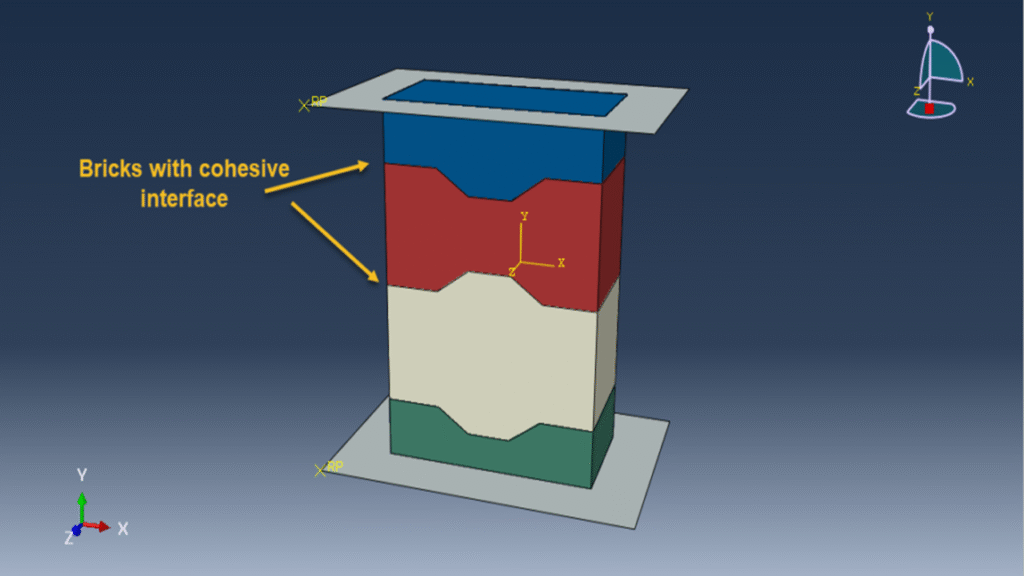
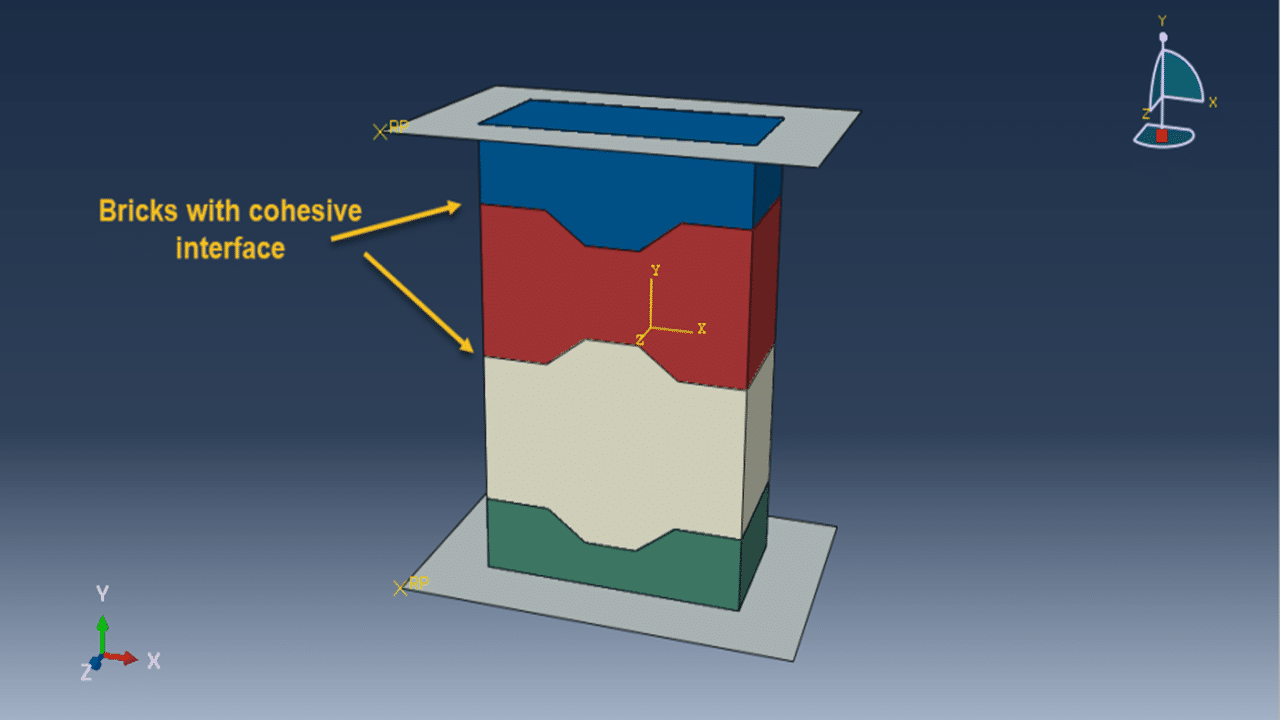
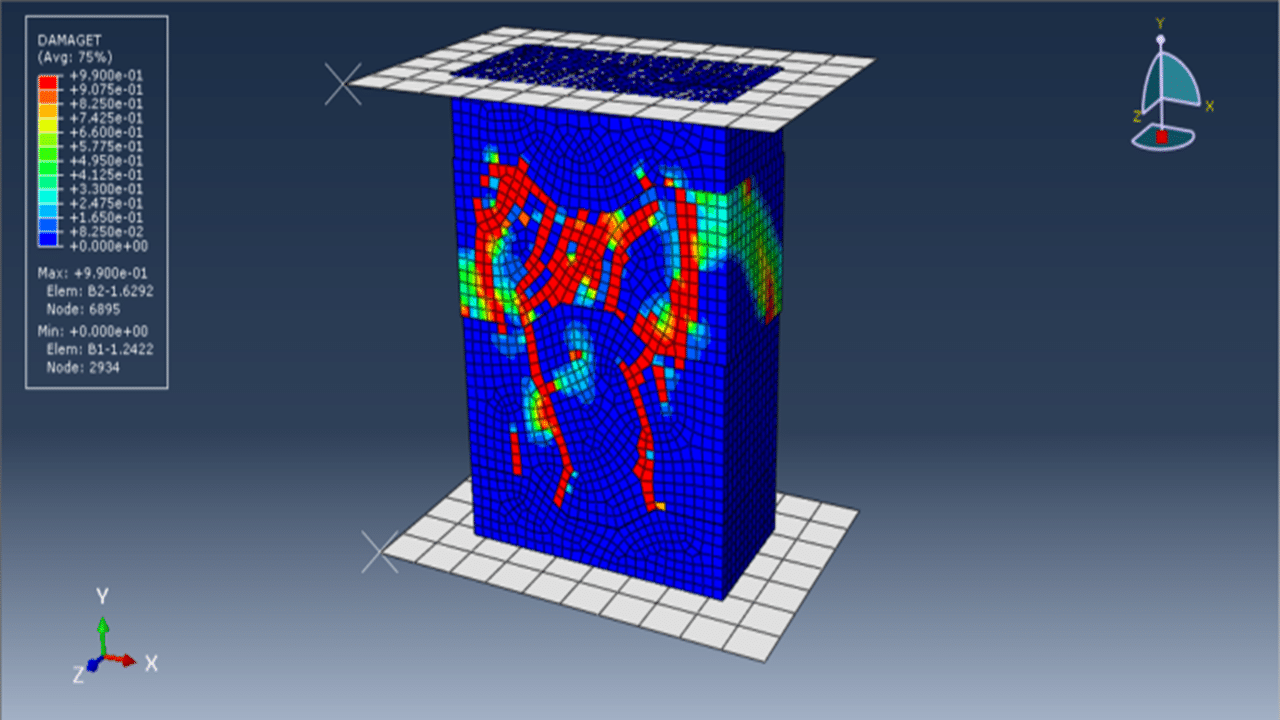
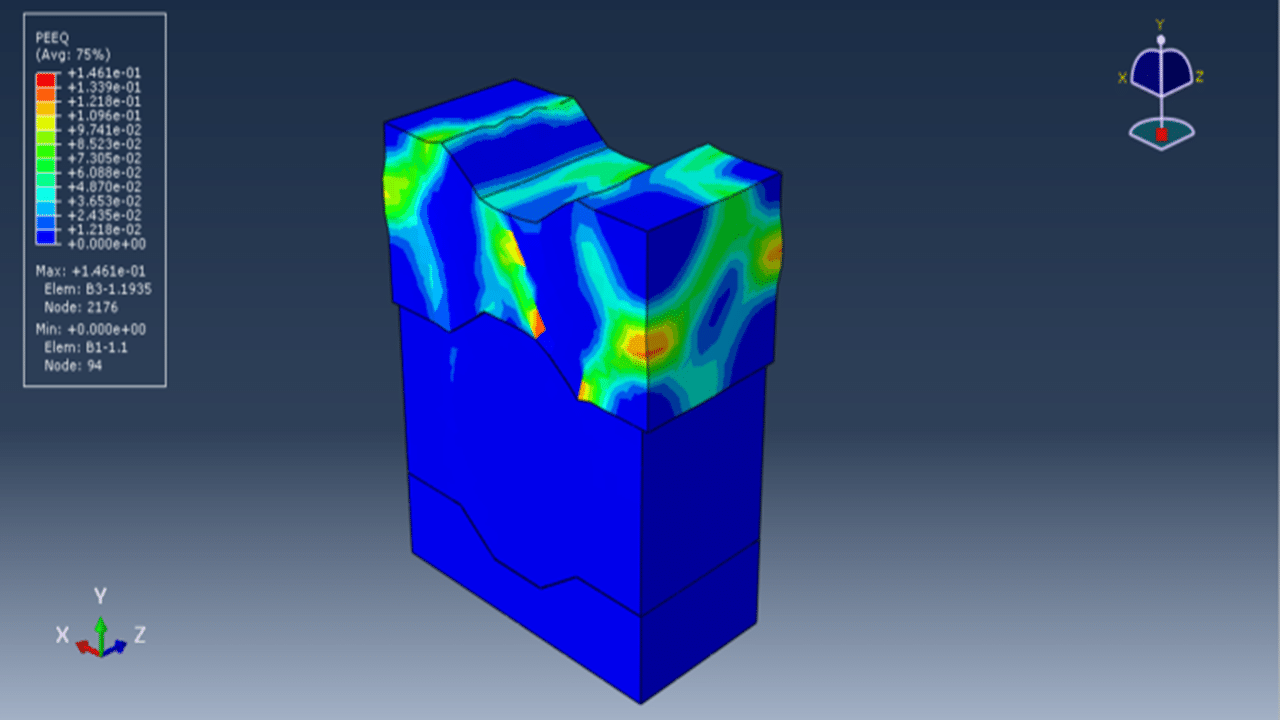
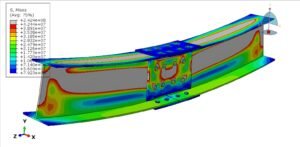
This tutorial presents the numerical simulation of interlocking masonry blocks subjected to compressive loading using Abaqus. The blocks are modeled as three-dimensional solid parts with detailed interlocking surfaces to realistically capture contact behavior.
