Masonry units remain one of the most widely used construction materials due to their durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of production. In recent years, the development of new empty (hollow) masonry blocks has gained increasing attention, primarily because of their reduced self-weight, improved thermal insulation, and sustainability benefits. However, the presence of cavities significantly influences the mechanical performance of these blocks, particularly under compressive loading, which governs the load-bearing capacity of masonry walls.
Understanding the shear and compressive behavior of hollow masonry units is essential for predicting structural performance, failure mechanisms, and serviceability limits. Experimental testing provides valuable insights but is often time-consuming and costly. Consequently, numerical simulation using the Finite Element Method (FEM) has become an efficient and reliable approach for investigating the structural response of masonry components under different loading conditions.
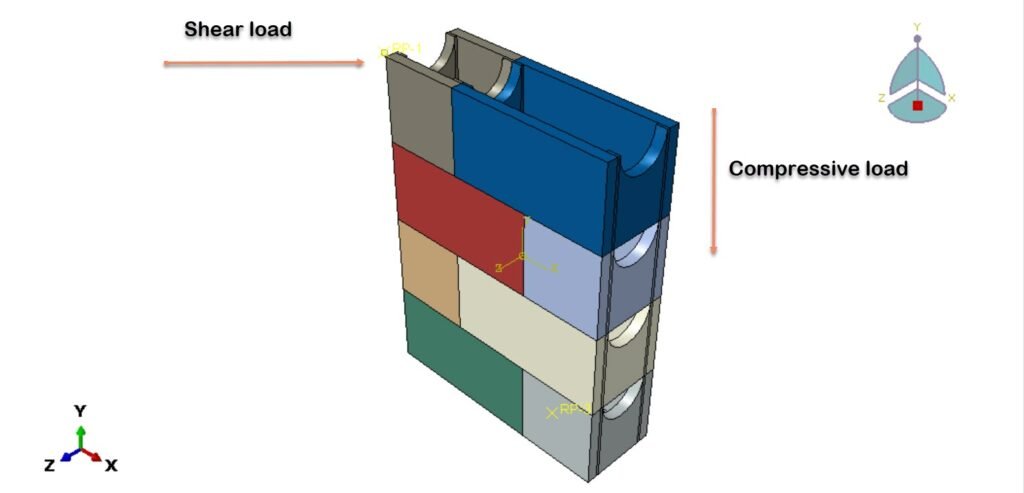
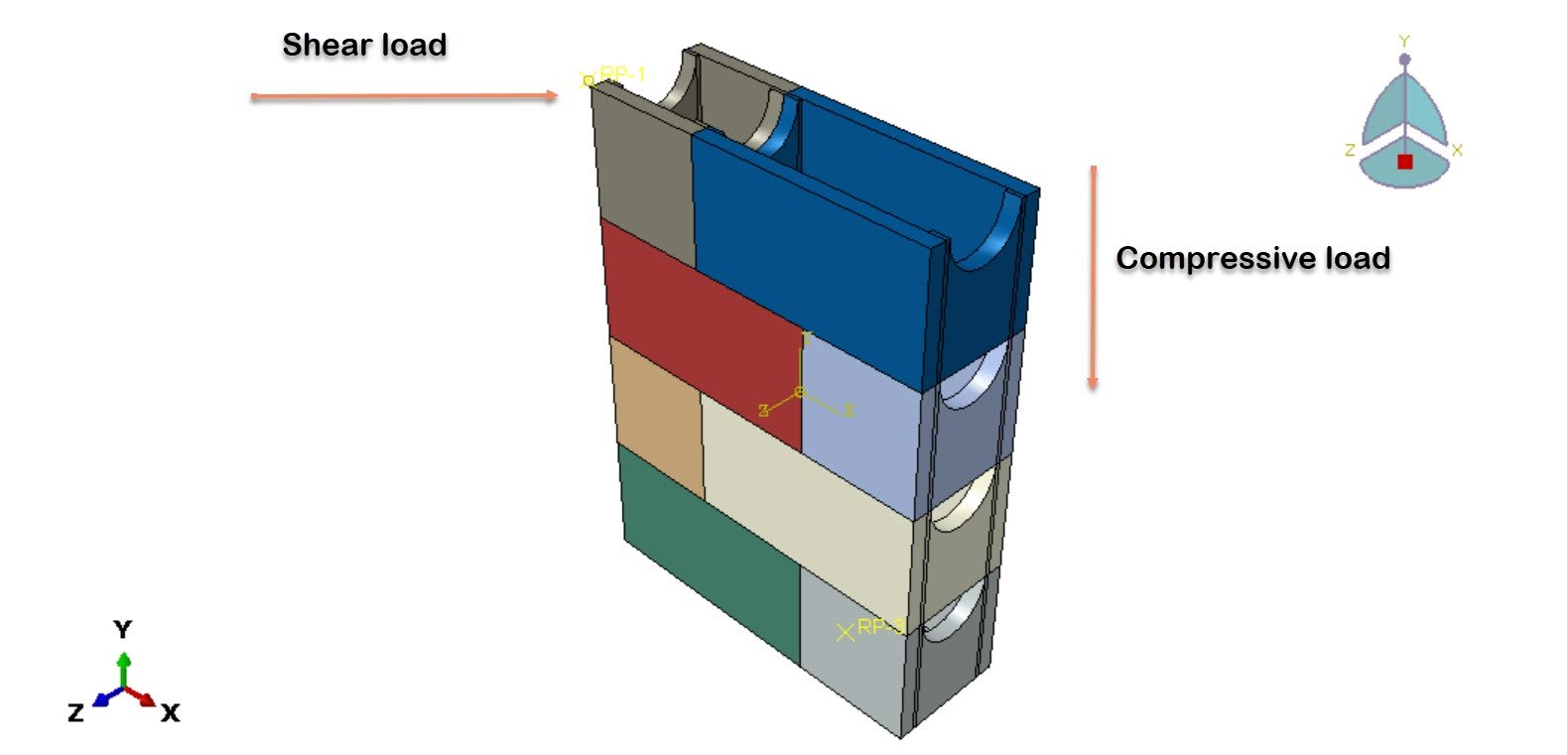
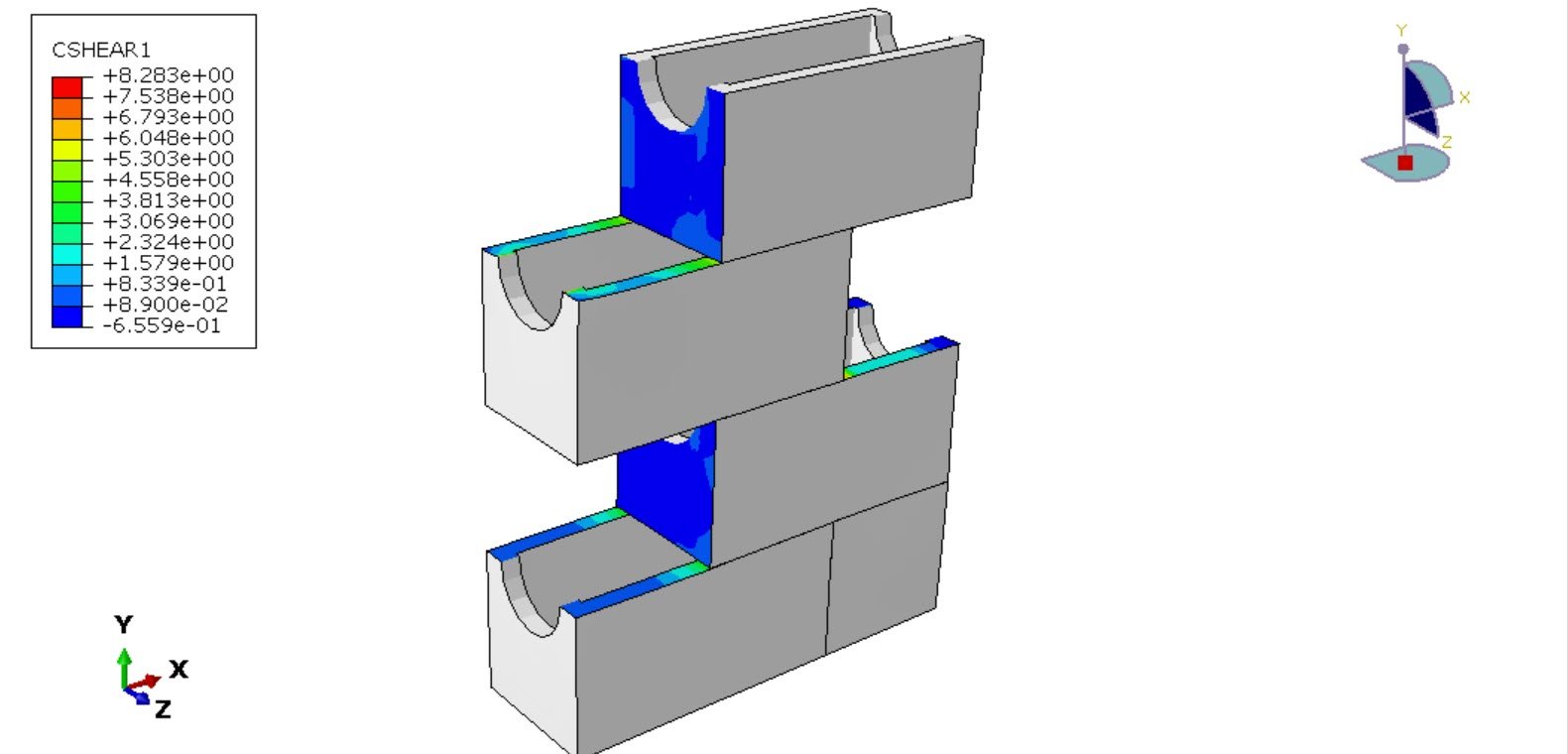
