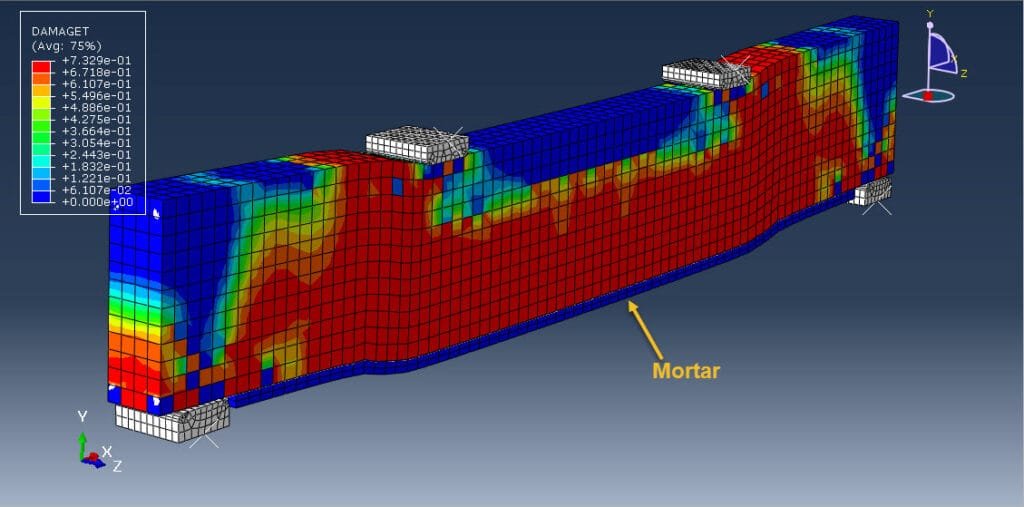
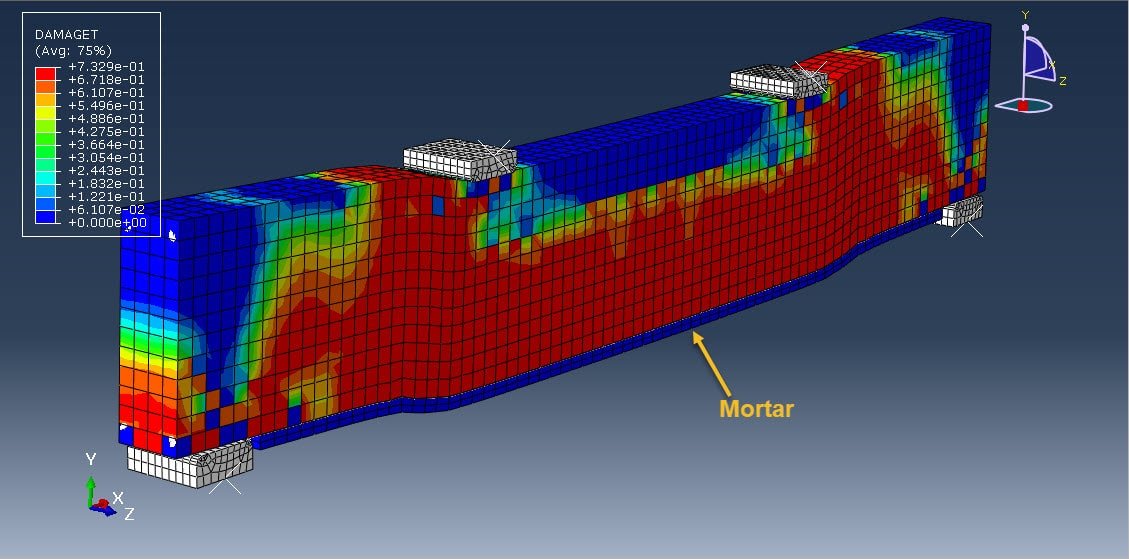
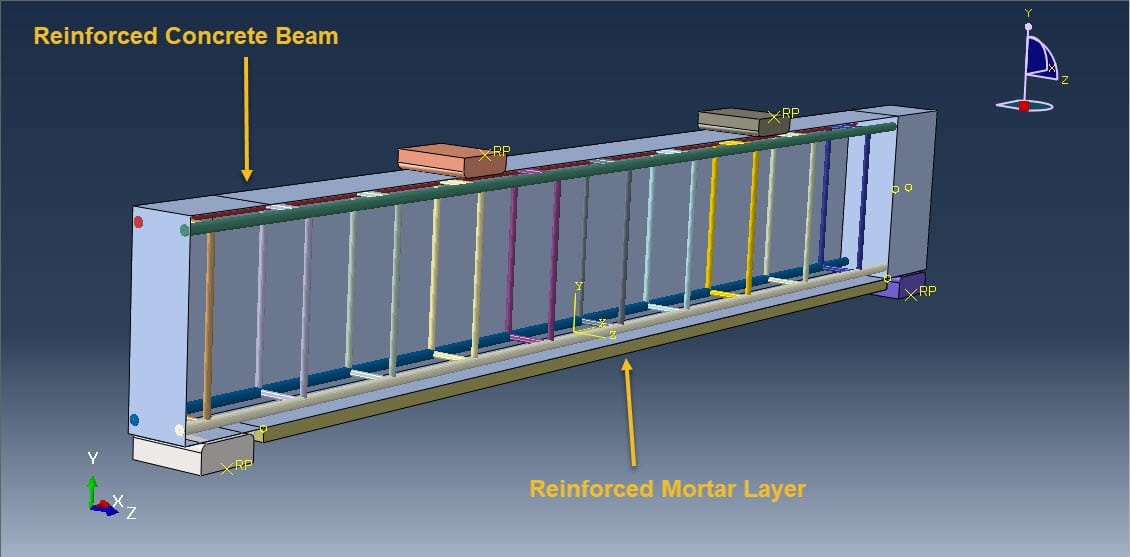
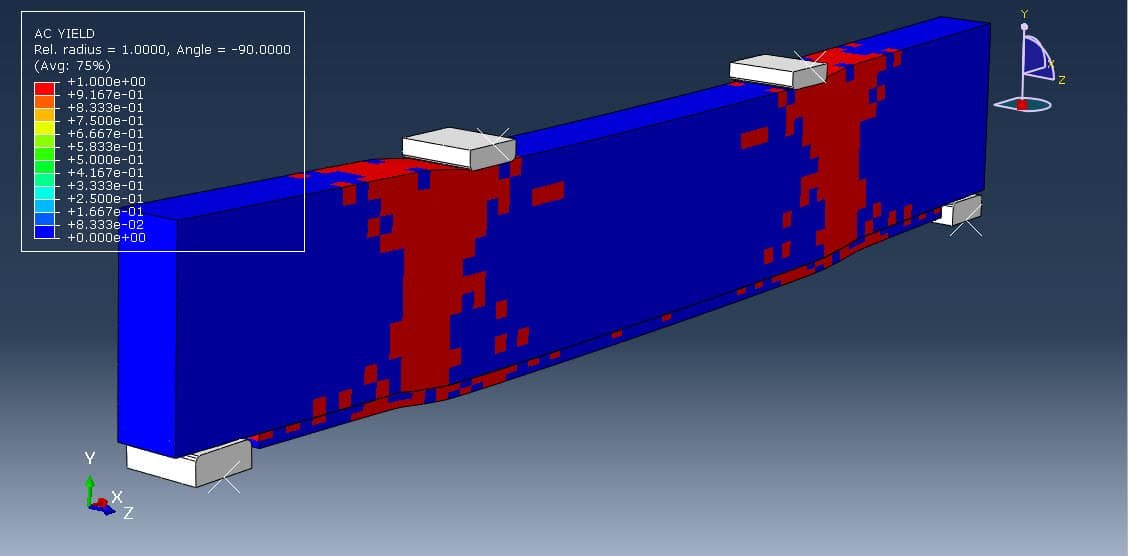
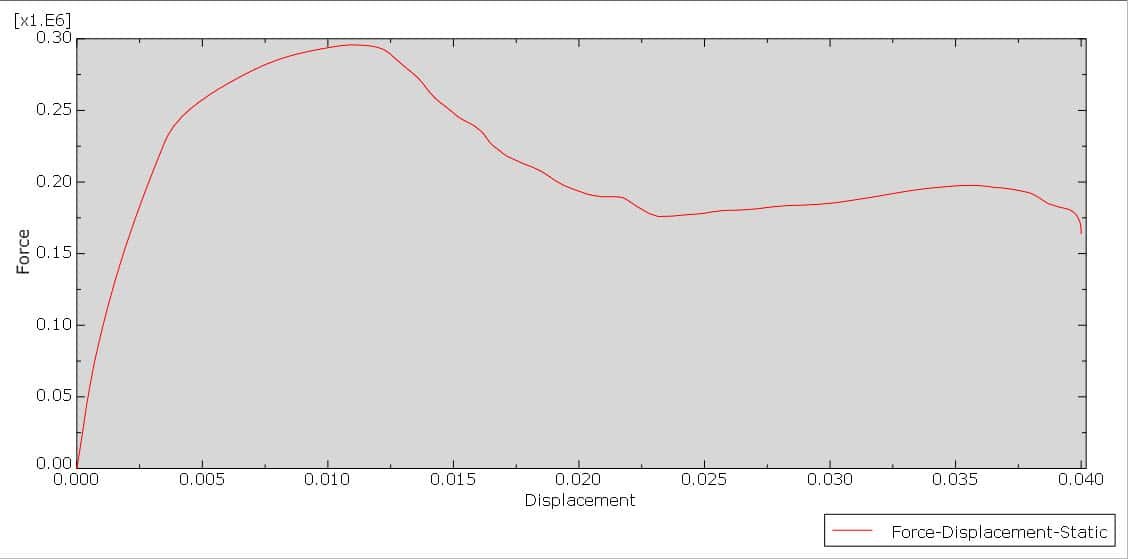
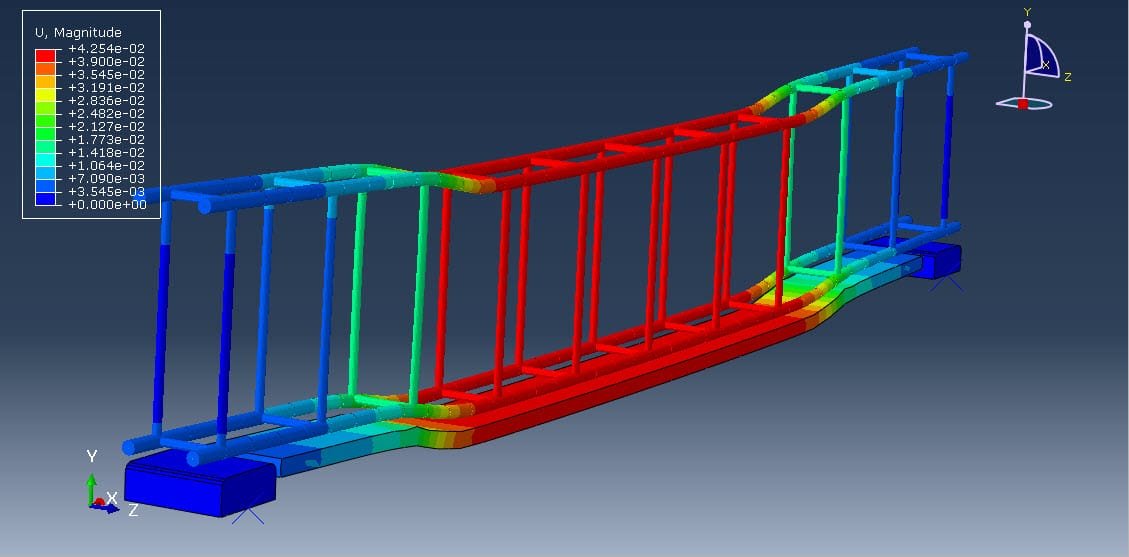
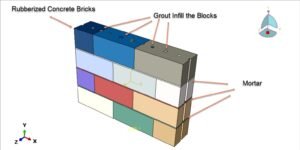
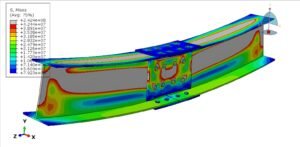
Reinforced concrete (RC) beams are widely used structural elements in buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure. Over time, these beams may experience deterioration due to overloading, aging, corrosion, or design deficiencies. To restore or enhance their structural capacity, strengthening techniques are employed. One such method is strengthening with a mortar layer, which is a cost-effective and practical solution, especially for flexural (bending) performance improvement.
Flexural analysis involves determining the bending capacity of a beam, specifically:
The moment of resistance (ultimate bending moment),
The neutral axis location, and
The stress and strain distributions across the cross-section under bending.
