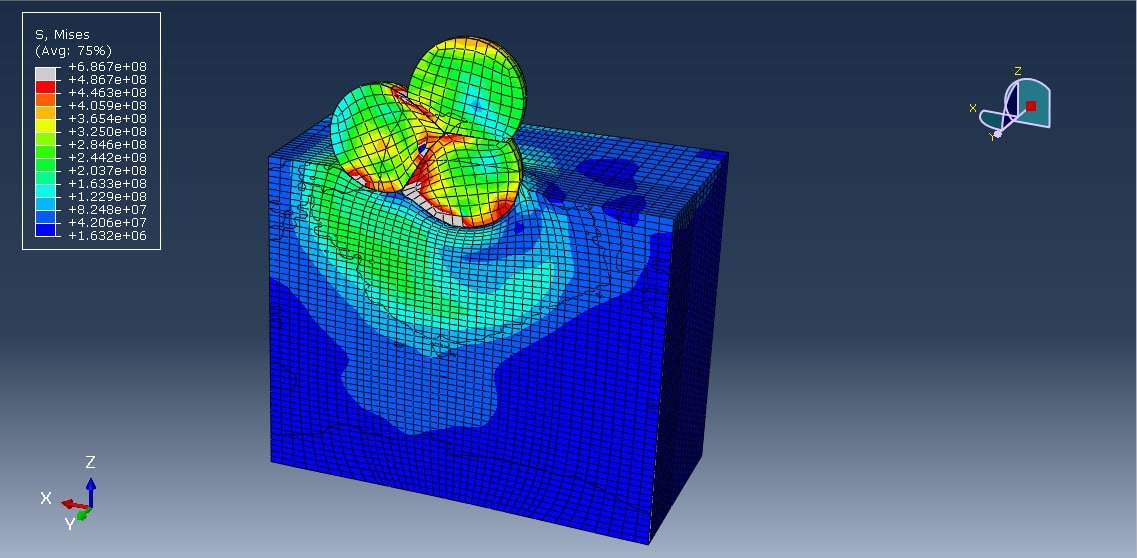
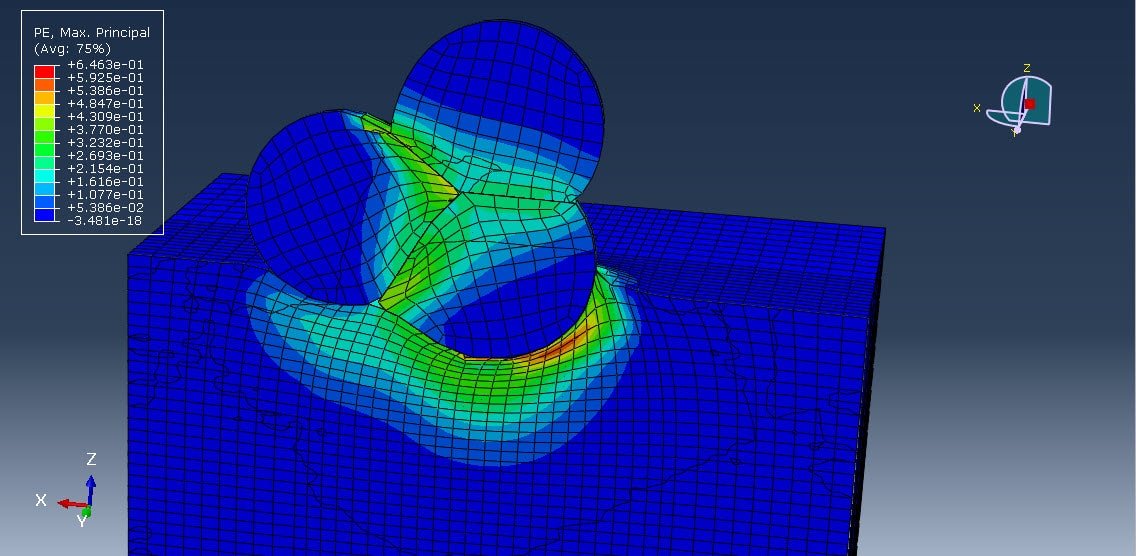
Introduction
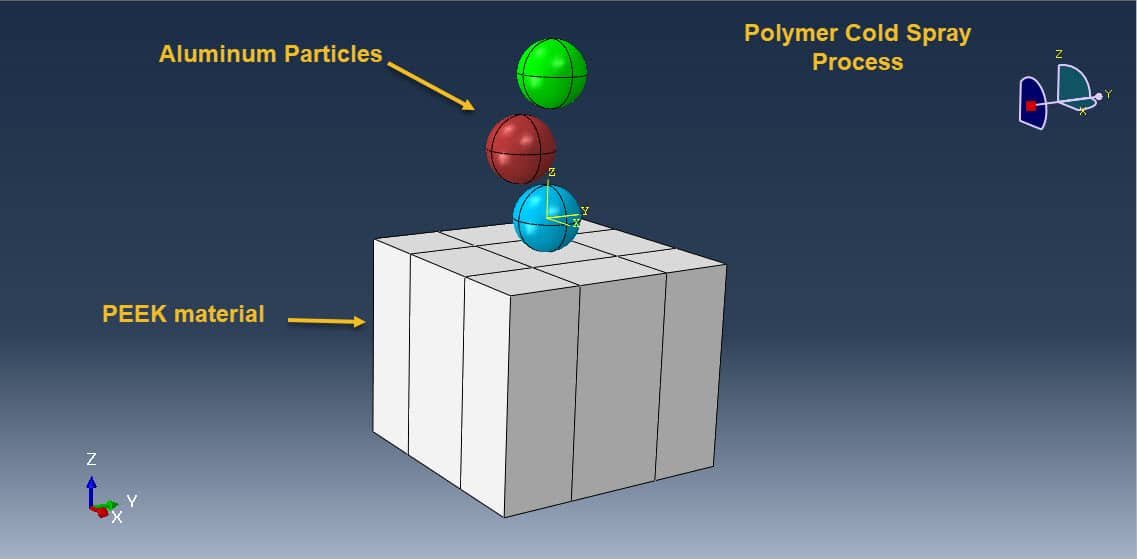
The integration of metal coatings with polymer substrates has become increasingly important in advanced engineering applications, especially in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. Among various polymers, Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) stands out due to its excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, thermal stability, and biocompatibility. However, to enhance its surface functionality—such as electrical conductivity, thermal management, and wear resistance—metallic coatings are often required.
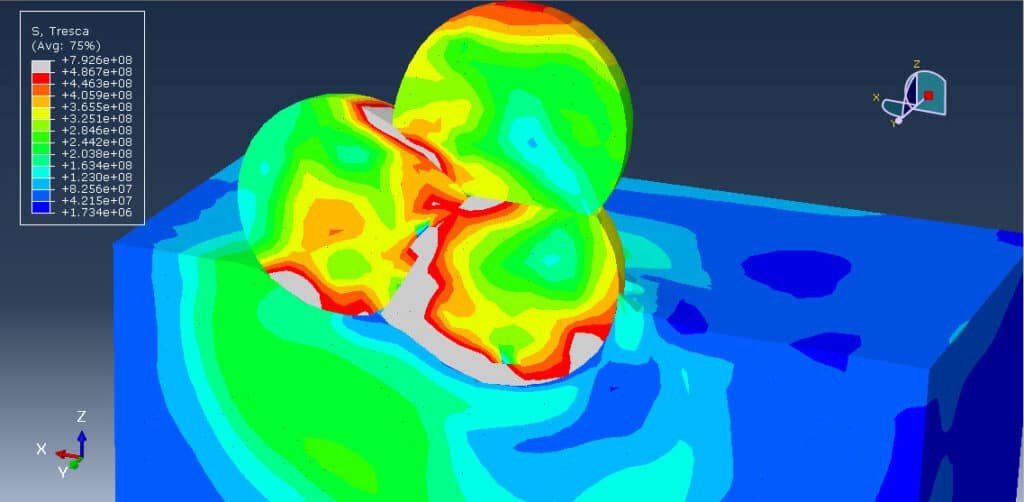
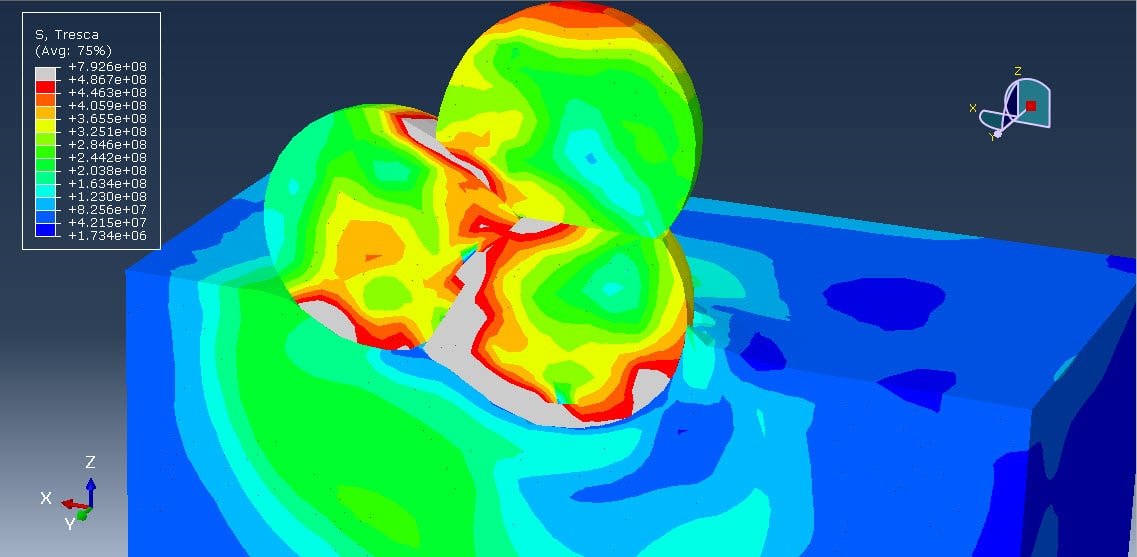
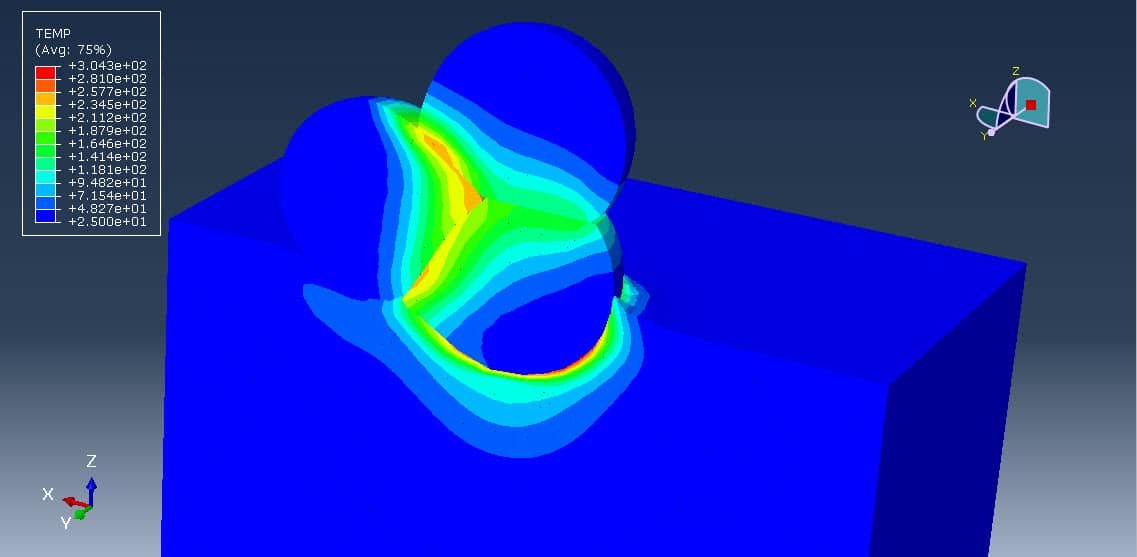
Cold Spray (CS) is a promising solid-state coating technique that allows the deposition of metals onto thermally sensitive substrates like PEEK without damaging them. Unlike conventional thermal spray methods, cold spray operates at temperatures significantly below the melting point of the feedstock material, making it suitable for polymers that would otherwise degrade under high heat.
Explanation of Cold Spray Process for Al-Based Coatings on PEEK
