
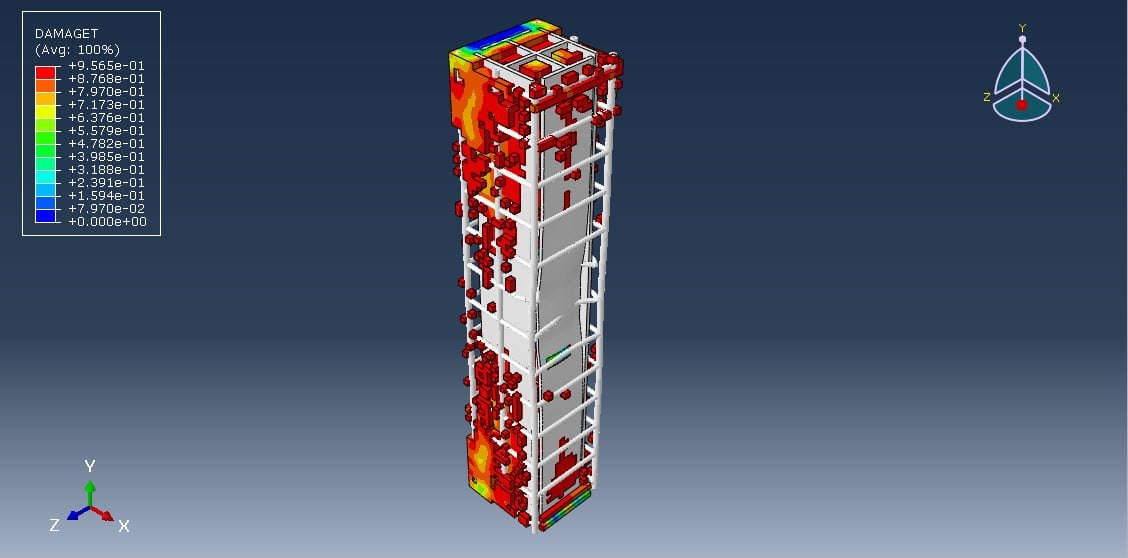
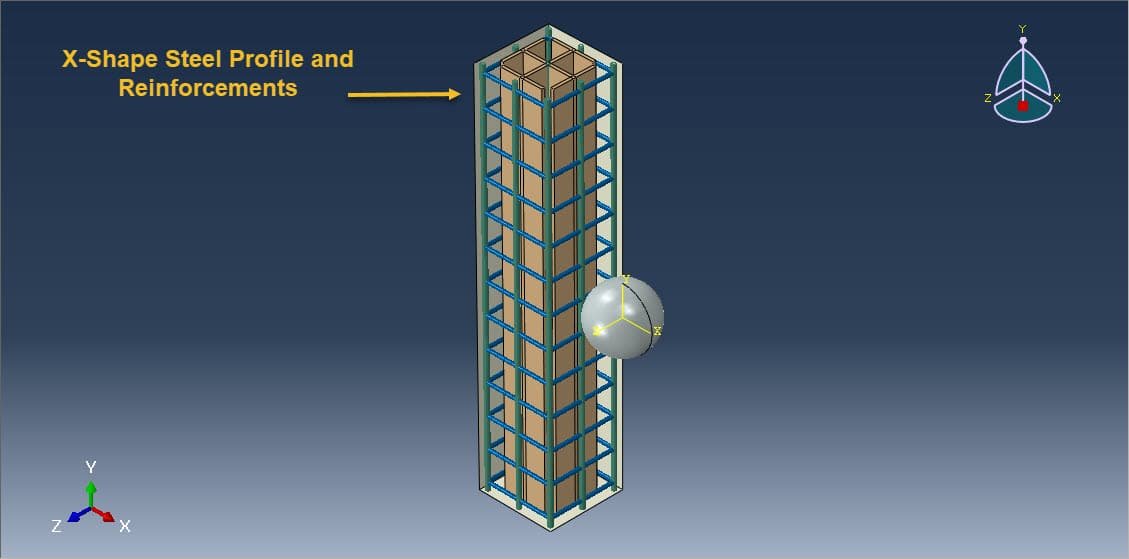
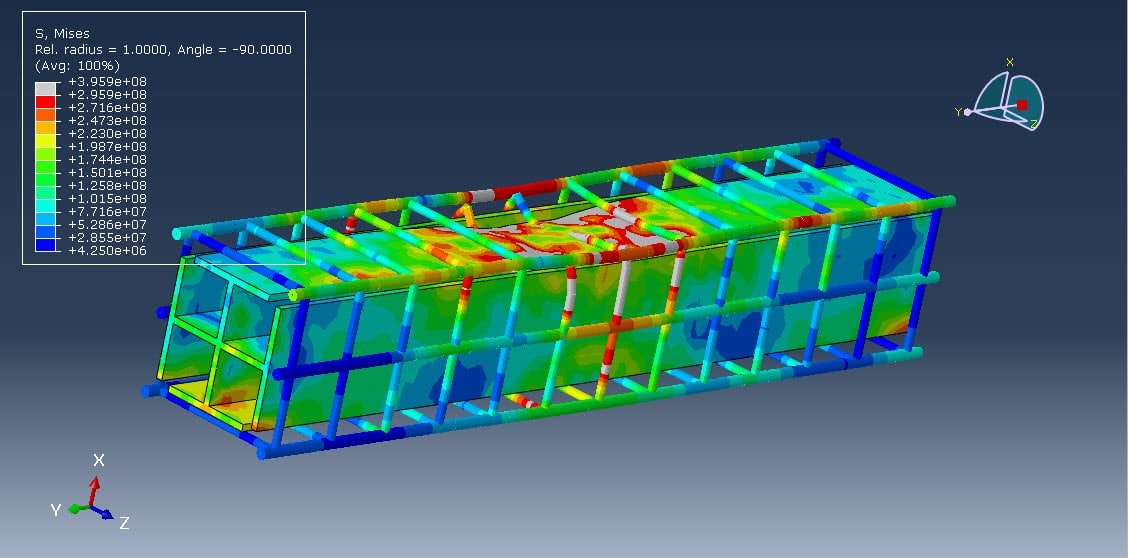
In modern structural engineering, improving the blast resistance of buildings is a critical concern, particularly in areas vulnerable to accidental or intentional explosions. Reinforced concrete (RC) columns, as key load-bearing elements, often require additional strengthening to withstand such extreme loads. One promising approach is the incorporation of a steel core, particularly with a unique geometry such as an X-shape, to enhance both energy absorption and structural integrity under blast loading.