For RC beams, the analysis considers the contributions of:
Concrete in compression,
Steel reinforcement in tension and compression,
Any added strengthening layer (like mortar) that contributes to flexural performance.
A mortar layer, typically applied to the tension face (bottom) of the beam, can:
Increase the effective depth of the beam,
Enhance the moment capacity,
Improve crack control,
Protect the reinforcement.
Mortar used for strengthening is often cement-based, possibly with fibers or polymers for improved bonding and mechanical properties.
When analyzing an RC beam strengthened with a mortar layer, the following assumptions are commonly made:
Plane sections remain plane after bending.
Full composite action (perfect bond) between the original concrete and the mortar layer.
Concrete and mortar are only effective in compression (no tension resistance after cracking).
Steel reinforcement and mortar layer behave elastically up to yielding.
Cross-Section Modeling:
Determine the geometry of the strengthened section, including the thickness and width of the mortar layer.
Material Properties:
Define material properties: fc′f’_{c} for concrete, fm′f’_{m} for mortar, and fyf_y for steel.
Flexural analysis can be done using:
Strain compatibility method (more accurate),
Simplified rectangular stress block (per design codes like ACI, Eurocode).
Benefits:
Low-cost and practical,
Easy application for in-service structures,
Improved flexural strength and serviceability.
Limitations:
Dependent on the bond quality between the mortar and the original concrete,
Might not be effective for severely deteriorated beams,
Requires surface preparation and curing control.
Flexural analysis of RC beams strengthened with a mortar layer provides insights into how structural capacity is enhanced. It integrates knowledge of composite behavior, material mechanics, and structural design principles. This method is particularly valuable for rehabilitation and retrofitting projects where performance upgrade and cost-efficiency are critical.

Abaqus
€81,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€299,00 €249,00

Uncategorized
€95,00 €80,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?