Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) composites are increasingly used in aerospace, automotive, marine, and civil engineering structures due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent fatigue performance. However, their behavior under fire exposure is a critical design concern, as CFRP materials differ significantly from metals in thermal response and degradation mechanisms.
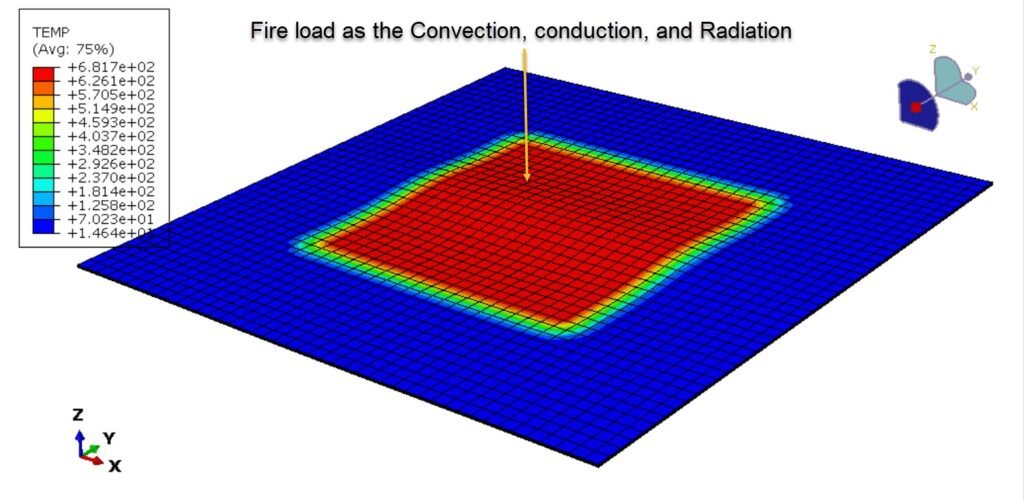
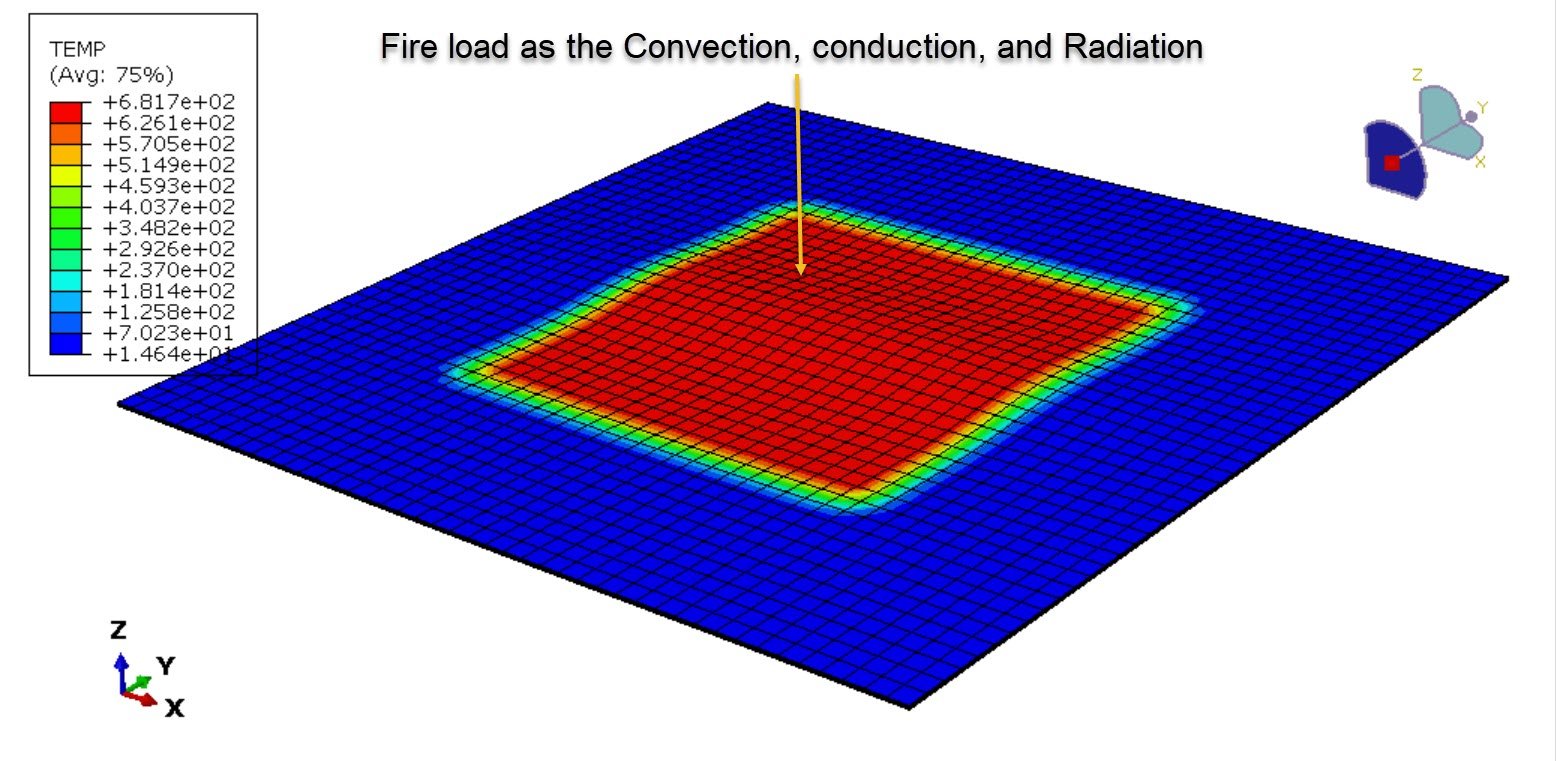
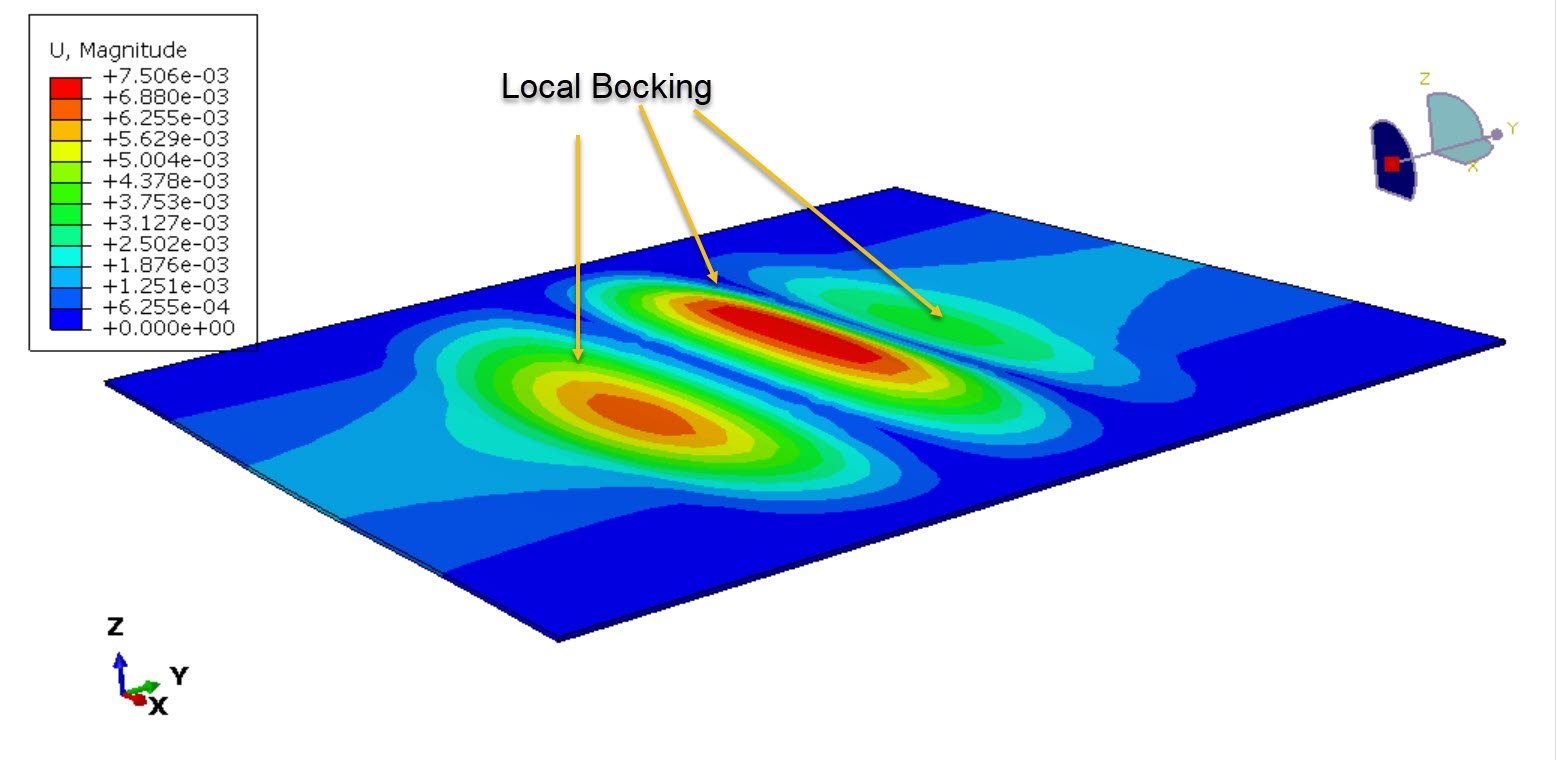
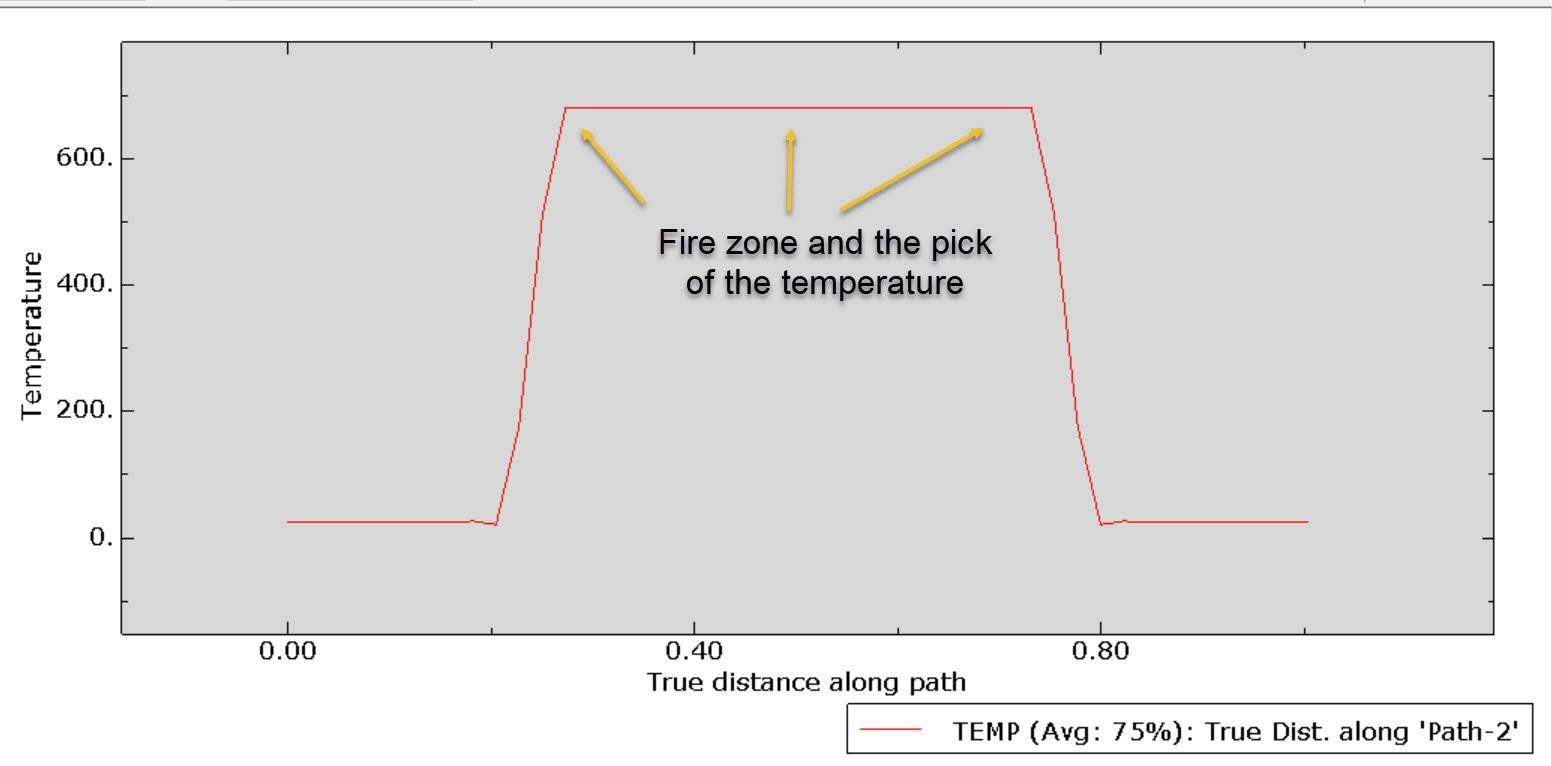
In this case, the 3D CFRP plate under all types of heat transfer methods, like convection, conduction, and radiation, is investigated.
Fire analysis of CFRP composites focuses on understanding how elevated temperatures, combustion products, and heat flux affect both the polymer matrix and the carbon fibers. When exposed to fire:
The polymer matrix softens, decomposes, or volatilizes, losing mechanical integrity.
Carbon fibers maintain strength longer, but oxidation can occur at high temperatures in the presence of oxygen.
Thermal expansion mismatch between fiber and matrix can induce micro-cracking.
Delamination, char formation, and resin burnout may reduce load-carrying capacity.
Key aspects evaluated in fire analysis include:
Thermal degradation kinetics of the polymer matrix.
Heat release rate, ignition temperature, and smoke/toxic gas production.
Residual mechanical properties after fire exposure.
