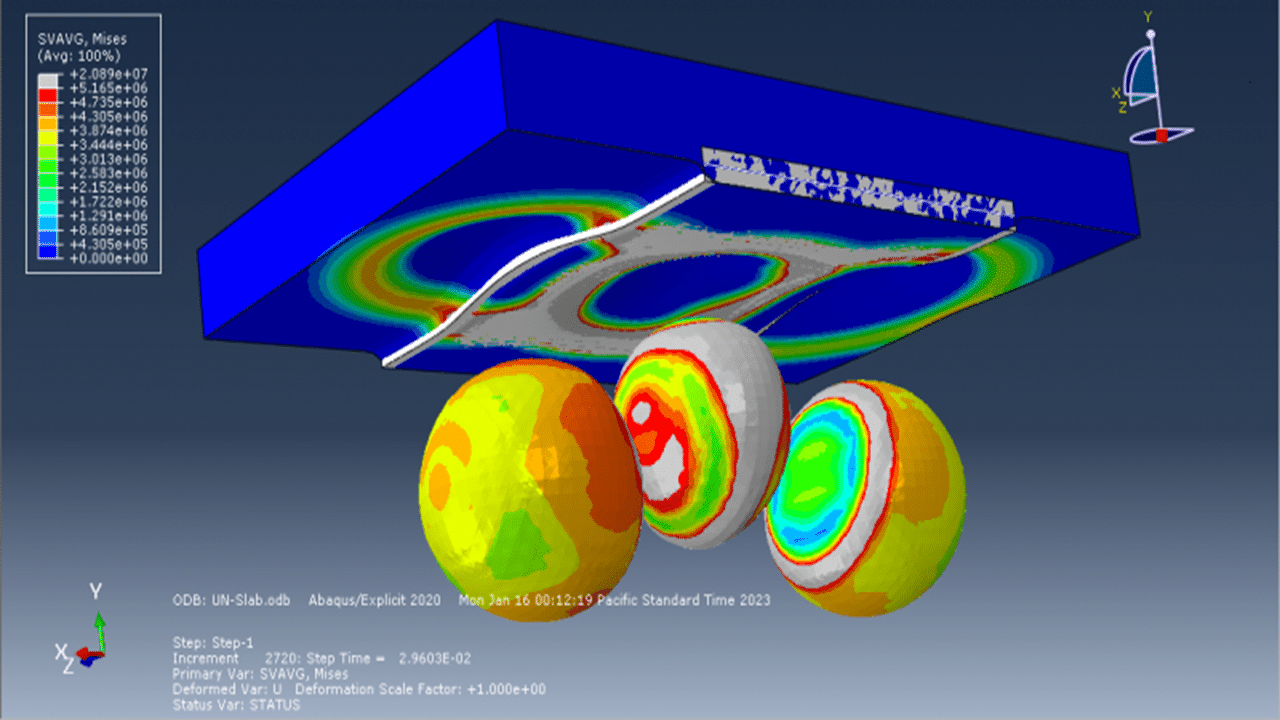
Post-simulation, key results such as stress, strain, damage, wave effects, and blast pressures are available for review and analysis.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?