Masonry structures are widely used for low-rise buildings due to their cost-effectiveness, good insulation, and solid performance compared to timber and other systems. However, conventional masonry with mortar often fails at the joints, especially under extreme loads like earthquakes or blasts. Interlocking designs enhance the structural integrity by allowing better force transfer and improving resistance under compression.
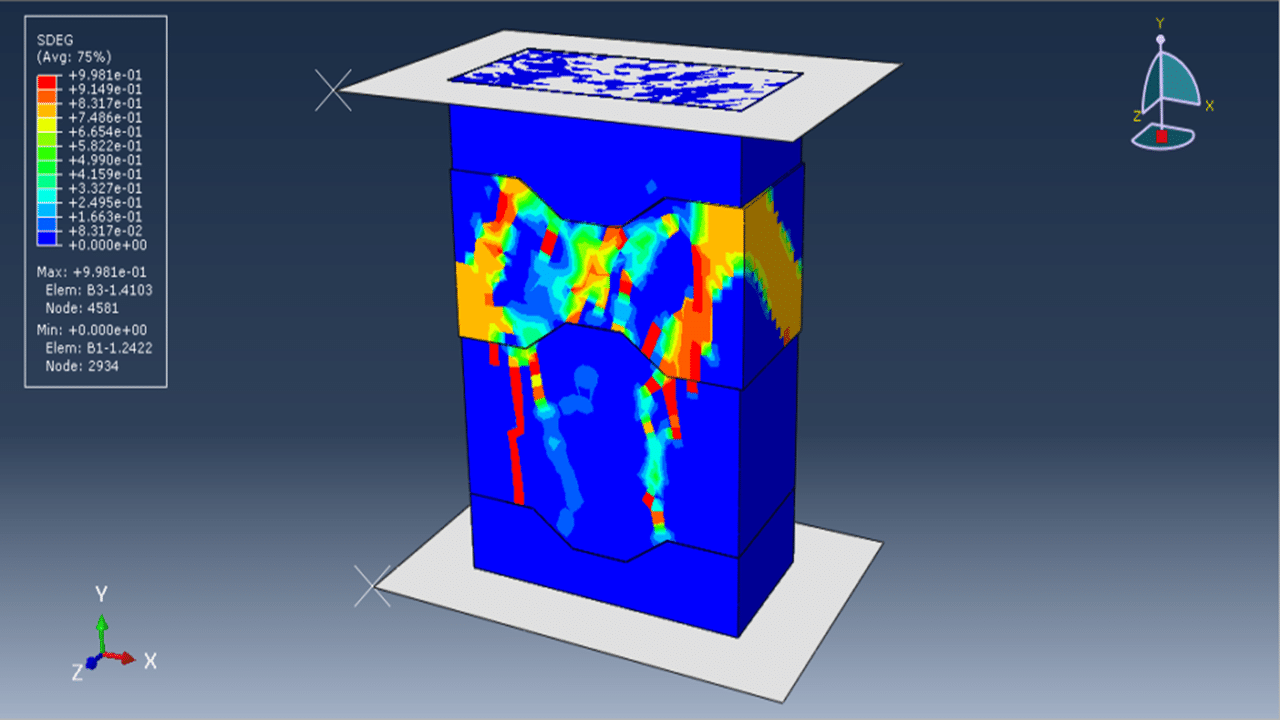
