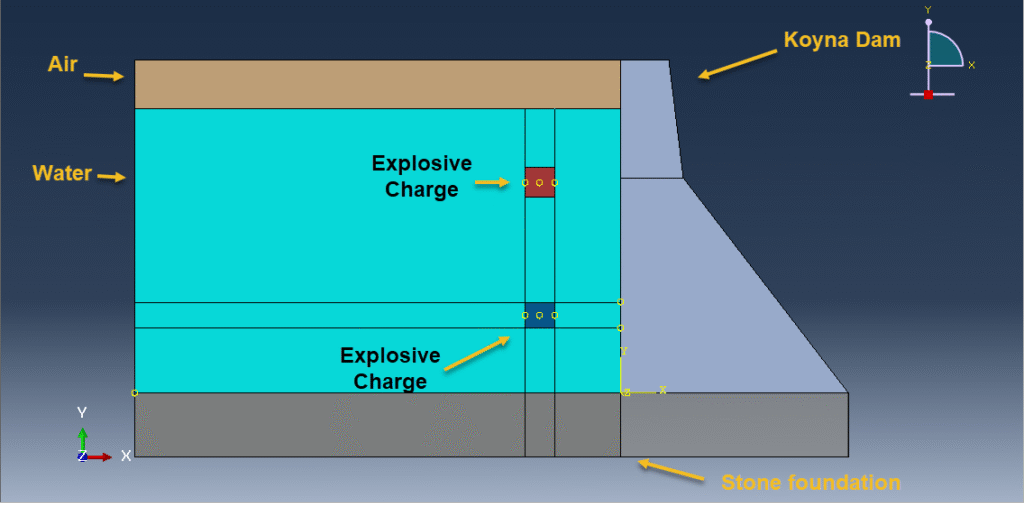
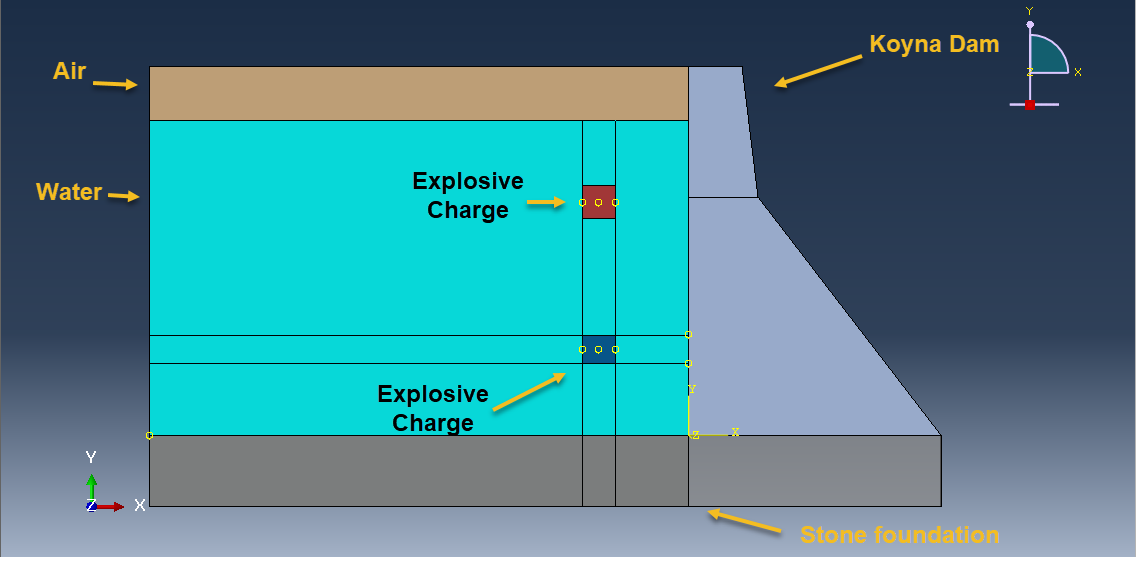
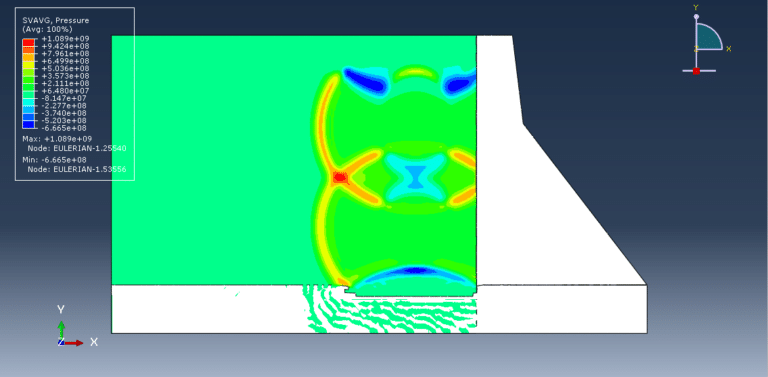
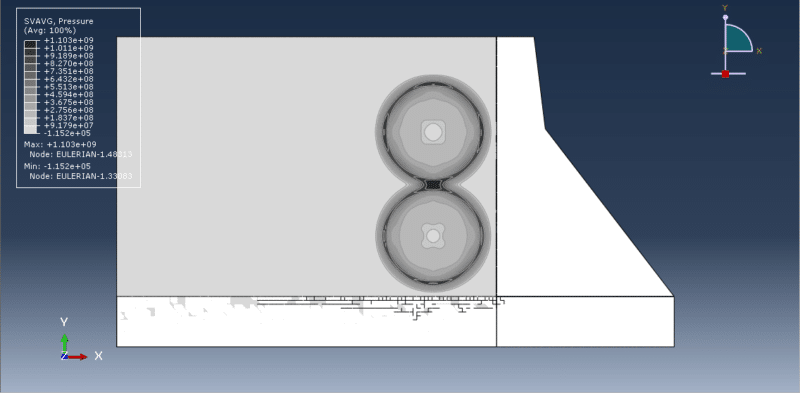
This tutorial presents the simulation of damage prediction in a concrete gravity dam subjected to underwater explosion shock loading using Abaqus. The concrete dam and the rock foundation are modeled as three-dimensional solids, while the TNT charge, surrounding water, and air are defined as Eulerian parts. Interest in blast load analysis has increased in recent years due to accidental explosions, intentional events, and terrorist attacks that threaten the safety of critical infrastructure such as government buildings, embassies, bridges, and high dams. Since dams retain vast quantities of water, their failure could result in catastrophic downstream devastation, making it essential to understand and predict their response to explosive loads.
