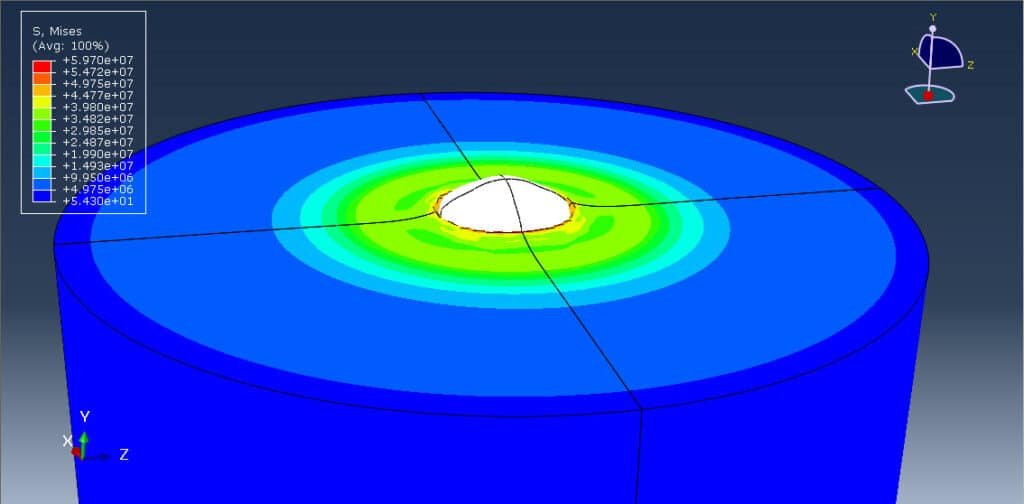
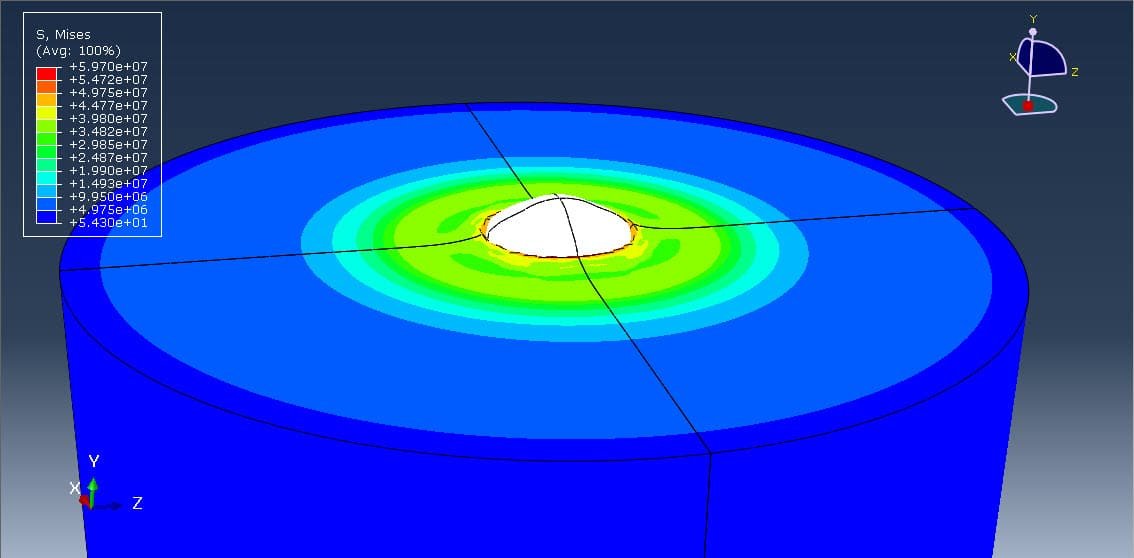
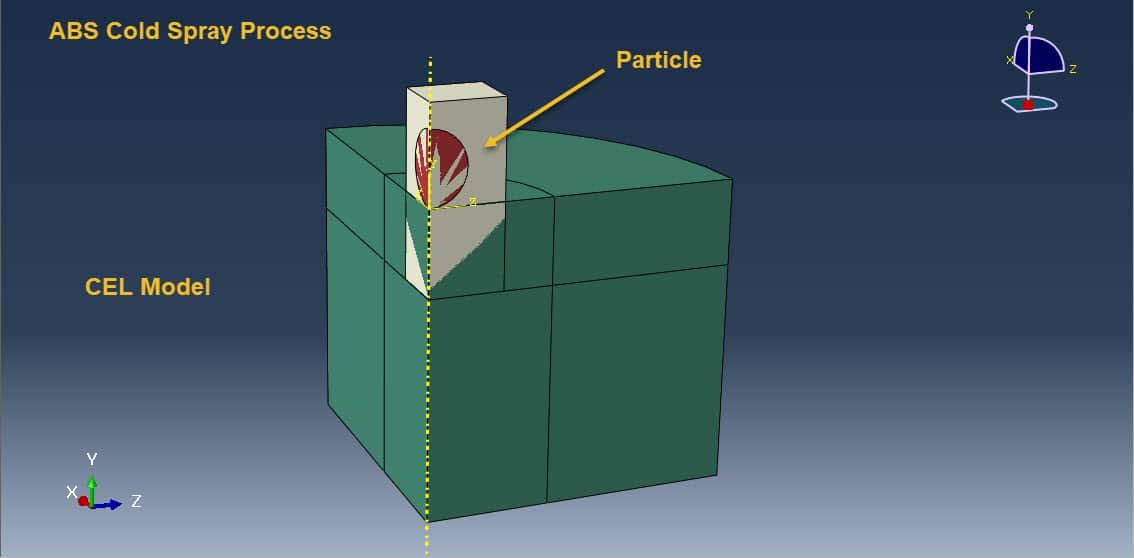
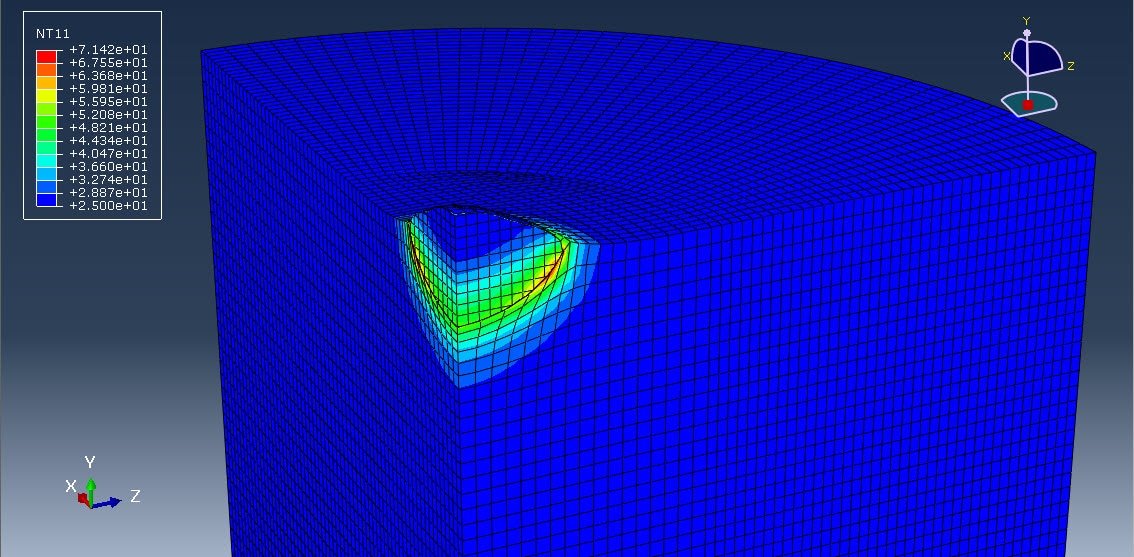
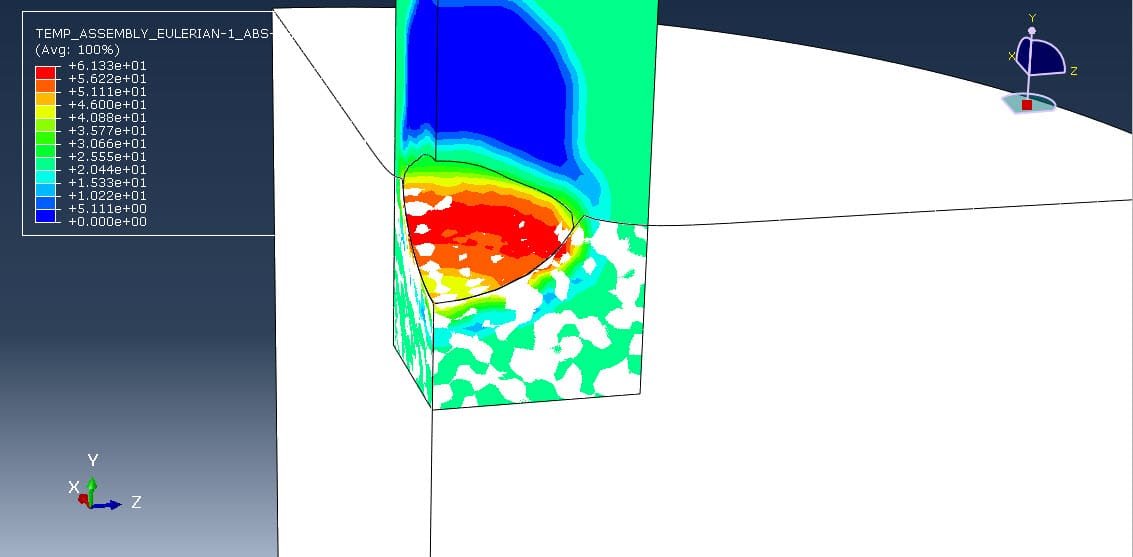
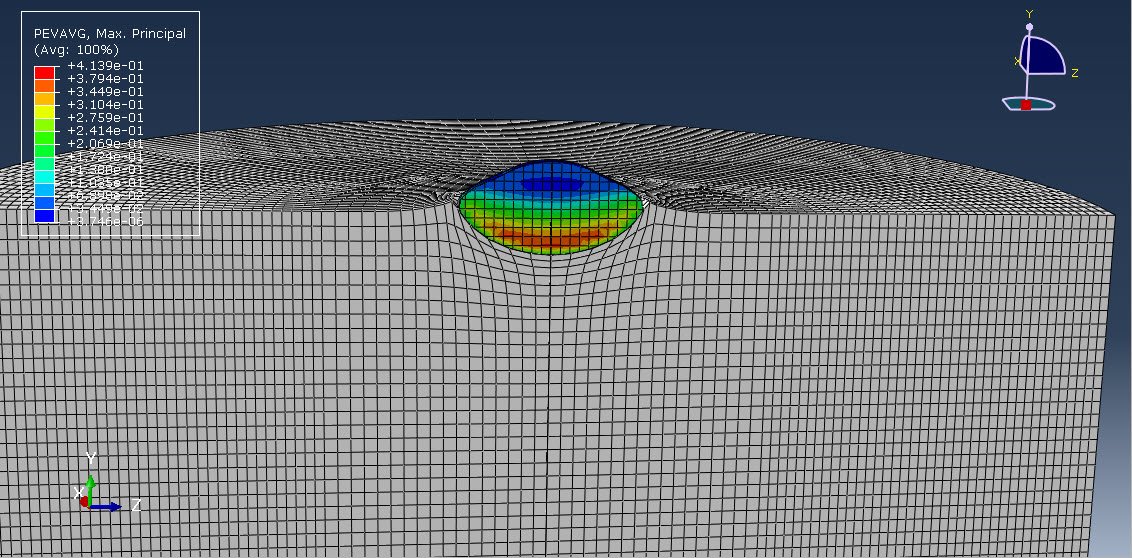
Cold spray (CS) is a solid-state coating and additive manufacturing process where fine metal or polymer particles are accelerated to high velocities (300–1200 m/s) using a supersonic gas jet (typically air, nitrogen, or helium) and directed toward a substrate. Upon impact, these particles deform plastically and bond to the surface without melting. This unique characteristic makes cold spray ideal for temperature-sensitive materials like ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), a common thermoplastic used in automotive and consumer electronics.
To understand and optimize particle impact dynamics during cold spray, numerical simulation methods are used. One of the most accurate techniques for such high-speed, large-deformation interactions is the Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) method.
Traditional simulation methods like the Lagrangian approach often struggle with mesh distortion when modeling large deformation events, such as high-speed particle impacts. The Eulerian method, on the other hand, handles large deformations well but isn’t ideal for tracking solid materials.
The CEL method combines the strengths of both:
This makes CEL ideal for simulating:
Cold spray analysis of ABS particles using the CEL method provides deep insights into the deformation and bonding mechanisms during impact. This simulation approach is particularly useful for optimizing spray parameters (e.g., velocity, particle size) and understanding failure modes (e.g., rebounding or fragmentation). The CEL method’s ability to handle complex material behavior and high deformation makes it a valuable tool in developing polymer-based cold spray technologies.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
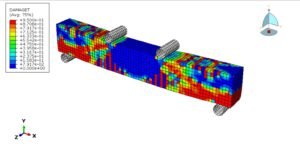
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
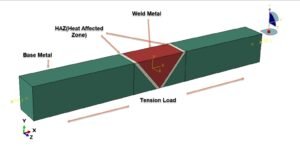
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?