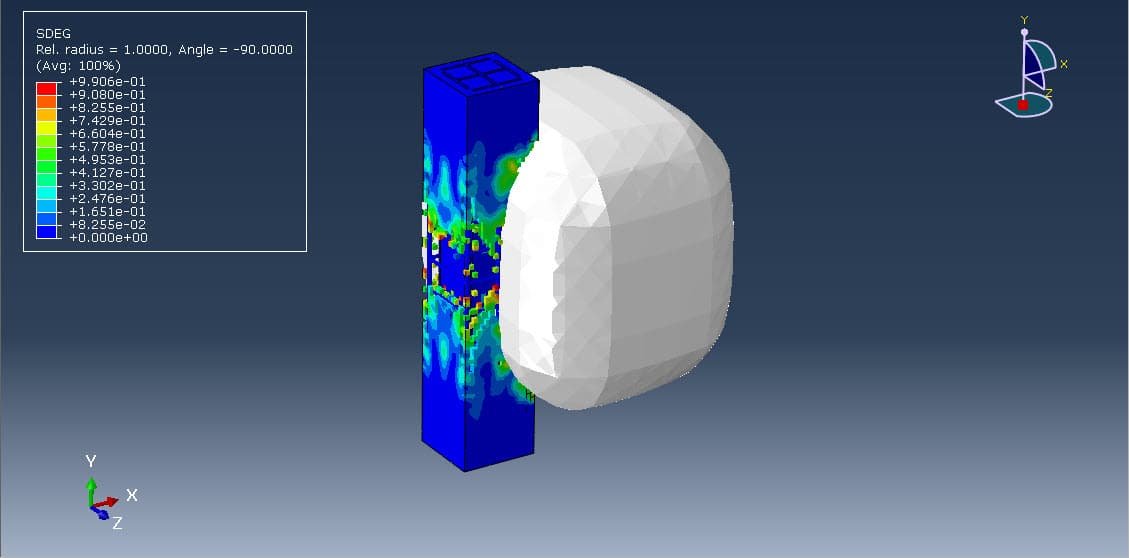
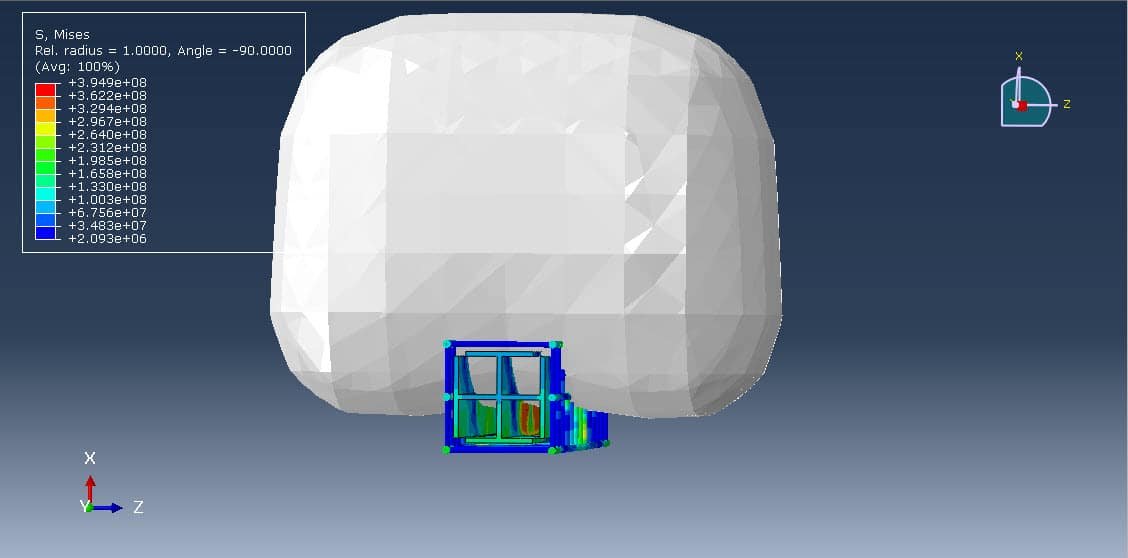
This study focuses on the numerical simulation of a coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) explosion acting on a composite RC column with an X-shaped steel core using Abaqus/Explicit. The CEL technique enables a detailed analysis of fluid-structure interaction (FSI) by modeling the air and explosive materials in an Eulerian domain and the structural components in a Lagrangian domain.
The main objective is to investigate the response and failure mechanisms of a composite RC column with an X-shaped steel core under blast loading. The simulation aims to:
Key outputs include:
The X-shaped steel core plays a dual role:
Its geometry is also beneficial for increasing torsional resistance and providing redundancy, making it superior to traditional reinforcement configurations under impulsive loads.

Abaqus
€81,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€299,00 €249,00

Uncategorized
€95,00 €80,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?