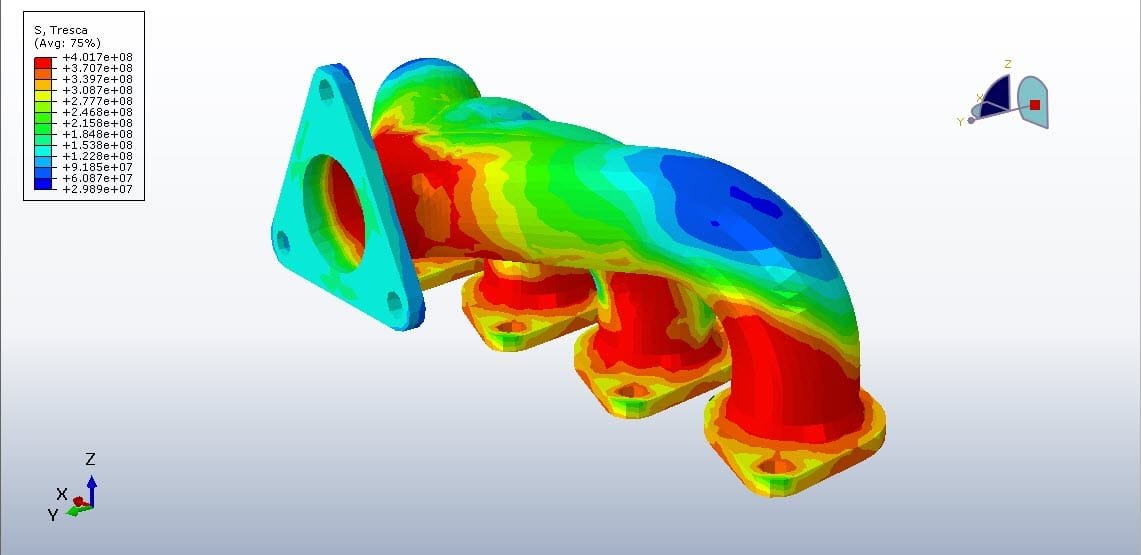
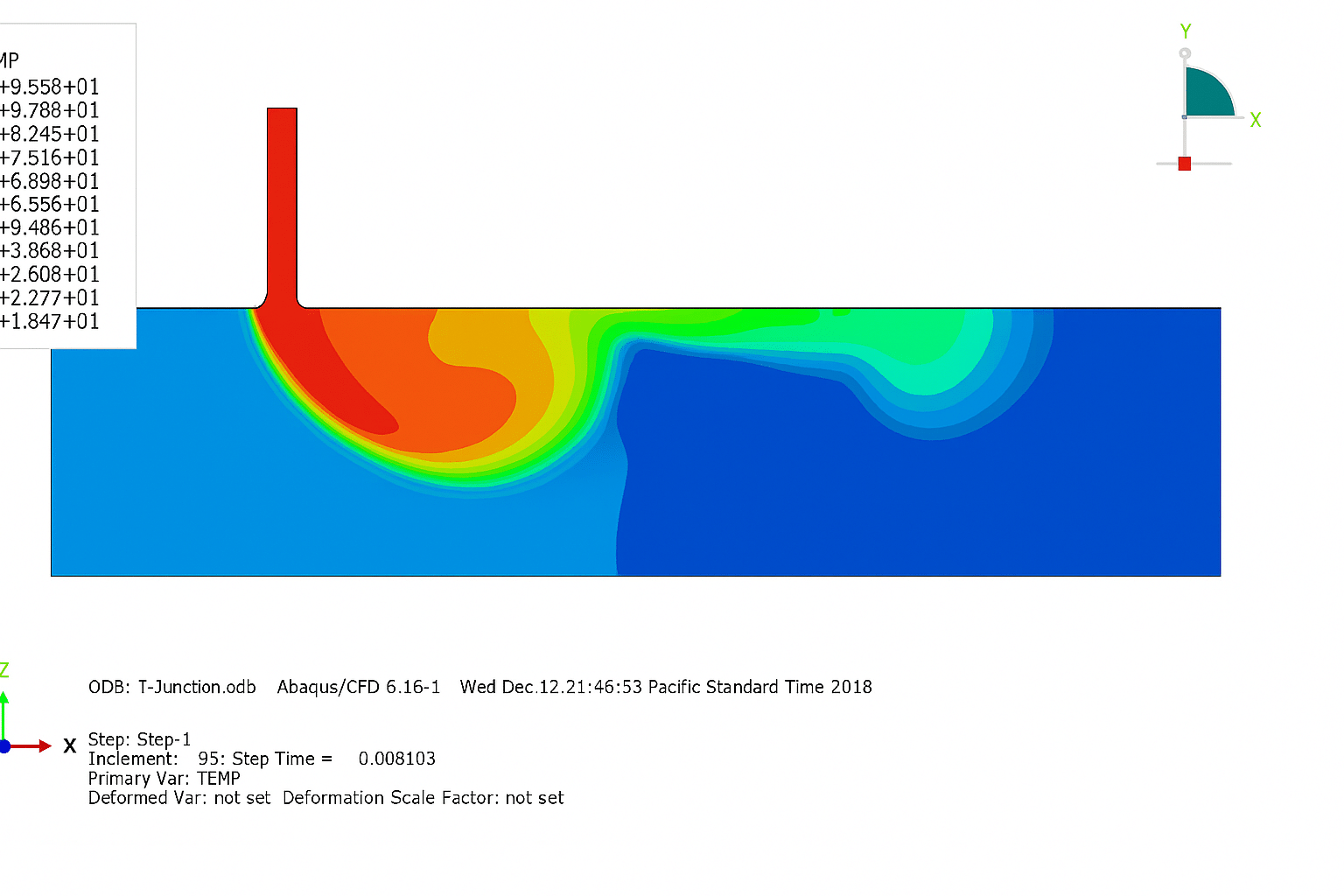
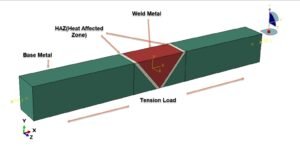
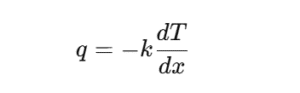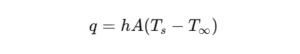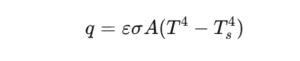Heat transfer analysis is the study of how thermal energy moves from one place to another and the rate at which it occurs. It’s a cornerstone of engineering and science, because nearly every system, from a coffee mug to a rocket engine, involves heat flow.
Here’s the big picture:
1. What Is Heat Transfer?
- Heat is energy in transit due to a temperature difference.
- Once temperatures equalize, there’s no net heat transfer — the system is in thermal equilibrium.
- In analysis, we care about how much heat moves, how fast, and by what path.
2. The Three Modes of Heat Transfer
- Conduction – Heat moves through a solid or stationary fluid because particles or electrons pass along energy.
- Convection – Heat transfer between a surface and a moving fluid (air, water, etc.).
- Radiation – Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves, no medium required.
-
Governed by the Stefan–Boltzmann Law:
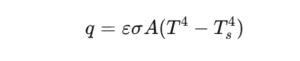
where ε\varepsilon is emissivity, σ\sigma is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant.
- Example: The Sun warms the Earth.
3. Why We Do Heat Transfer Analysis
- Design: Ensuring engines, electronics, and buildings operate safely and efficiently.
- Energy efficiency: Minimizing losses in insulation, power plants, and thermal systems.
- Temperature control: Preventing overheating or freezing in critical components.
4. How It’s Analyzed
Heat transfer problems can be:
- Steady-state: Conditions don’t change with time (e.g., a wall at constant temperature difference).
- Transient: Conditions change over time (e.g., cooling of hot metal in water).
Methods used:
- Analytical equations (for simple shapes and conditions).
