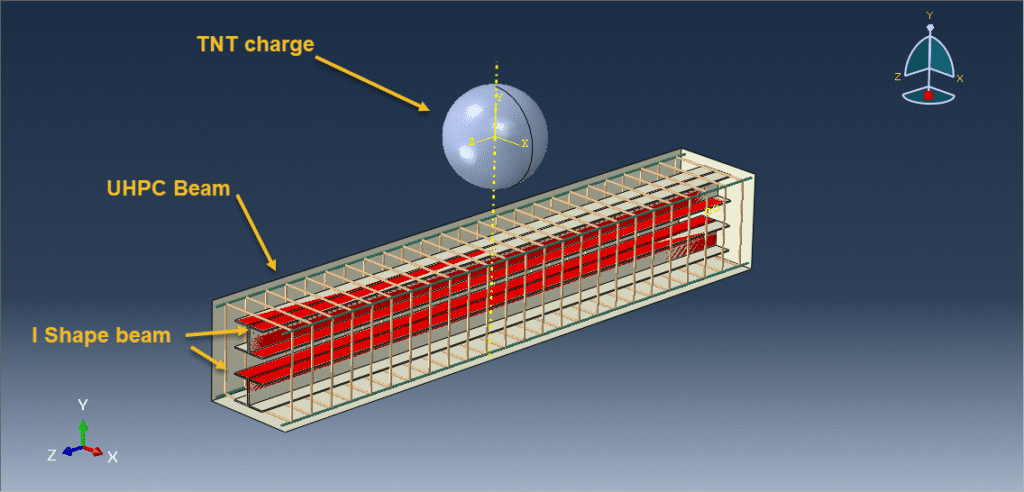
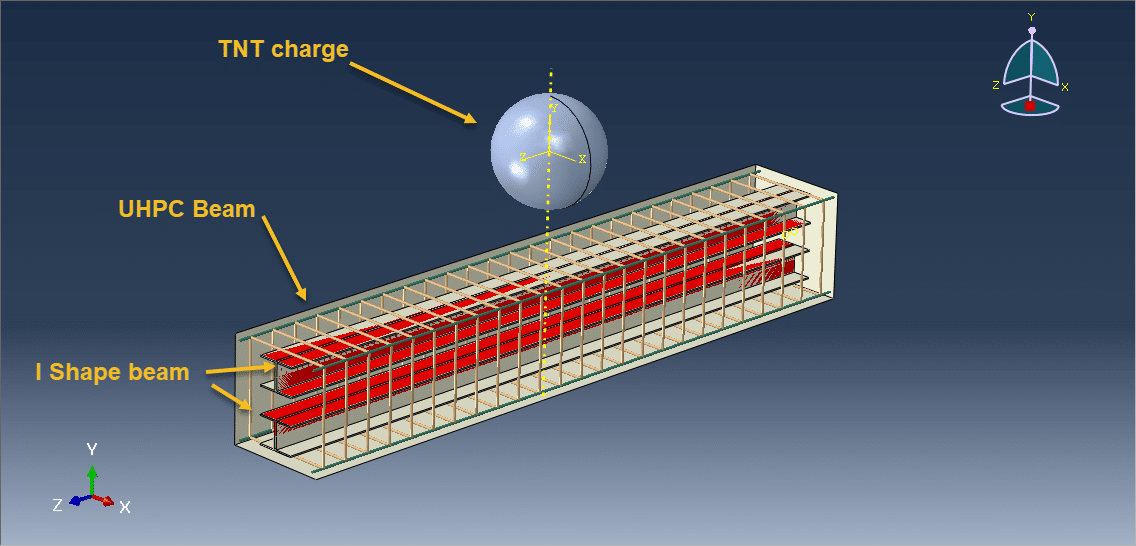
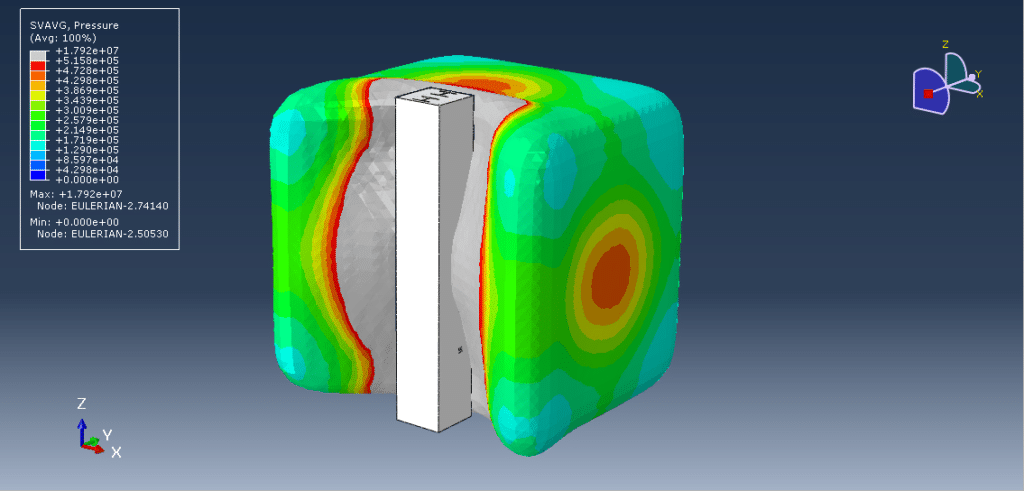
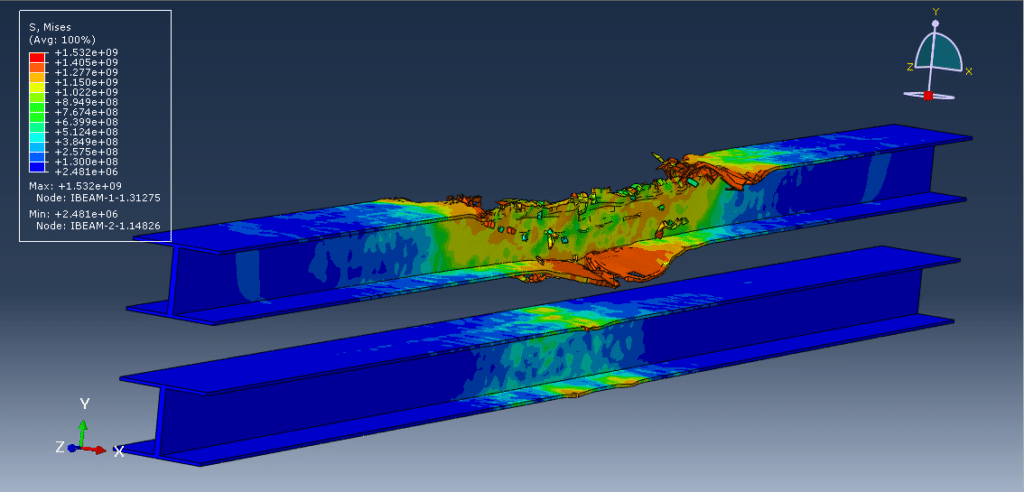
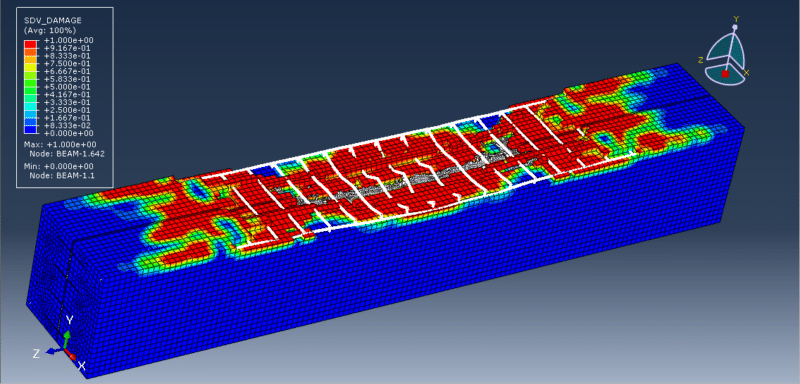
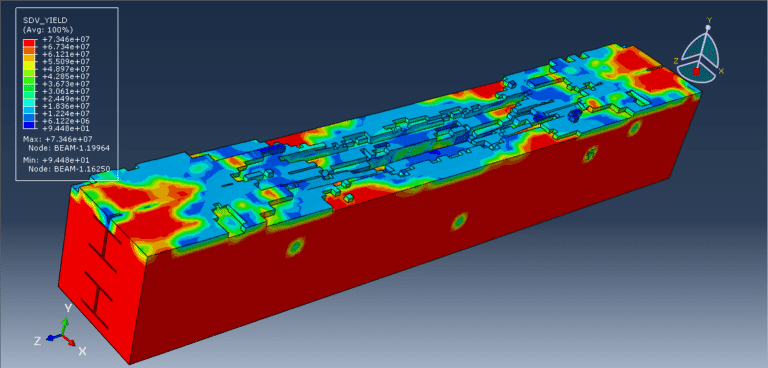
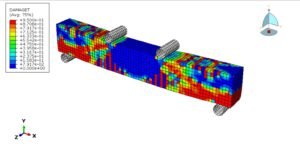
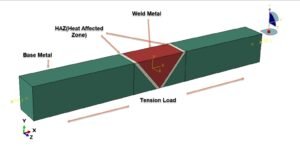
In this tutorial, the CEL explosion simulation of a steel-UHPC composite RC beam (or column) with multiple encased steel profiles has been carried out in Abaqus. The ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part, the bars and strips are modeled as wire parts, the steel beam core and TNT charge are modeled as solid parts, and the domain is defined as an Eulerian part. In recent years, localized wars and terrorist attacks have raised concerns about the vulnerability of critical infrastructure such as government and embassy buildings, which may be exposed to bombing threats. Understanding the structural response to explosive loads is therefore vital to improving protective designs. RC beams, being primary load-carrying elements in building structures, play a central role in force transmission, and damage assessment of these members has been a significant research focus. Under explosive loading, RC beams are subjected to cracking, crushing, and spalling, which are influenced by factors such as reinforcement details, concrete permeability, stress waveform, detonation point, and surrounding air pressure. In this study, UHPC behavior under severe blast loading is modeled using the Johnson-Holmquist material method, which captures both the strength increase under hydrostatic pressure and the strength reduction due to damage. TNT behavior is represented using the Jones-Wilkins-Lee (JWL) equation of state, which describes the pressure-volume-energy relationship of detonation products based on parameters derived from cylinder expansion tests. The steel beam core is modeled using the Johnson-Cook hardening and damage model, while steel bars and strips are represented with an elastic-plastic formulation. A dynamic explicit step is chosen for the analysis, as it is highly effective for solving linear and nonlinear dynamic problems. General contact with default properties is applied to the domain, while the steel bars and strips are embedded inside the UHPC beam. Proper boundary conditions are defined for the beam and Eulerian domain, and TNT is introduced using either the volume fraction or uniform material method to define its mass and location. A sufficiently fine mesh is applied to ensure accurate results. After the simulation, detailed outputs such as stress, strain, damage, failure, and blast wave propagation are obtained for evaluation.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?