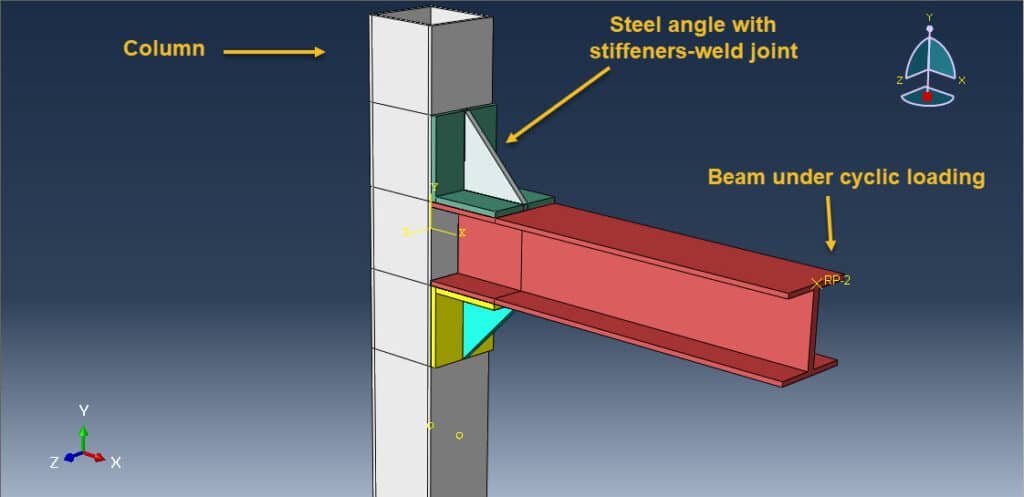
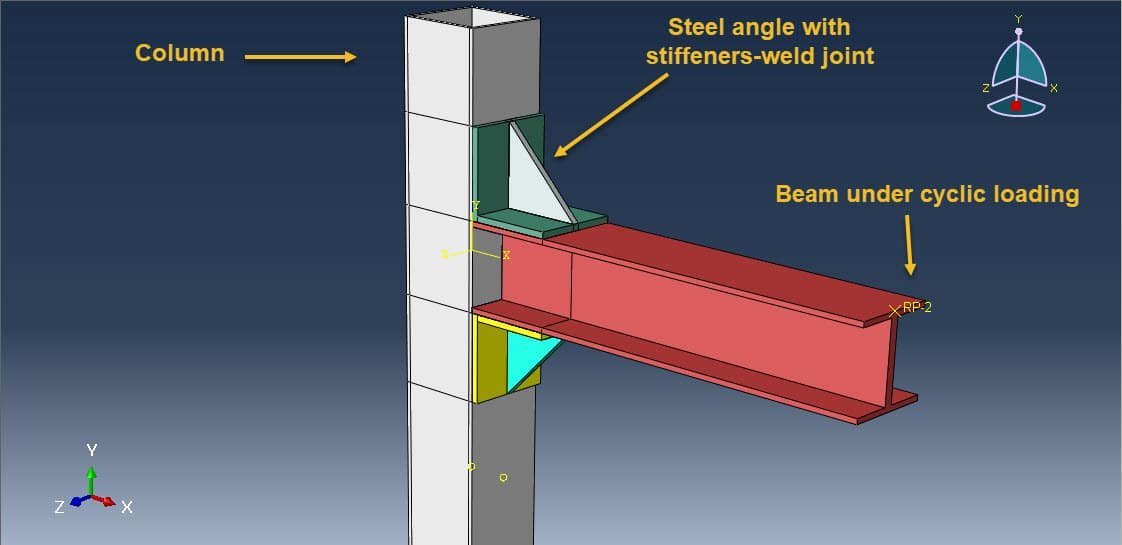
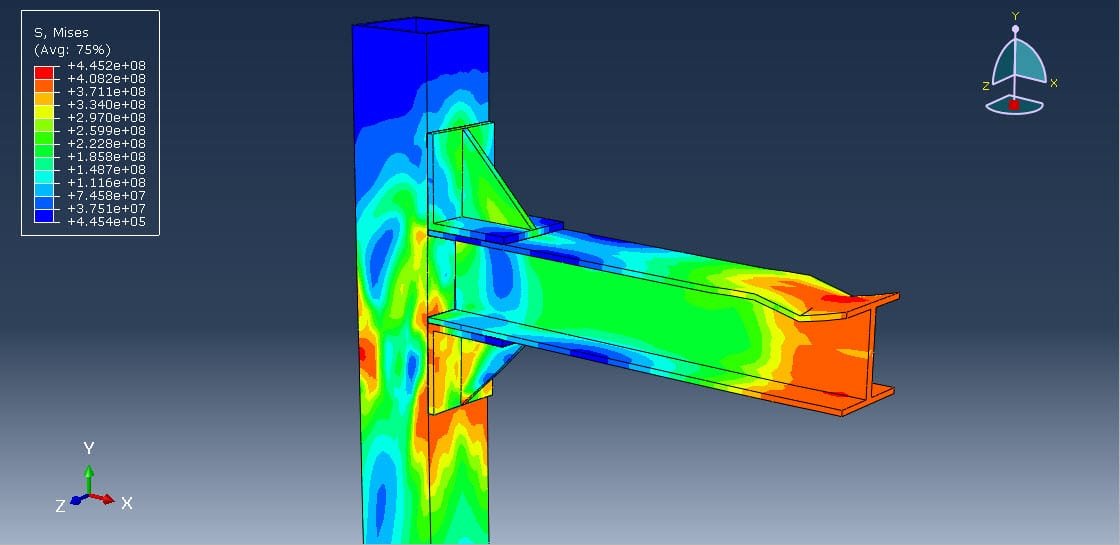
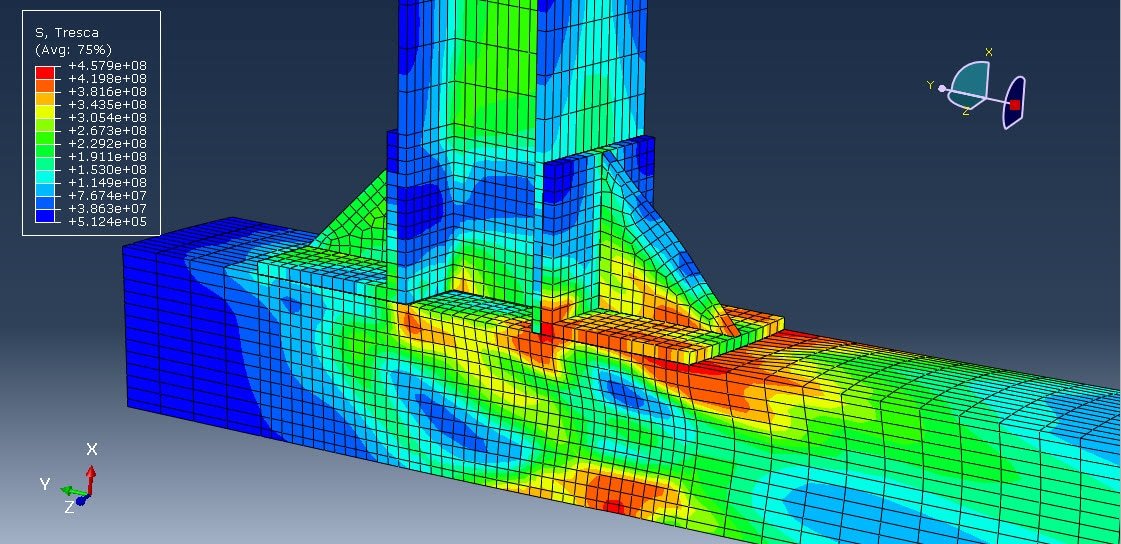
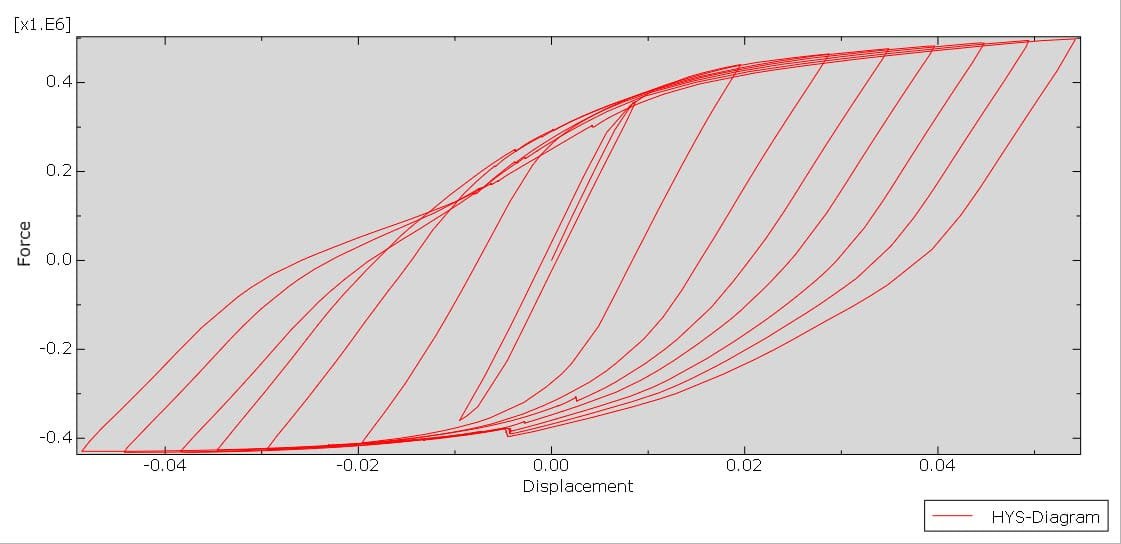
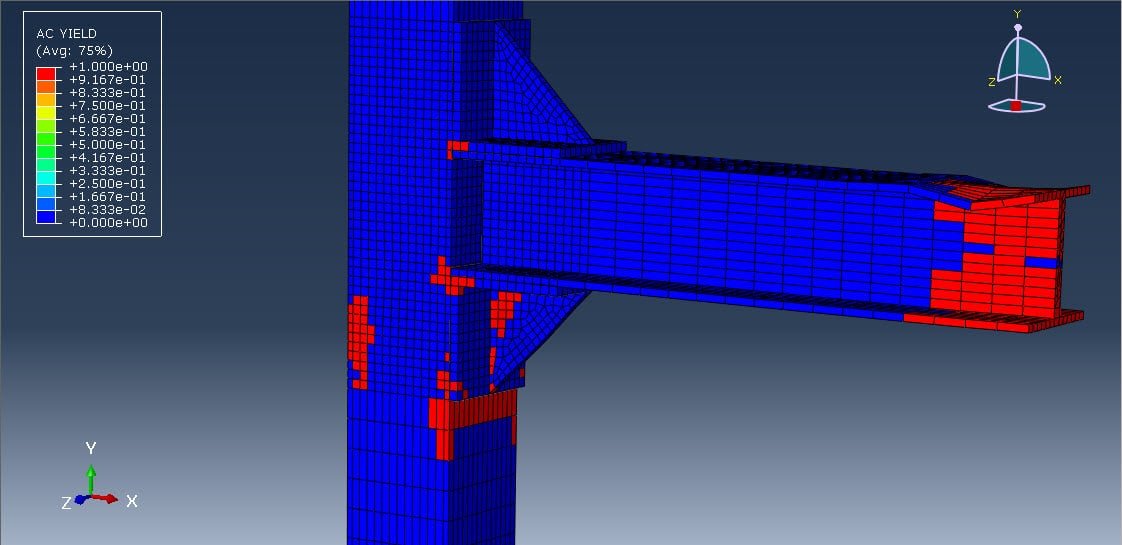
In structural engineering, beam-column joints play a critical role in transferring forces and ensuring stability within steel frame structures. When subjected to cyclic loading, such as those experienced during earthquakes or wind loads, these joints must withstand repeated stress reversals without significant degradation in strength or stiffness.
One common detailing method for these joints involves the use of welded steel angles, which are used as connectors between the beam and the column. These angles can be configured in various ways (e.g., top-and-seat angles, double angles at the beam web), and their design and behavior under cyclic loads are crucial for the joint’s overall seismic performance.
Cyclic loading refers to the application of repeated or reversing loads over time. In seismic design, structures must absorb and dissipate energy through inelastic deformation without collapsing. Therefore, understanding how a welded angle connection performs under such conditions is vital for:
Angles may be used as:
Cyclic analysis of such joints typically includes:

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
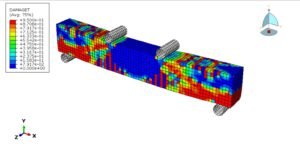
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
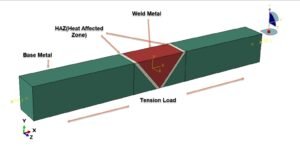
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?