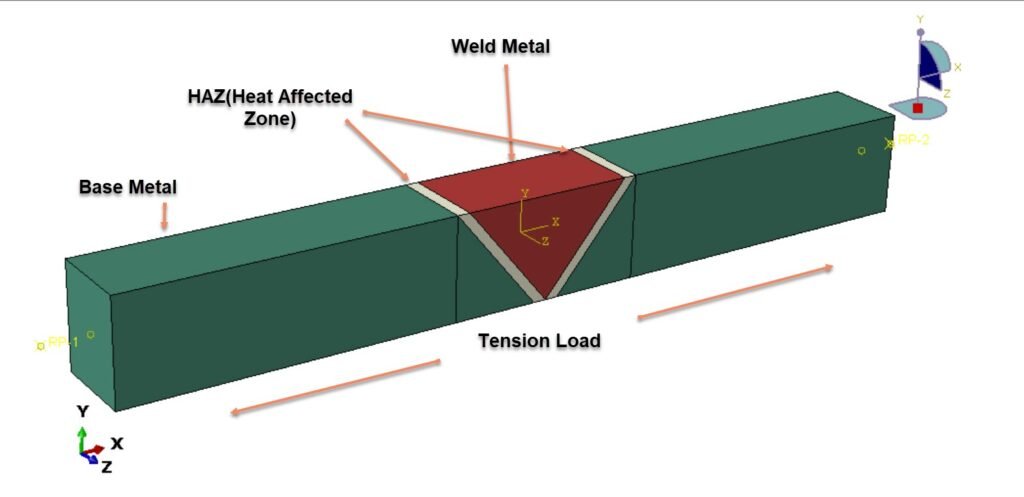
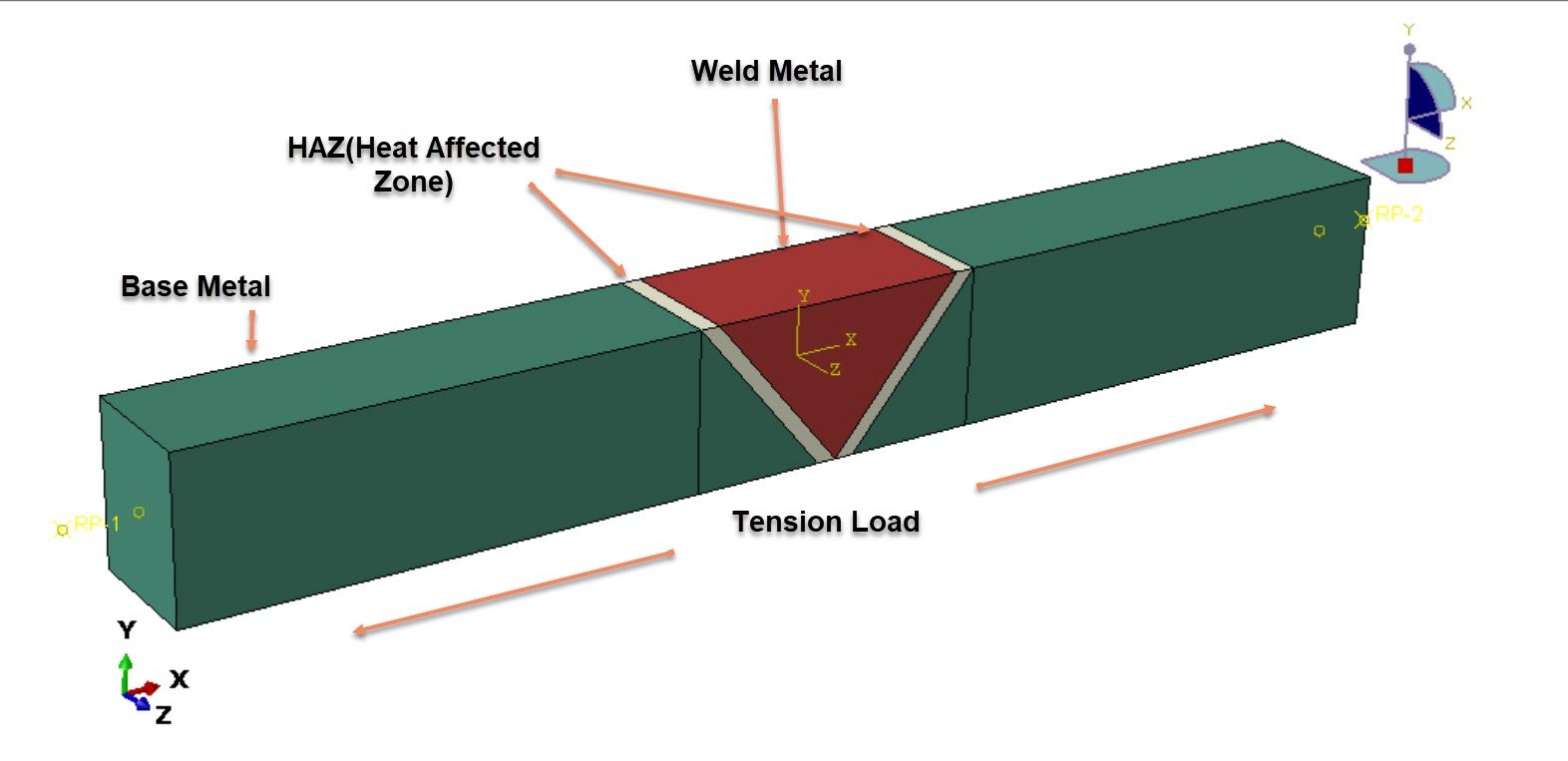
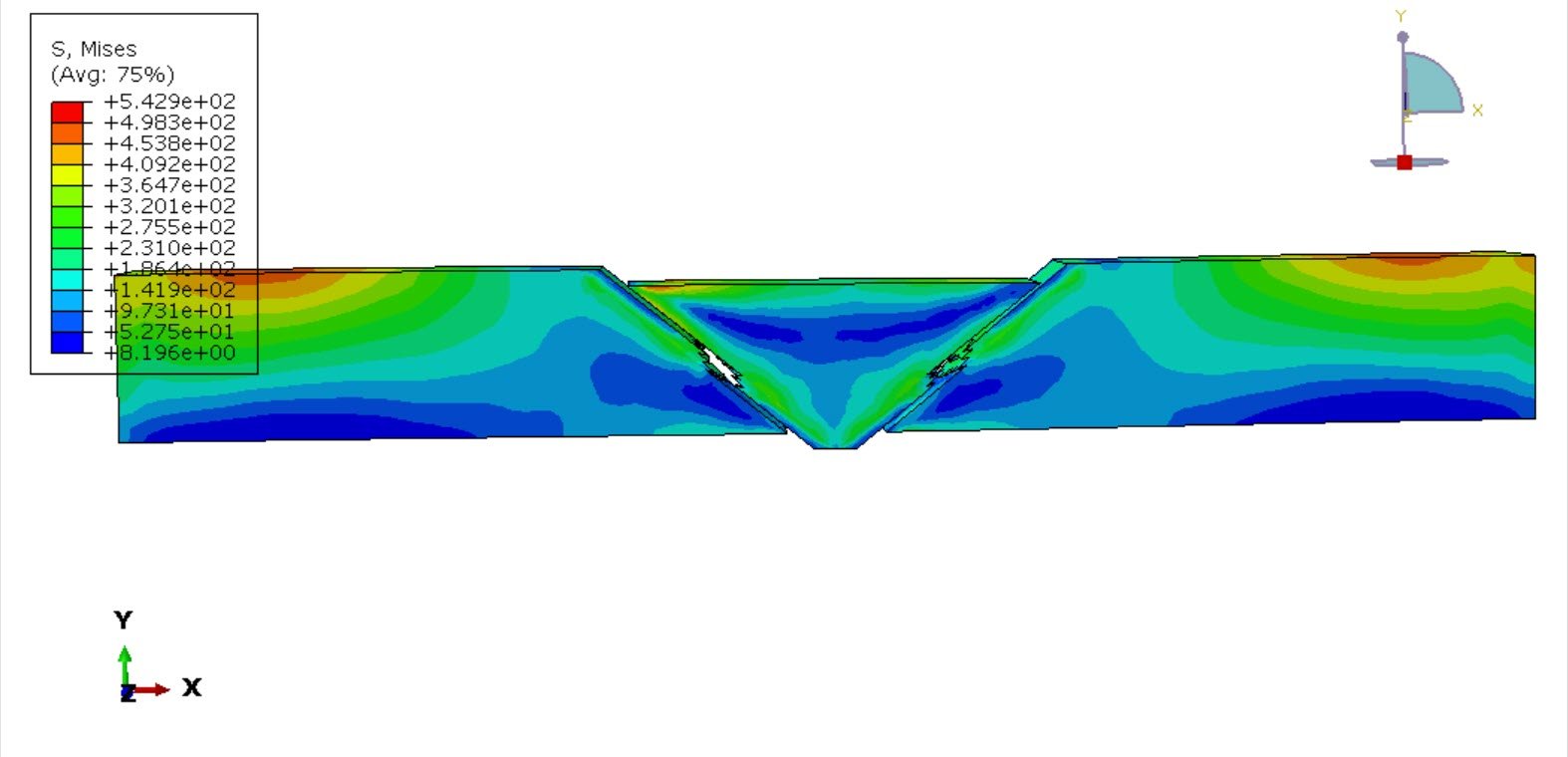
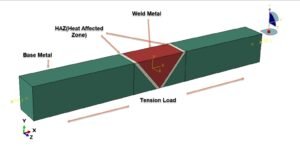
Dynamic tensile behavior of welded steel structures is a critical consideration in engineering applications where components are subjected to high-strain-rate loading, such as automotive crashes, impact events, blast loading, and defense structures. Welding processes inherently introduce material heterogeneity due to thermal cycles, resulting