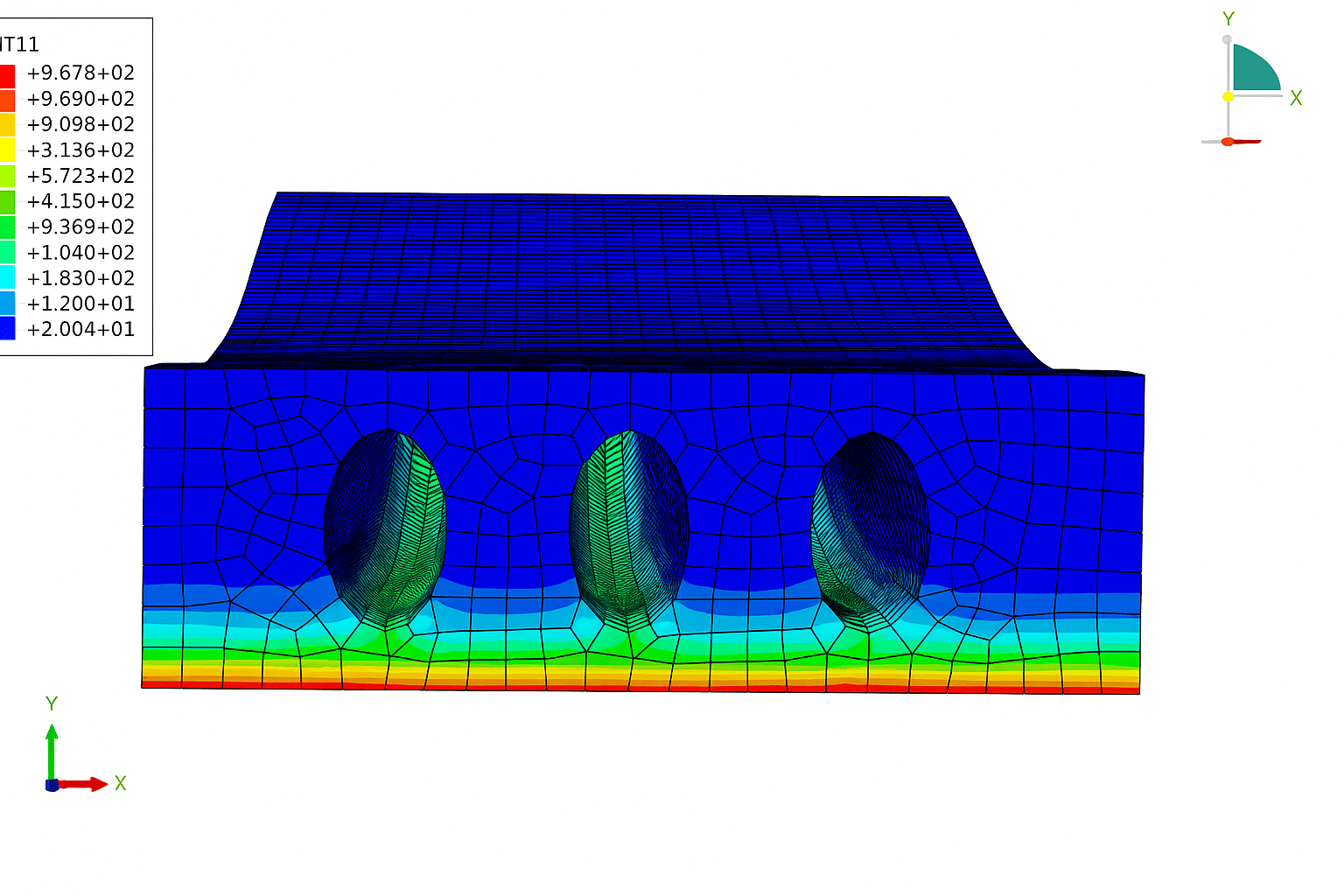
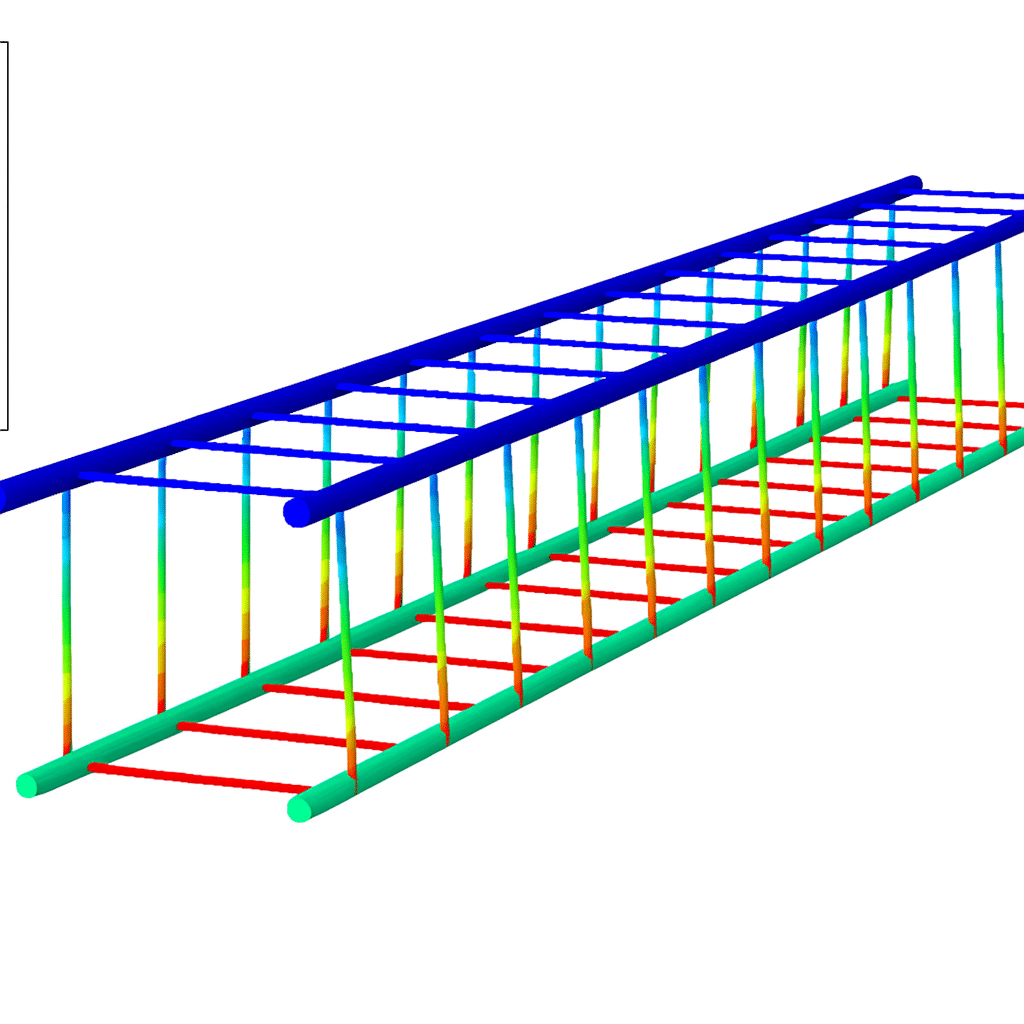
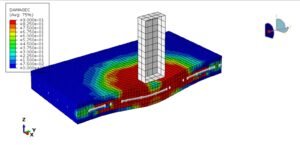
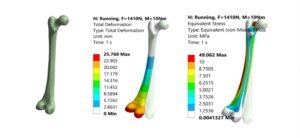
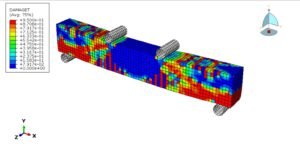
- Numerical simulations like FEA/CFD for complex geometries.
- Experimental measurements for real-world validation.
5. Key Parameters in Heat Transfer Analysis
- Thermal conductivity (k) – material’s ability to conduct heat.
- Heat transfer coefficient (h) – how well a surface and fluid exchange heat.
- Thermal diffusivity (α\alpha) – how quickly temperature changes within a material.
- Biot number, Fourier number, Nusselt number – dimensionless numbers that guide design and scaling.
In this package, you’ll learn all the heat transfer and thermal-structure analysis methods through 16 lectures.