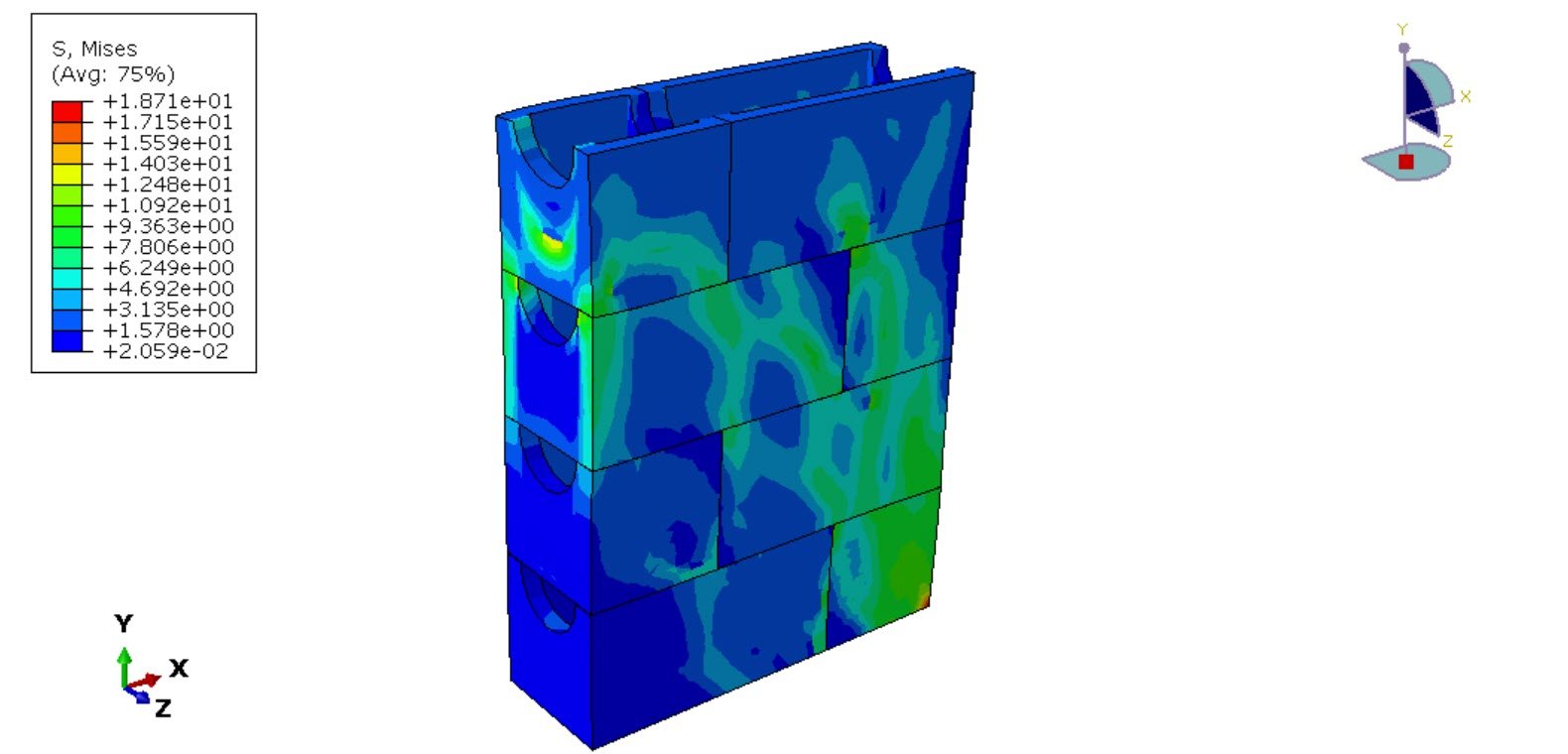
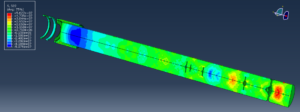
In this study, the shear and compressive performance of a newly developed empty masonry block is analyzed using Abaqus finite element software. A three-dimensional (3D) numerical model is developed to realistically represent the geometry of the block, including its hollow cavities. The material behavior of the concrete block is simulated using the Concrete Damaged Plasticity (CDP) model, which is capable of capturing nonlinear phenomena such as cracking, crushing, stiffness degradation, and plastic deformation under compressive stresses.
To replicate the interaction between masonry units and mortar, cohesive interaction properties are introduced at the contact interfaces. This approach allows for the simulation of bonding behavior, including stiffness transfer, damage initiation, and potential debonding between materials. The analysis is conducted using a general static step, suitable for evaluating quasi-static compressive loading conditions and capturing the progressive development of stress, strain, and damage within the block.