in distinct microstructural regions with different mechanical properties. The primary regions include the base metal (BM), the weld metal (WM), and the heat-affected zone (HAZ). Among these, the HAZ is often the most susceptible to damage initiation because of microstructural transformations and residual stresses induced during welding. Therefore, understanding the dynamic tensile response and failure mechanisms across these zones is essential for reliable structural integrity assessment.
In this study, a dynamic tensile test simulation of a steel plate containing a central welded joint is performed using finite element analysis in Abaqus. The welded plate is idealized as a three-zone model representing the base metal, heat-affected zone, and weld metal. Each region is assigned distinct elastic–plastic material properties to capture the mechanical mismatch produced by the welding process.
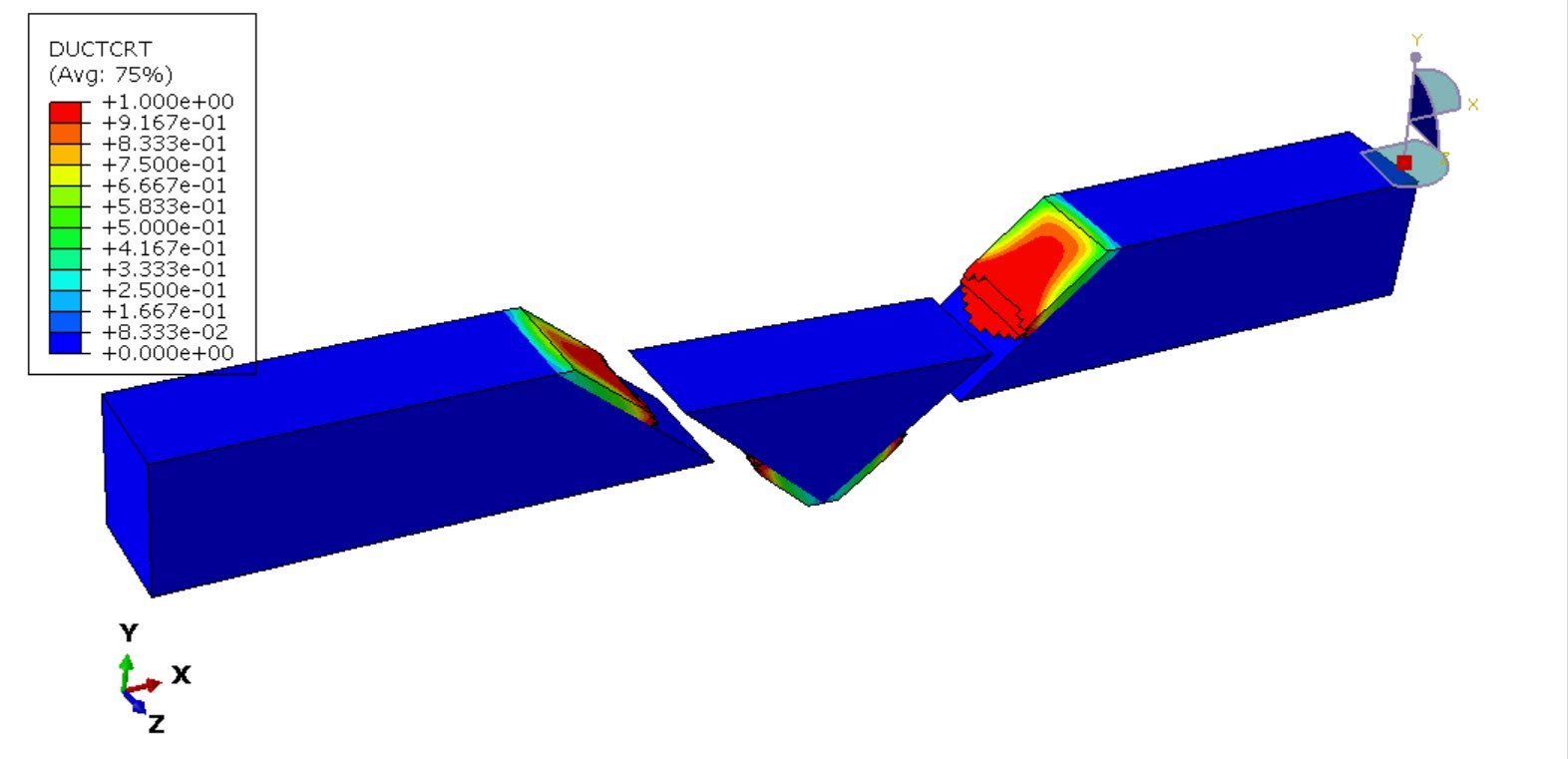
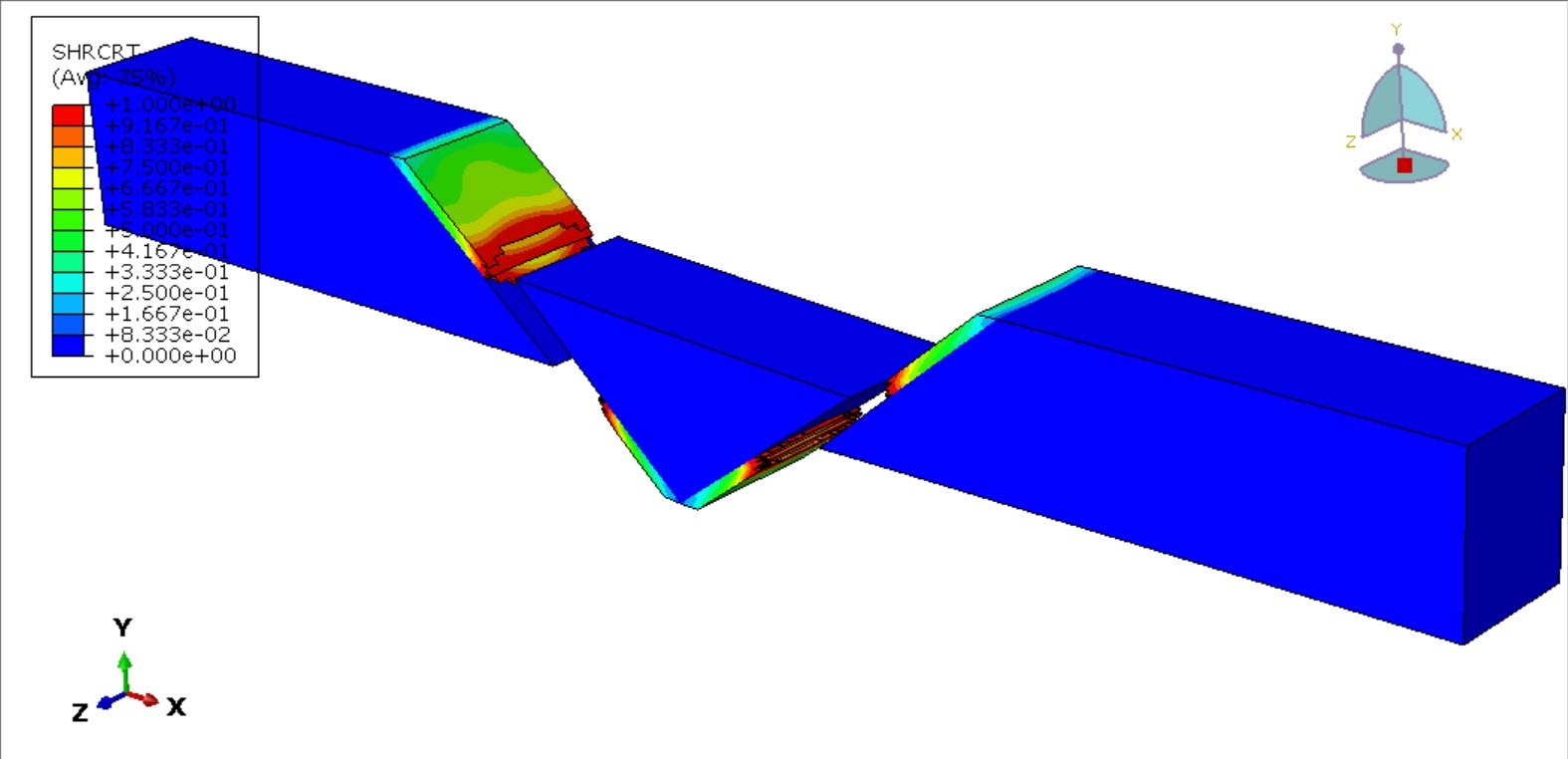
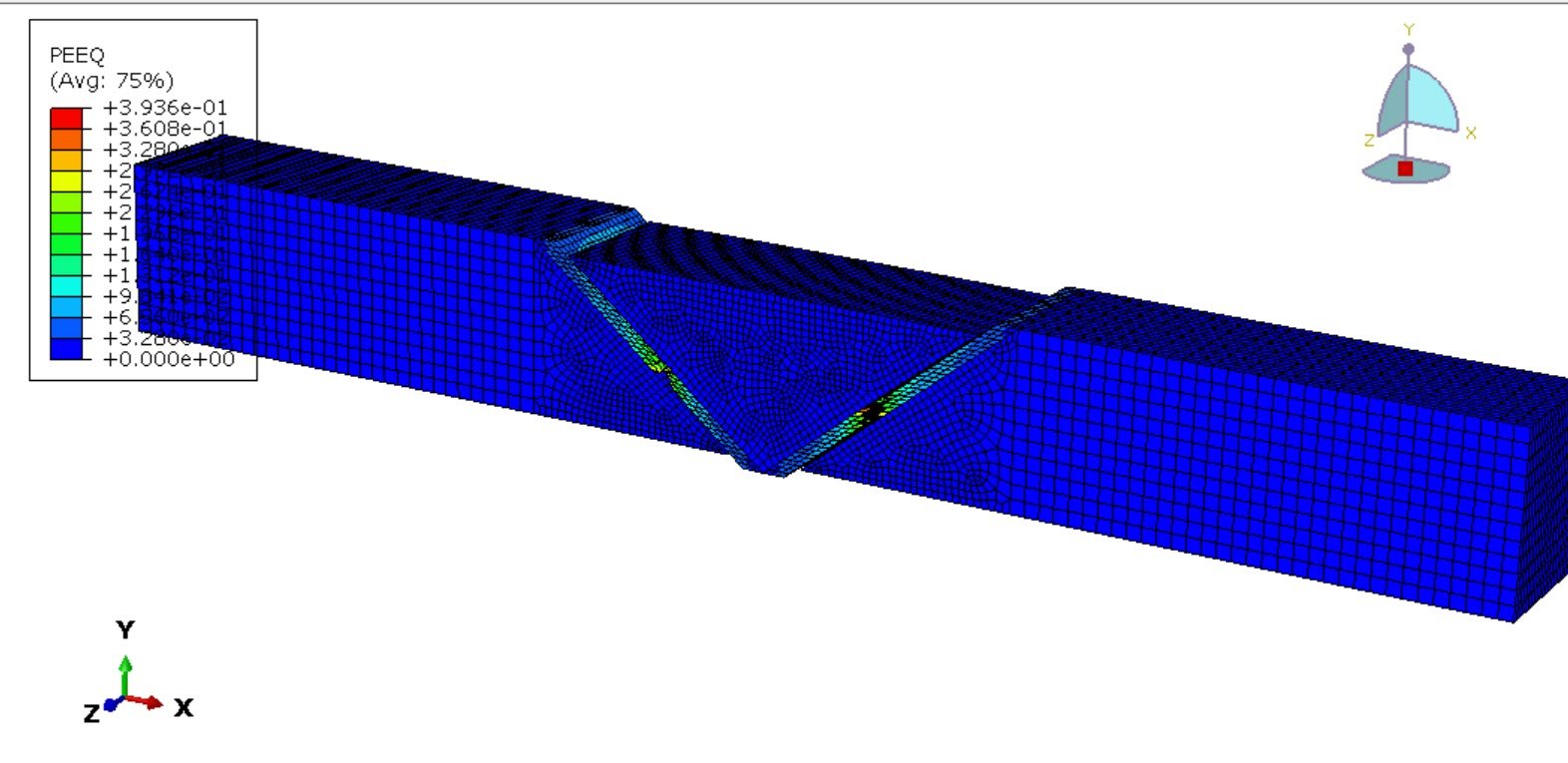