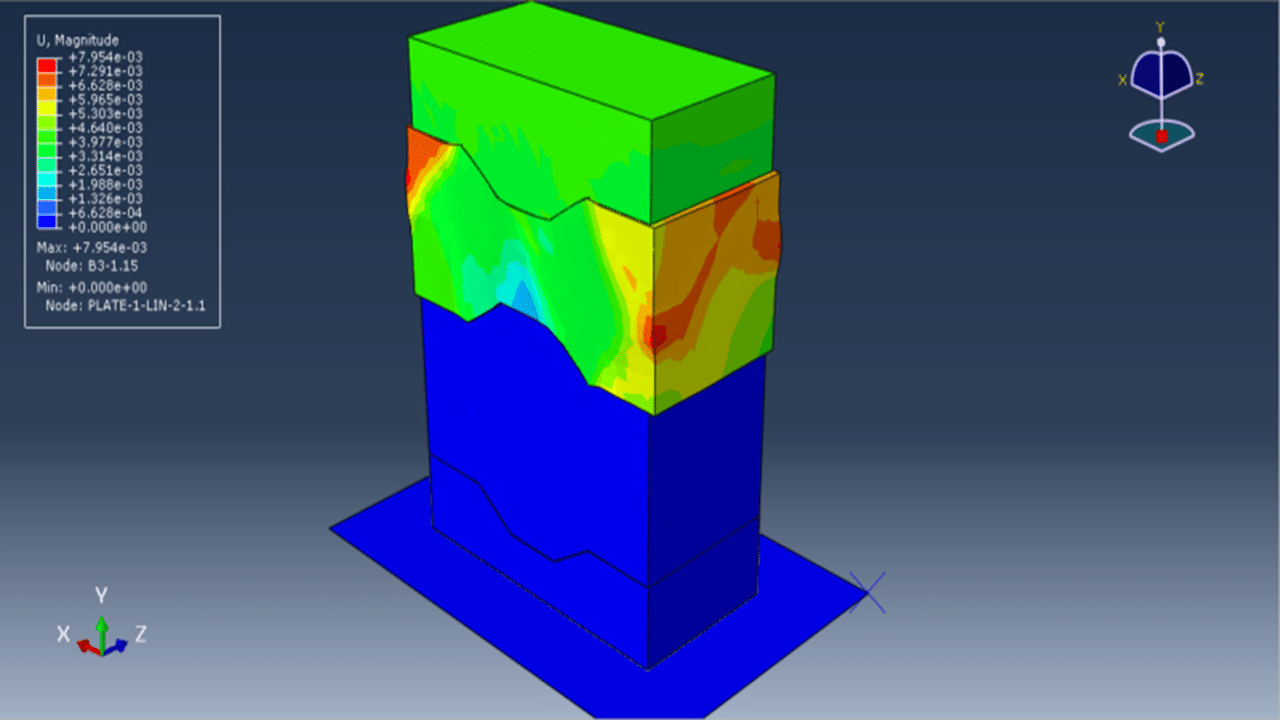
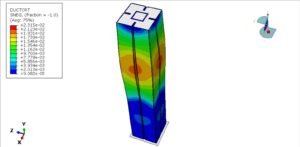
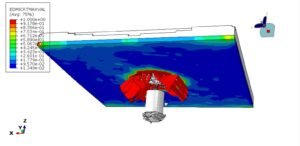
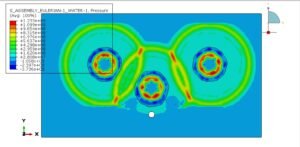
The Concrete Damaged Plasticity model is used to simulate both tensile cracking and compressive crushing behavior of the blocks. A dynamic explicit step is selected to handle complex contact interactions and nonlinearities efficiently. Cohesive interaction is defined between the blocks by assigning stiffness, damage initiation, and evolution parameters—effectively modeling the mortar-free contact. A fixed boundary condition is applied to the bottom rigid plate, and the compressive load is applied to the top plate using a smooth amplitude to ensure stability.
A fine mesh is essential to capture accurate stress distributions, contact behavior, and failure mechanisms.

Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€75,00 €37,00
Abaqus
€76,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?