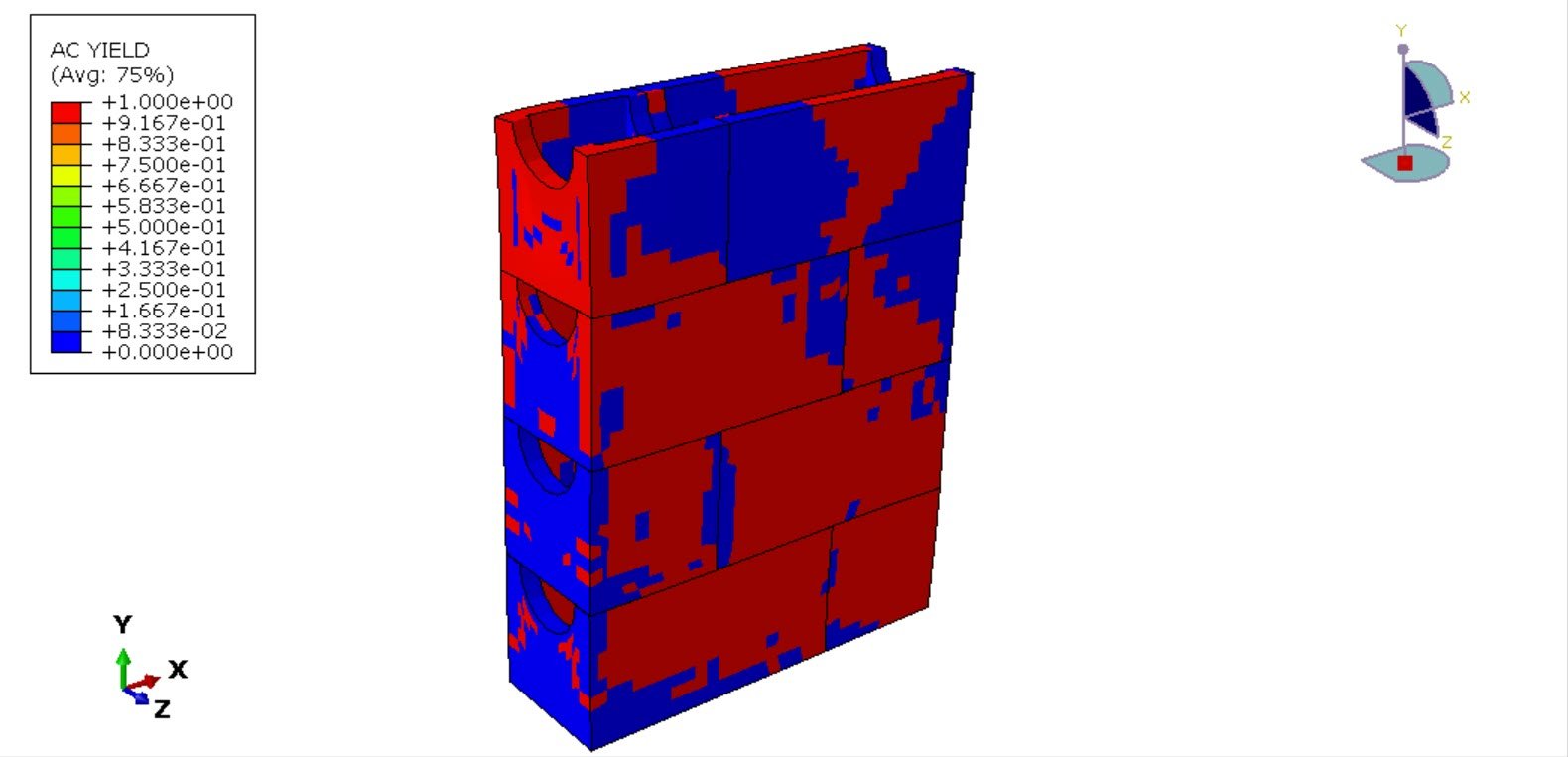
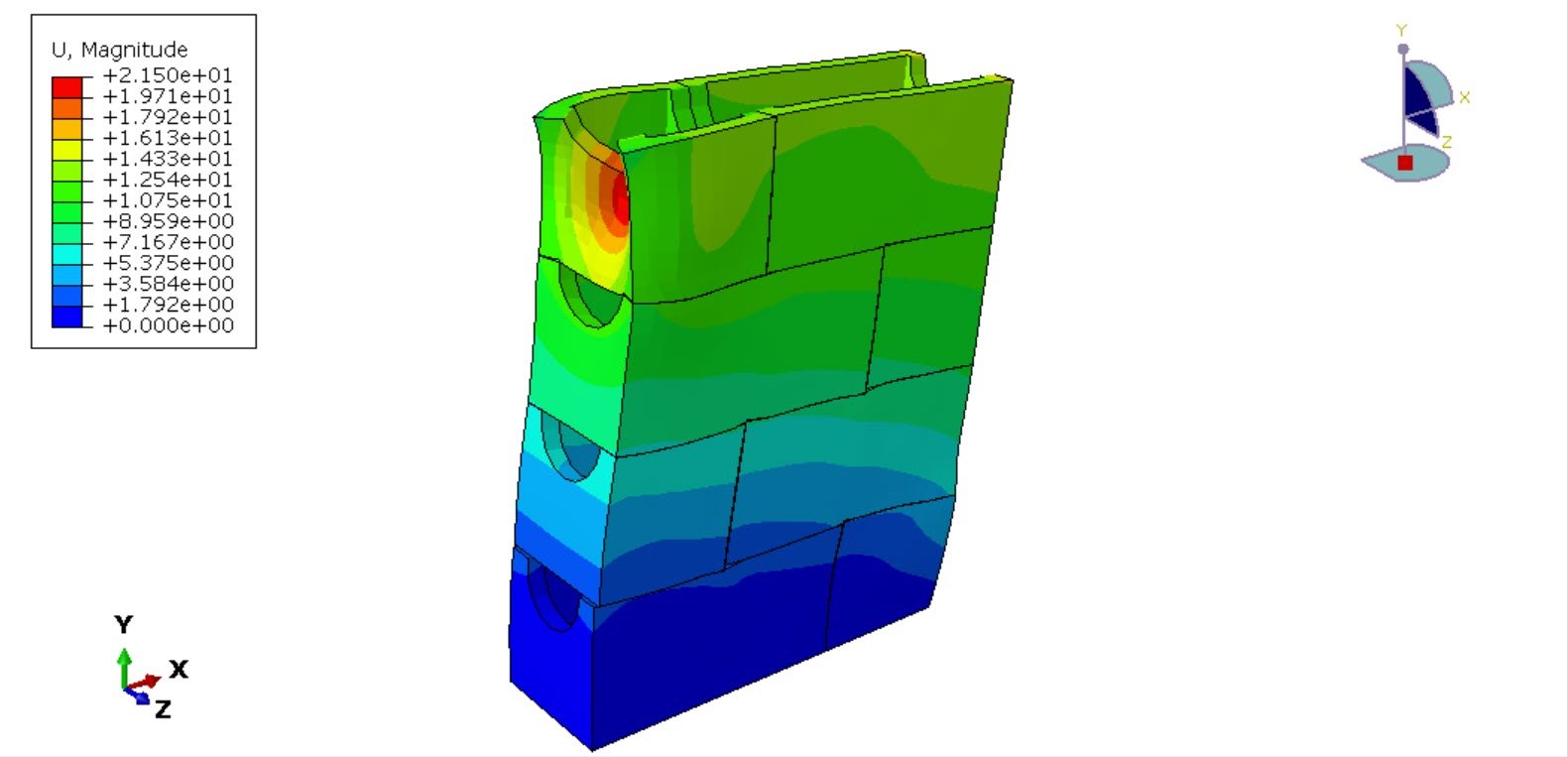
The primary objective of this analysis is to investigate the stress distribution, deformation characteristics, and failure modes of the new hollow masonry block under compressive load. The numerical results provide insight into the structural efficiency of the block design and contribute to optimizing its geometry and material performance for practical construction applications.


Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€84,00 €41,00
Abaqus
€86,00 €43,00
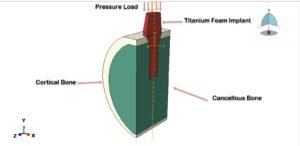
Abaqus
€88,00 €49,00
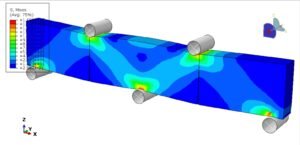
Abaqus
€86,00 €42,00
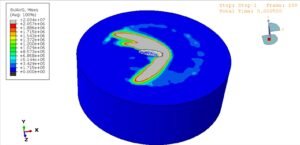
Abaqus
€86,00 €42,00
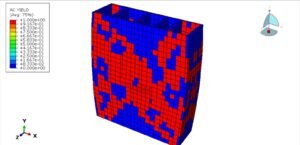
Abaqus
€78,00 €41,00
Abaqus
€100,00 €80,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?