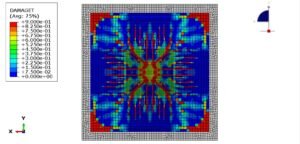
To realistically represent material failure under high strain rates, a coupled damage formulation is employed. All three metallic zones are modeled using an elastic–plastic constitutive law combined with ductile damage and shear damage initiation and evolution criteria. This approach enables simulation of void nucleation, growth, and coalescence (ductile fracture) alongside shear-dominated failure, which is particularly relevant under dynamic loading conditions.
Given the transient and highly nonlinear nature of the problem—characterized by rapid loading, progressive damage, and element deletion—an explicit dynamic solver is utilized. The Abaqus/Explicit step is well-suited for capturing inertia effects, complex contact conditions (if present), and severe material degradation without convergence difficulties typically associated with implicit solvers.
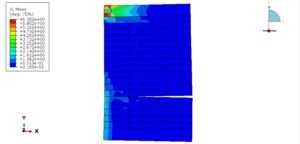
The objective of this simulation is to evaluate the stress–strain response, strain localization patterns, and damage evolution across the welded joint under dynamic tensile loading. Special attention is given to identifying the zone most vulnerable to crack initiation and propagation, as well as quantifying the influence of material heterogeneity on the global mechanical performance of the welded steel plate.

Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€84,00 €41,00
Abaqus
€86,00 €43,00
Abaqus
€88,00 €49,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?