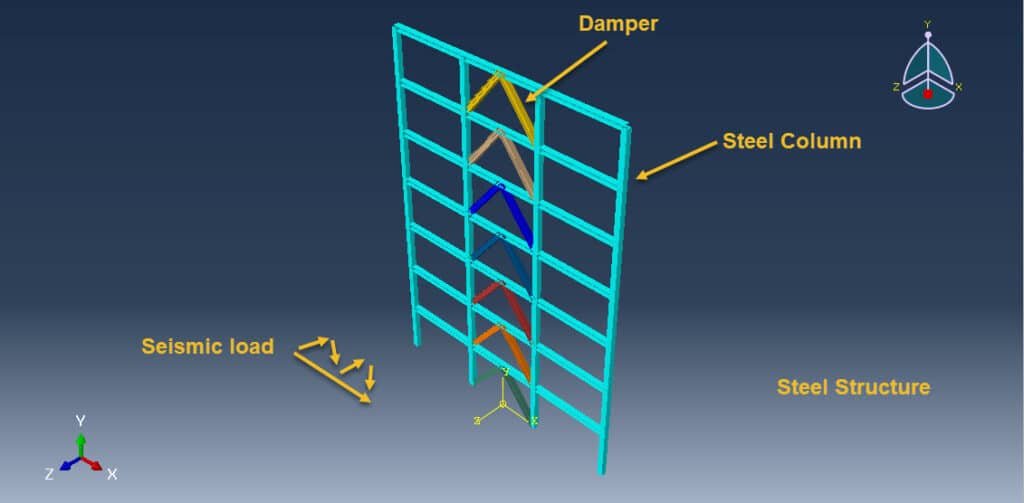
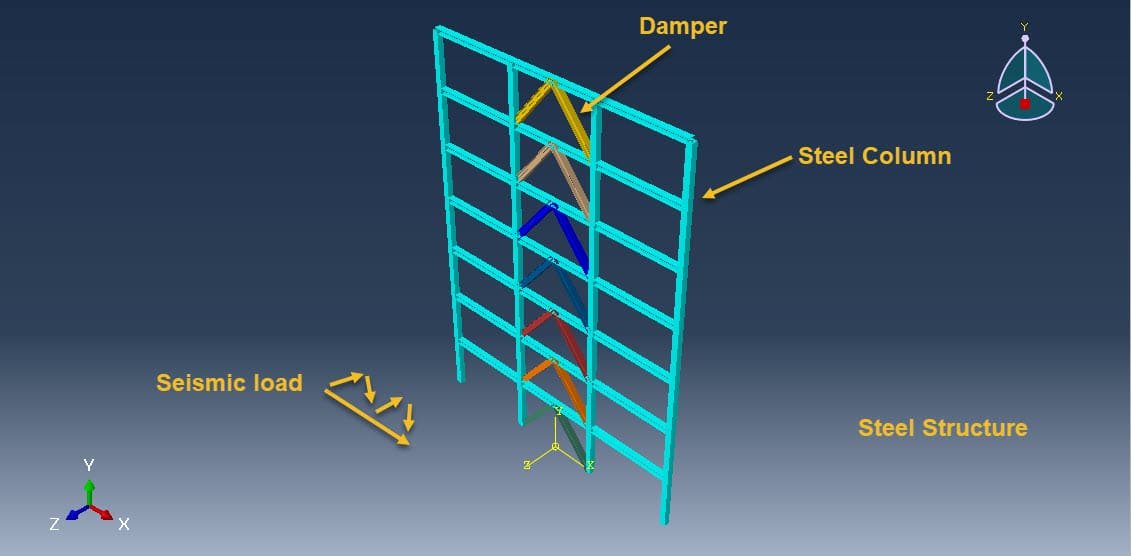
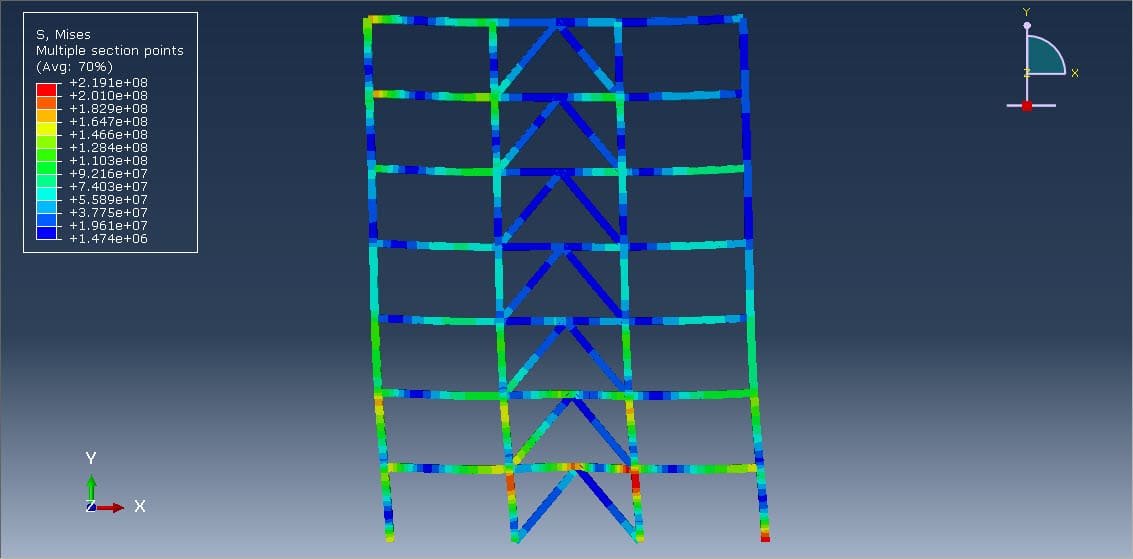
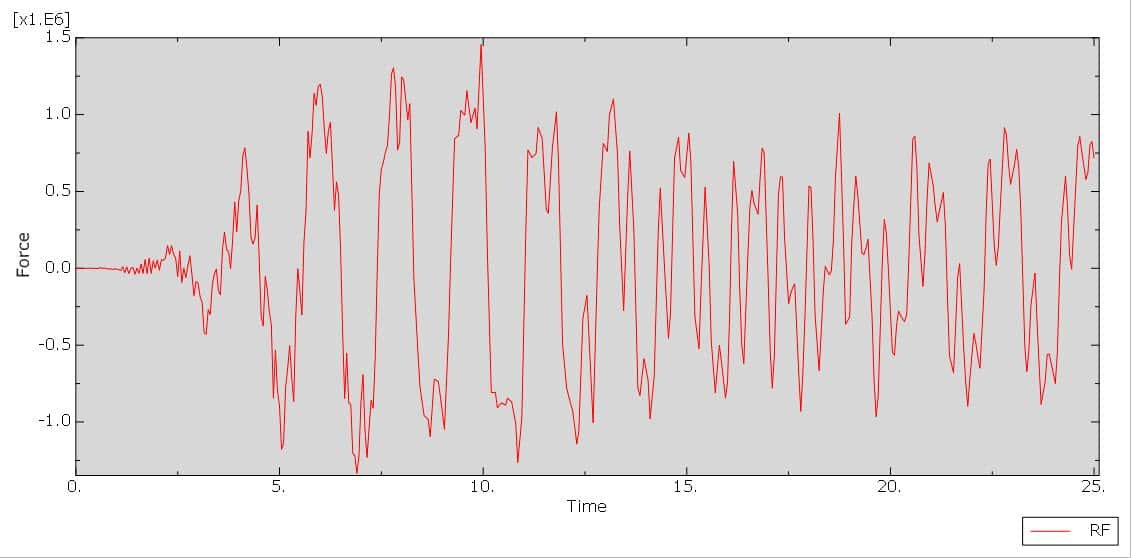
Seismic analysis is a critical part of structural engineering, aimed at evaluating how buildings respond to earthquake-induced forces. Steel building frames are widely used in seismic regions due to their ductility, high strength-to-weight ratio, and ease of construction. However, even these robust structures can suffer significant damage during strong earthquakes unless they are equipped with specialized energy dissipation systems.
One such system involves accordion dampers — a type of passive energy dissipating device designed to reduce the seismic response of structures. When incorporated into steel frames, accordion dampers can significantly enhance seismic performance by absorbing and dissipating a portion of the earthquake energy, thereby reducing the demand on the structural components.
Accordion dampers are structural devices made of folded or corrugated metal plates that act like bellows. These plates deform plastically under seismic loads, converting kinetic energy into heat through hysteresis. Their unique configuration allows for:
Large inelastic deformations,
Stable energy dissipation over multiple cycles,
Simple construction and maintenance,
Customization for different stiffness and damping requirements.
They are typically installed in braces or between floors in steel moment-resisting frames.