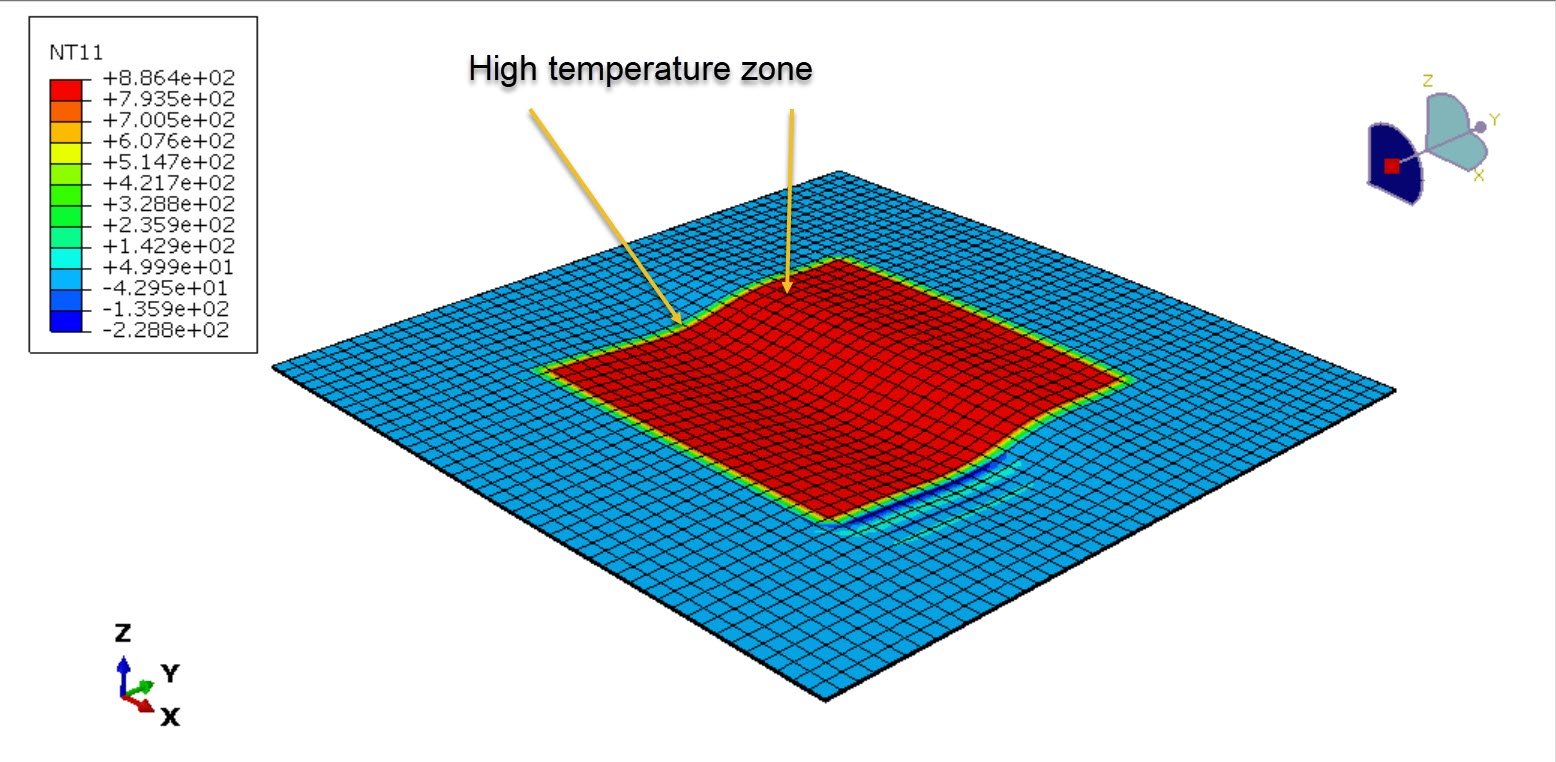
Heat transfer modeling, including conduction through the laminate and surface heat flux.