- Principle of Cold Spray
In cold spray, metallic powder particles (in this case, aluminum or aluminum-based alloys) are accelerated to supersonic speeds using a high-pressure, high-velocity gas stream (e.g., nitrogen or helium). When these particles impact the substrate at high velocity, they deform plastically and adhere due to mechanical interlocking and localized bonding mechanisms—without melting.
- Challenges in Coating PEEK
- Low surface energy and thermal conductivity of PEEK make it difficult for metallic particles to adhere effectively.
- The mismatch in thermal expansion coefficients between metal and polymer can lead to internal stresses or delamination.
- PEEK’s relatively soft and elastic nature compared to metals requires careful control of particle velocity and temperature to avoid substrate damage or poor adhesion.
- Advantages of Using Aluminum-Based Coatings
- Lightweight and corrosion resistant, ideal for aerospace and lightweight structures.
- Good thermal and electrical conductivity, expanding the functional range of PEEK components.
- Environmental resistance, providing a protective barrier for the polymer substrate.
- Cold Spray Analysis Techniques
- Microstructural Characterization: SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) and optical microscopy are used to assess coating morphology, interface quality, and porosity.
- Adhesion Testing: Pull-off or scratch tests evaluate the bond strength between the Al coating and PEEK.
- Mechanical and Thermal Evaluation: Hardness testing, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity measurements ensure coating performance meets application requirements.
- Surface Roughness and Pretreatment Analysis: Since PEEK’s surface may require roughening (e.g., grit blasting or plasma treatment) to enhance adhesion, surface topography is analyzed before and after coating.
- Optimization Parameters
- Particle size and velocity
- Gas type and temperature
- Standoff distance
- Surface preparation techniques
Cold spray is an innovative and effective technique for applying Al-based metallic coatings onto PEEK substrates. By avoiding the high temperatures of traditional methods, it preserves the integrity of the polymer while still providing a robust metallic layer. However, due to the inherent differences between metals and polymers, detailed analysis and process optimization are essential to achieve strong adhesion, desirable mechanical properties, and consistent coating quality.