Introduction
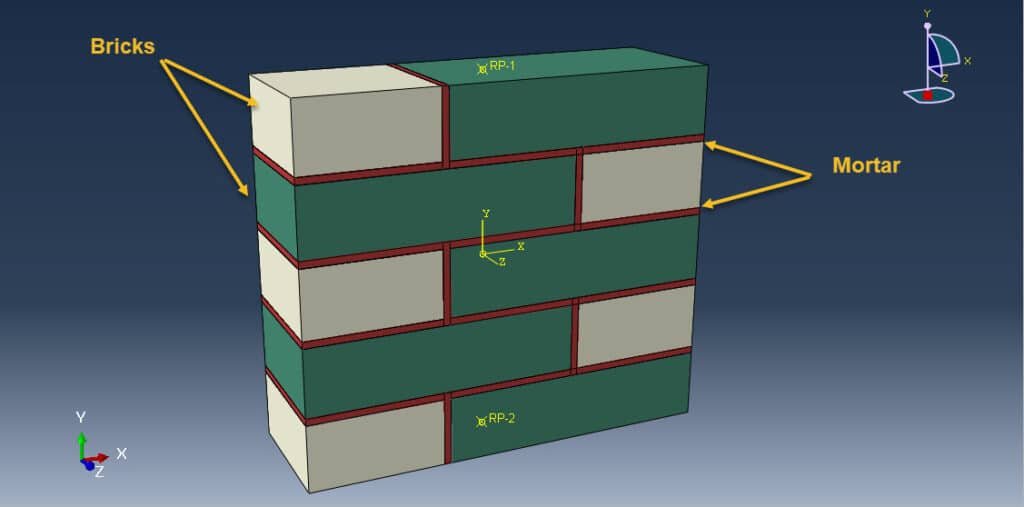
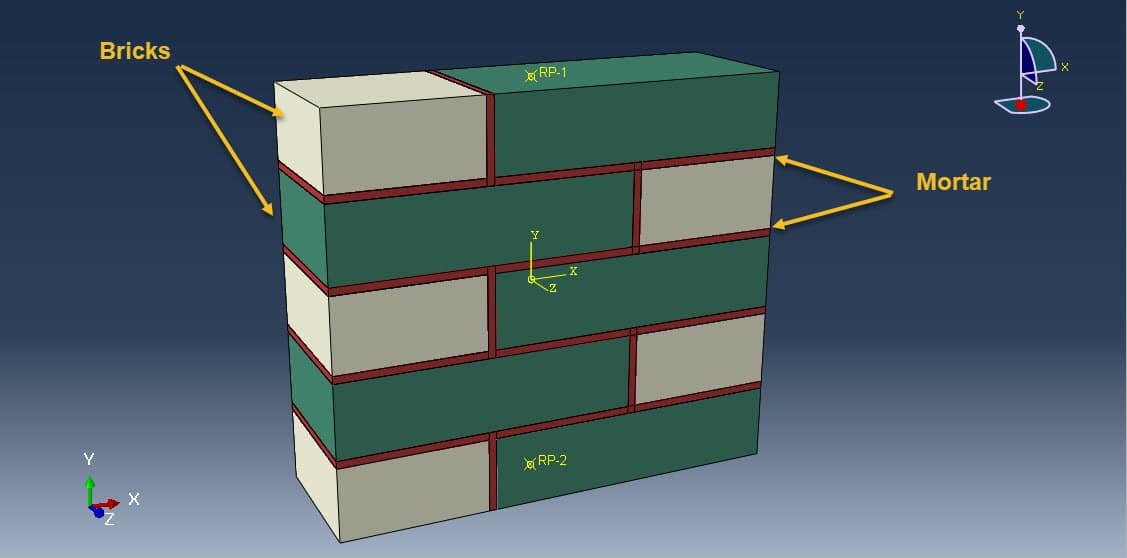
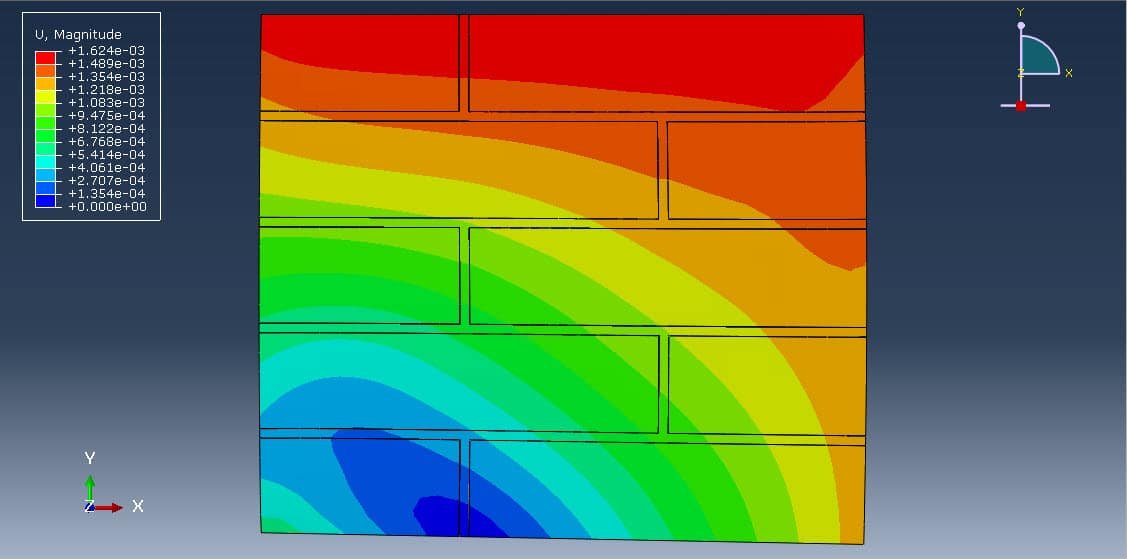
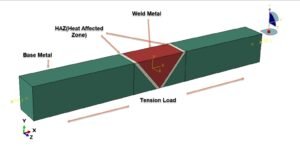
Masonry walls are widely used in structural and non-structural applications due to their durability, fire resistance, and load-bearing capacity. Understanding how these walls behave under compressive loads is crucial for evaluating their structural performance and safety, particularly in seismic or high-load environments. One advanced method for analyzing this behavior is micro-modeling, a detailed numerical technique that simulates the interaction between the individual components of masonry: units (bricks or blocks), mortar joints, and their interfaces.
