🔥 Introduction to Fire Analysis of Timber Beams
Timber is a widely used construction material known for its sustainability, ease of handling, and aesthetic appeal. However, being an organic material, timber is combustible, and its behavior under fire conditions is a critical factor in structural design. Fire analysis of a timber beam involves assessing how the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of the beam are affected when exposed to elevated temperatures or fire scenarios.
This analysis is essential in ensuring the fire safety of timber structures, meeting building code requirements, and enabling the use of timber in multi-storey and public buildings.
🔍 Explanation of Fire Analysis of Timber Beams
Fire analysis of a timber beam includes:
1. Charring Mechanism
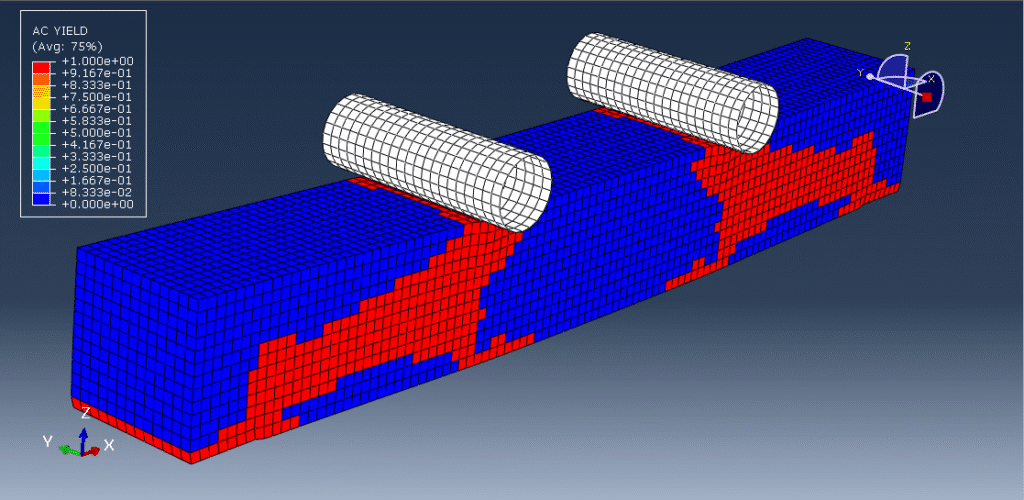
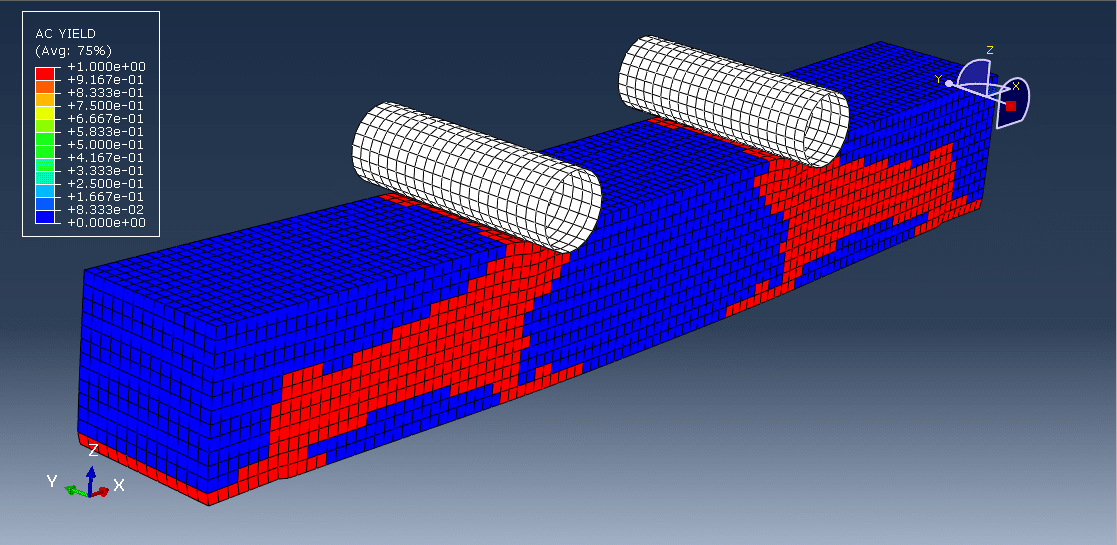
- When exposed to fire, timber undergoes pyrolysis, forming a char layer on its surface.
- The charred layer acts as an insulator, protecting the unburnt “core” or inner timber.
- Charring reduces the effective cross-section of the beam, thus reducing its strength and stiffness.
2. Effective Cross-Section Method
- Fire design assumes a reduced cross-section by subtracting the char depth from all exposed surfaces.
- Structural capacity is then calculated using this residual cross-section.
- Engineers may apply modification factors for strength reduction due to elevated temperatures in the heated zone just behind the char layer.