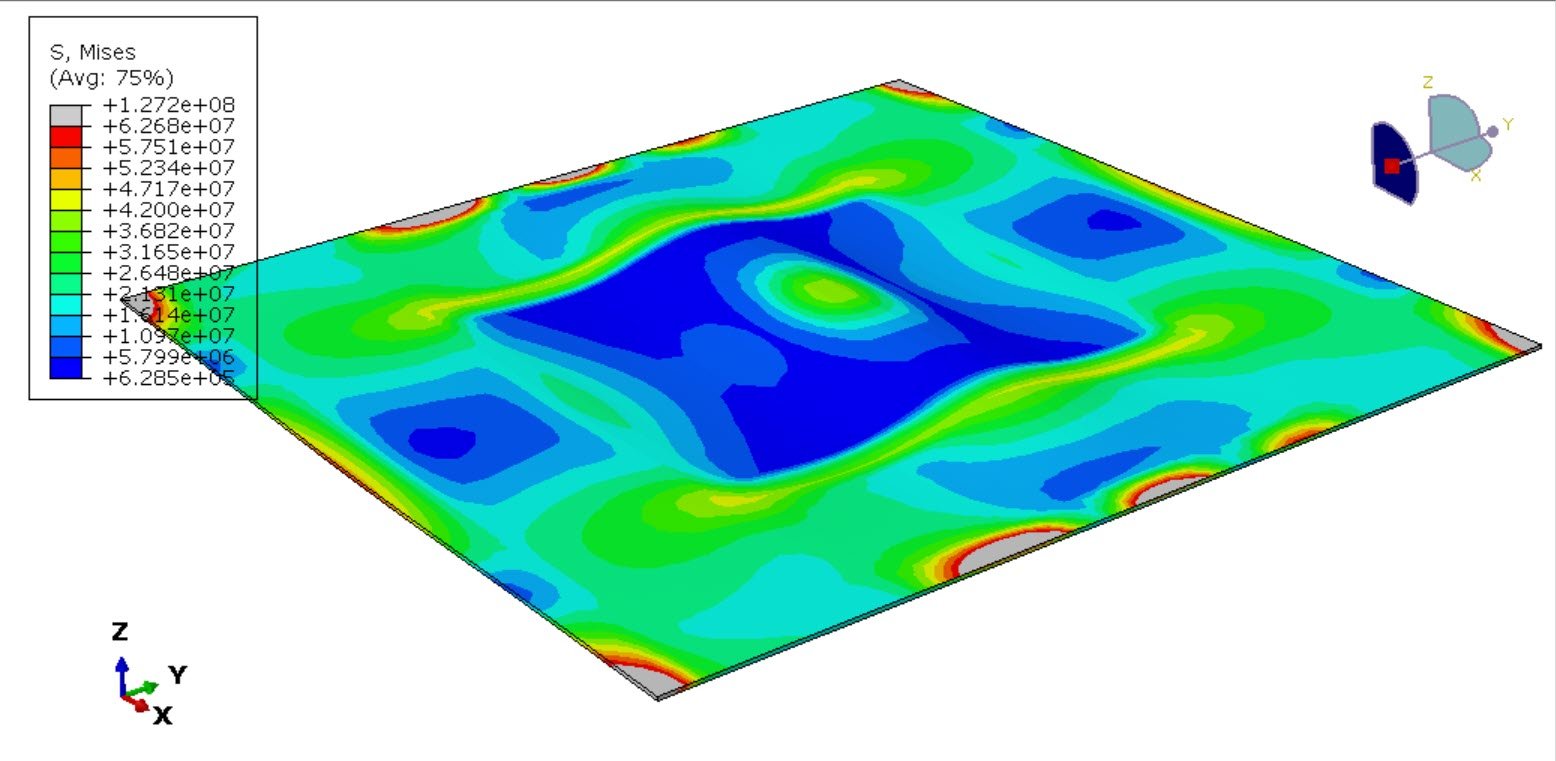
Failure mechanisms, such as matrix decomposition, interlaminar debonding, or fiber oxidation.
Analytical, numerical, and experimental methods are used together to study fire behavior:
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) characterize material decomposition.
Cone calorimetry measures ignition, mass loss, and heat release.
Finite Element (FE) simulations predict thermal gradients and structural weakening.
Mechanical tests after heating determine residual strength.
Improving fire performance may involve:
Fire-retardant additives in the resin,
Protective coatings,
Intumescent layers, or
Hybrid laminates incorporating fire-resistant materials.
Fire simulation of CFRP in Abaqus typically involves coupled thermal–mechanical analysis to capture:
Heat transfer into the composite structure,
Thermal degradation of the polymer matrix,
Loss of stiffness and strength with temperature,
Structural failure (delamination, softening, fiber failure).
Overall, fire analysis of CFRP composites is essential for safety-critical applications, ensuring that structural integrity and failure behavior are well understood under high-temperature and fire conditions

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?