The main objective of seismic analysis is to predict the behavior of a building during earthquake excitation and to ensure that the structure can withstand such forces without collapse. For buildings equipped with accordion dampers, the analysis focuses on evaluating:
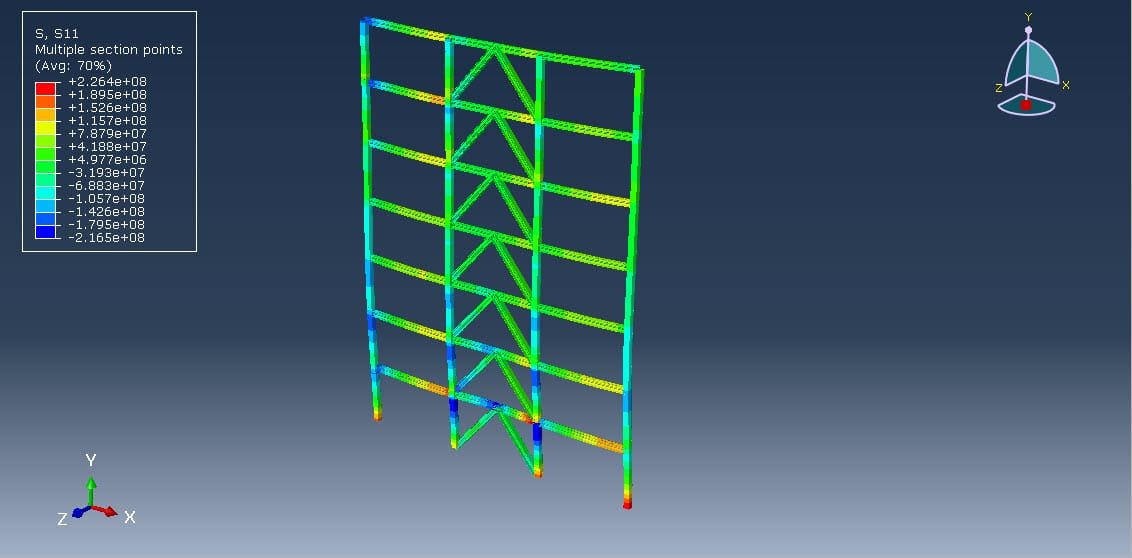
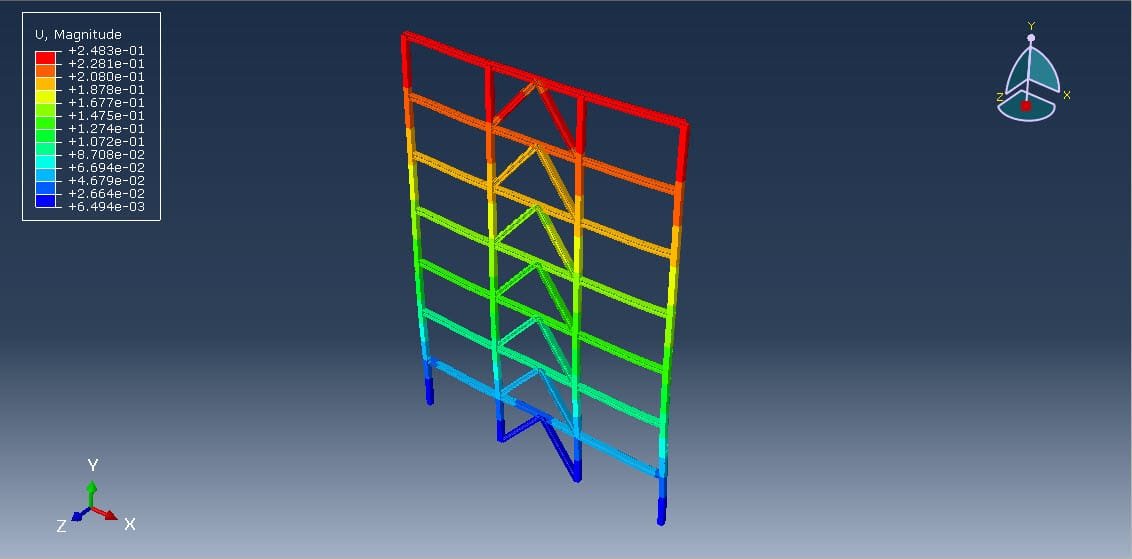
Reduction in lateral displacements (inter-story drift),
Decrease in base shear and overall force demands,
Improved energy dissipation and system damping.
Common methods used for seismic analysis include:
Linear Static Analysis (Equivalent Lateral Force Method): A simplified method where a static load approximates the effect of earthquake forces.
Linear Dynamic Analysis (Response Spectrum Analysis): Considers modal properties and provides more accurate demand predictions.
Nonlinear Static Analysis (Pushover Analysis): Simulates the progressive yielding of the structure under increasing lateral loads.
Nonlinear Time History Analysis: Uses actual or synthetic ground motion records to simulate the building’s dynamic response in real time, accounting for the nonlinear behavior of both the steel frame and accordion dampers.
Increased Ductility: They allow the structure to undergo large deformations without significant damage.
Energy Dissipation: Reduce seismic energy transferred to the main structure.
Structural Damage Reduction: By lowering inter-story drifts and internal force demands.
Cost-Effective Retrofitting Option: Can be used to upgrade existing buildings.
Seismic analysis of steel building frames equipped with accordion dampers provides a comprehensive understanding of how the structure behaves under earthquake loads. These dampers enhance structural resilience by improving energy dissipation and reducing the demand on the primary structural system. As seismic design evolves, incorporating advanced damping systems like accordion dampers is increasingly becoming a preferred solution for achieving performance-based earthquake engineering goals.
The dynamic implicit step is selected to apply the earthquake load, the proper connection among all parts is considered, and he axial damper is generated on each floor. The proper mesh and boundaries are assigned to all parts. After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, displacement, acceleration, and others are available.

Abaqus
€81,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€299,00 €249,00

Uncategorized
€95,00 €80,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?