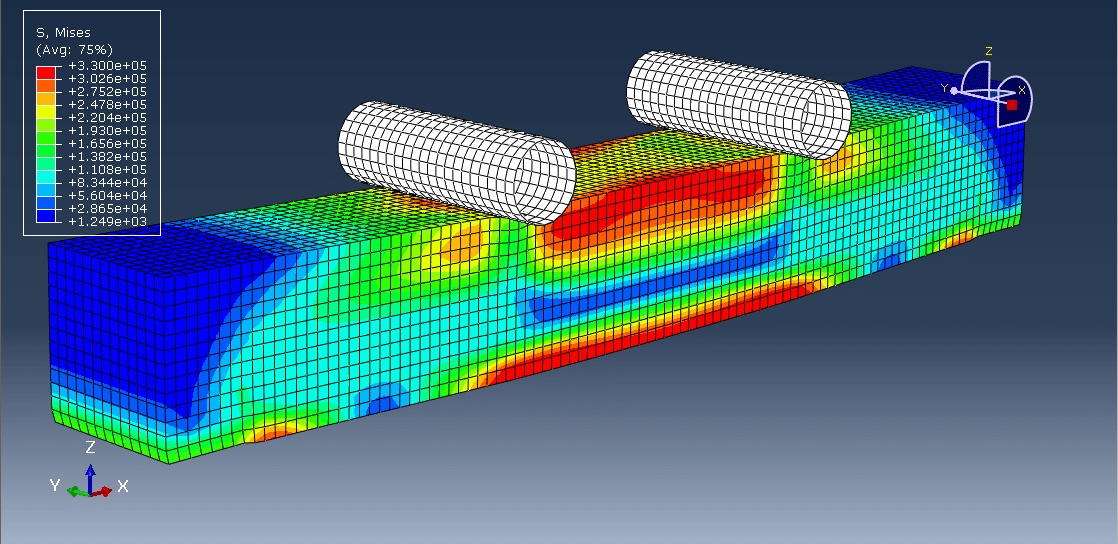
3. Structural Performance Evaluation
- After calculating the reduced cross-section:
- Bending strength, shear strength, and deflection under load are evaluated.
- Time to failure can be predicted for given fire exposure durations.
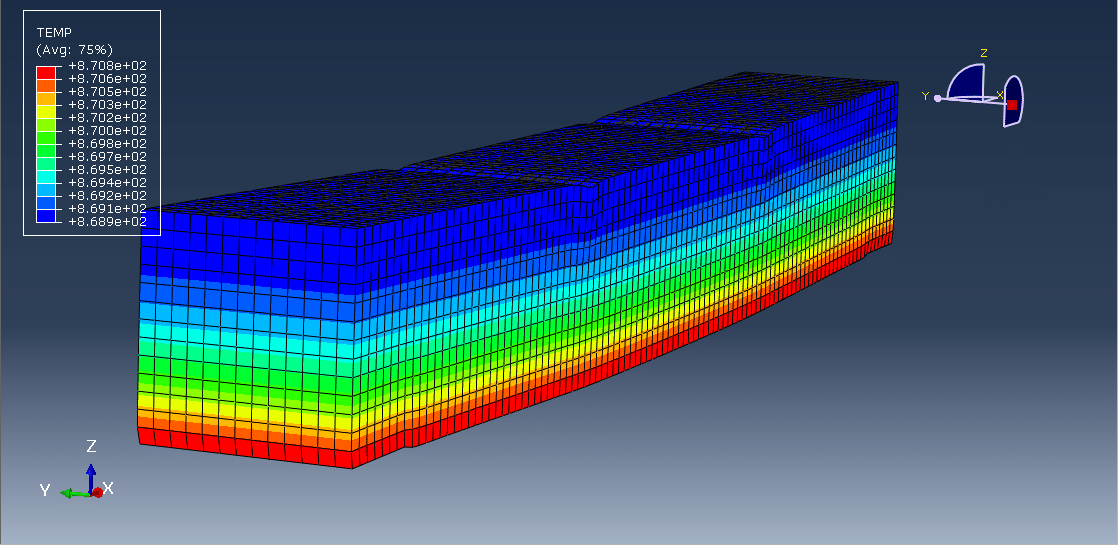
- In advanced analysis, thermal gradients, moisture content, and mechanical properties degradation with temperature are considered.
4. Fire Resistance Rating
- The fire resistance period (e.g., 30, 60, 90 minutes) is the time the beam can maintain its load-bearing function during fire.
- This can be determined:
- Using prescriptive design tables (e.g., in building codes).
- Through calculated fire resistance based on charring and strength reduction.
- With finite element modeling for complex scenarios.
🛠️ Practical Applications
- Used in the design of mass timber structures (e.g., CLT, glulam).
- Important for retrofitting or assessing existing buildings.