The Concrete Damage Plasticity (CDP) model is used to capture the tension and compression damage in the dam under blast loading. The air is modeled with the ideal gas equation of state, water behavior is defined using the Us–Up equation of state, and the TNT charge is represented with the JWL equation of state to accurately reproduce detonation effects. For the rock foundation, the Johnson–Holmquist material model is applied through code to evaluate damage and failure.
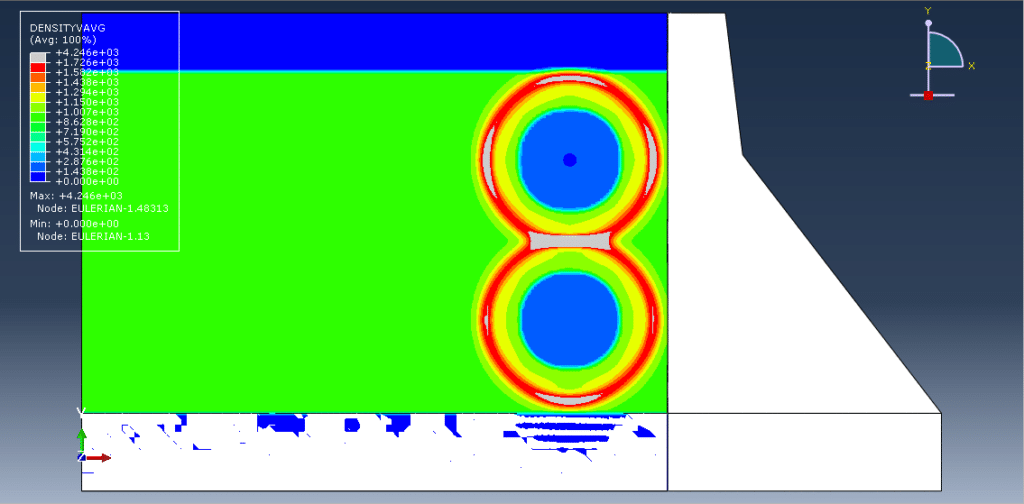
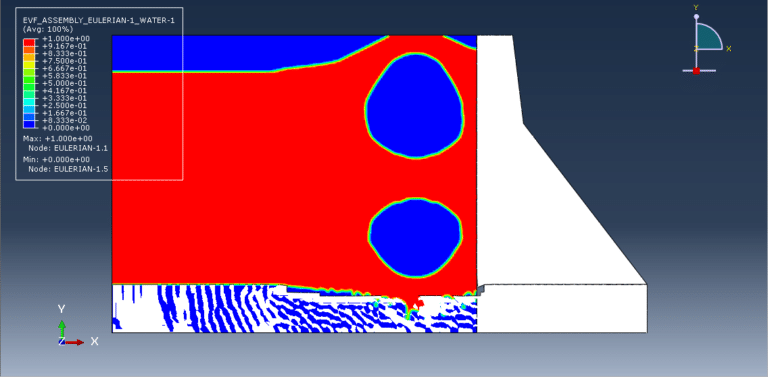
The analysis uses a dynamic explicit step with the general contact capability, along with appropriate boundary conditions and predefined fields. A refined mesh is adopted to ensure reliable results. After completion, the simulation provides outputs related to stress, strain, damage, and overall structural response under explosive loading.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?