What is Micro-modeling?
Micro-modeling is a finite element analysis (FEA) approach that captures the individual behavior of masonry constituents. It involves explicitly modeling each unit and the mortar, as well as their interface behavior. This contrasts with macro-modeling, where masonry is treated as a homogeneous continuum.
There are typically three types of micro-modeling approaches:
Micro-modeling Under Compression Load:
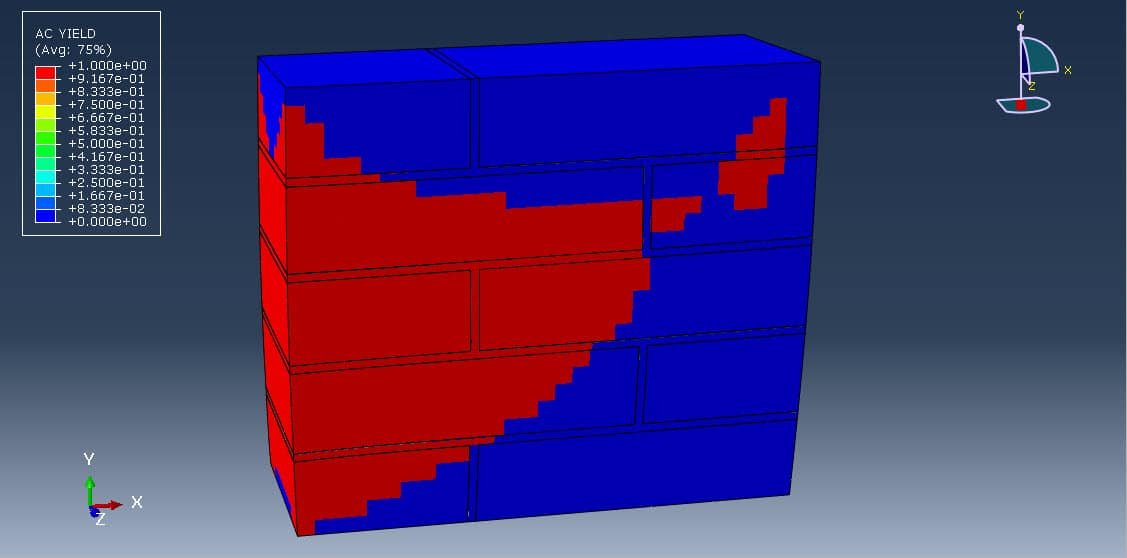
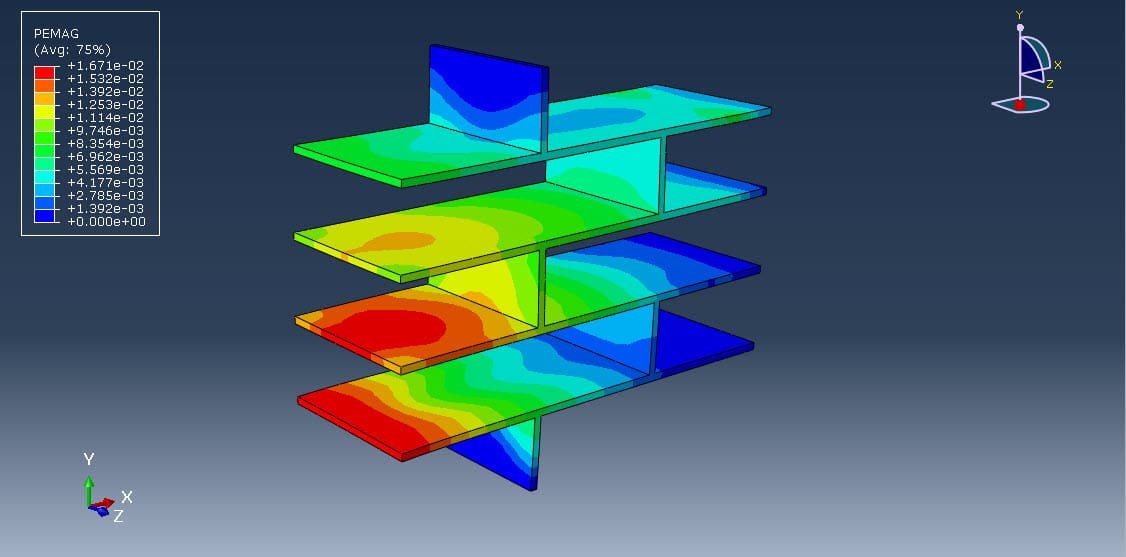
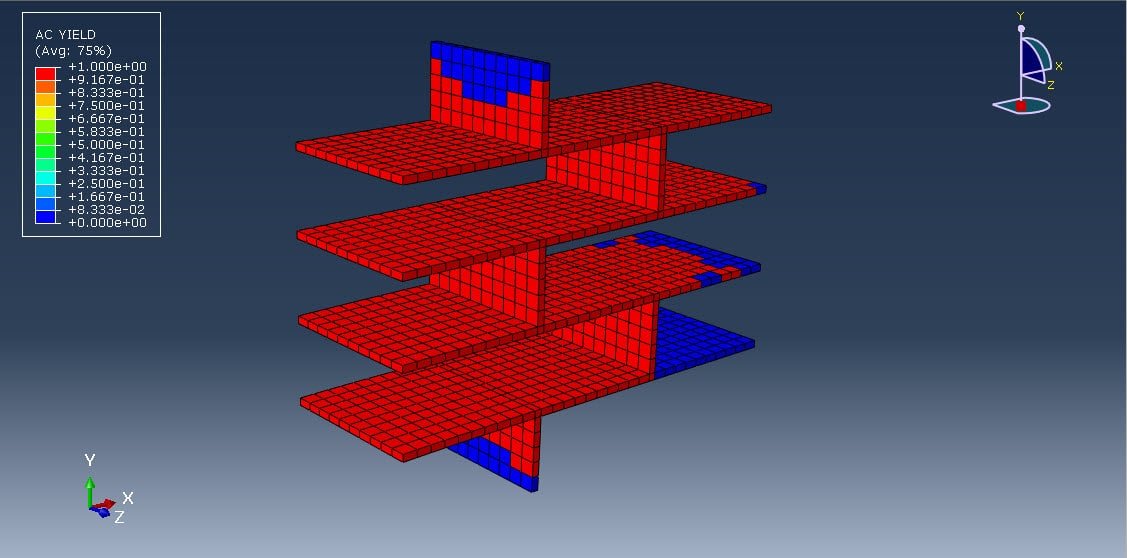
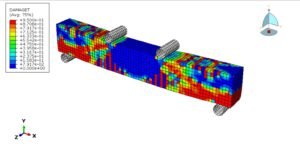
When a masonry wall is subjected to a compressive load, the complex interaction between bricks and mortar leads to non-linear behaviors such as cracking, crushing, and interfacial slip or separation. Micro-modeling helps analyze:
Applications:
Advantages of Micro-modeling:
Challenges:
Micro-modeling is a powerful tool for investigating the compressive behavior of masonry walls at a granular level. While computationally intensive, it yields high-fidelity results essential for the design, retrofit, and safety assessment of masonry structures. It serves as a foundation for improving code provisions and engineering practices, particularly in regions prone to seismic activity or where masonry is widely used.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?