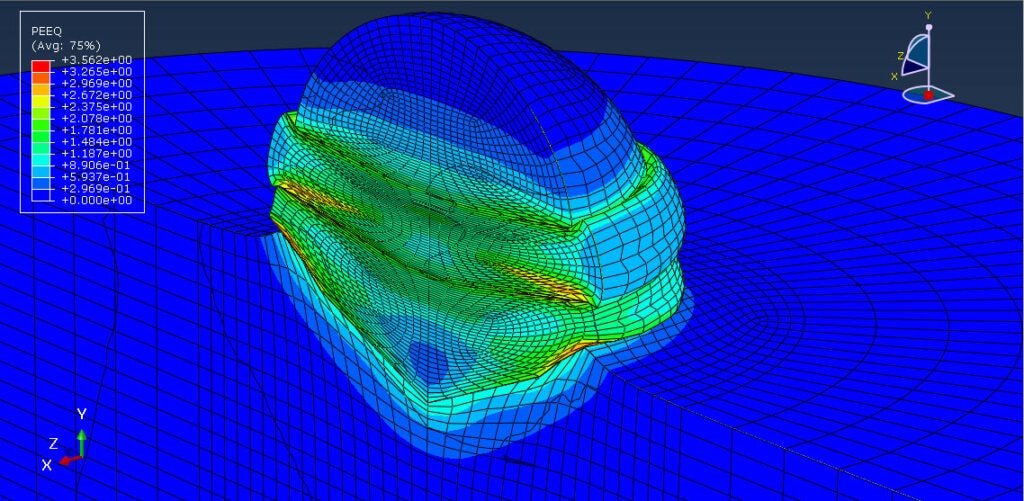
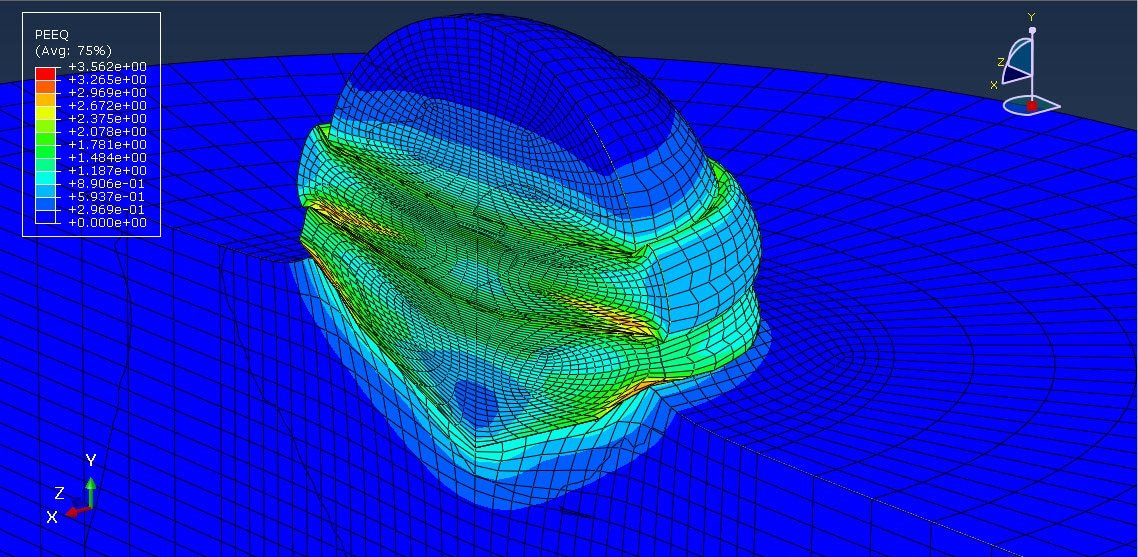
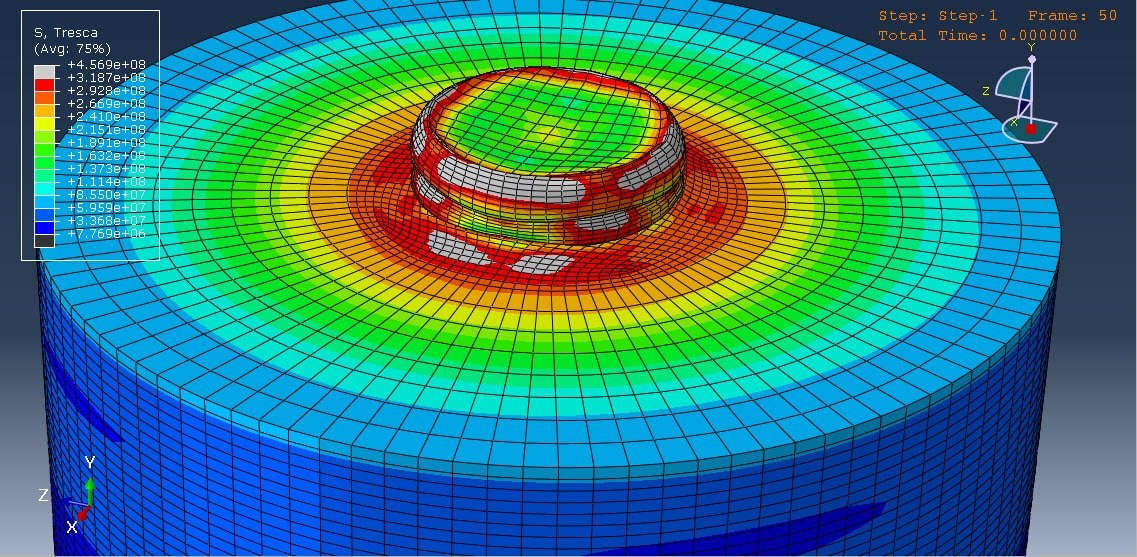
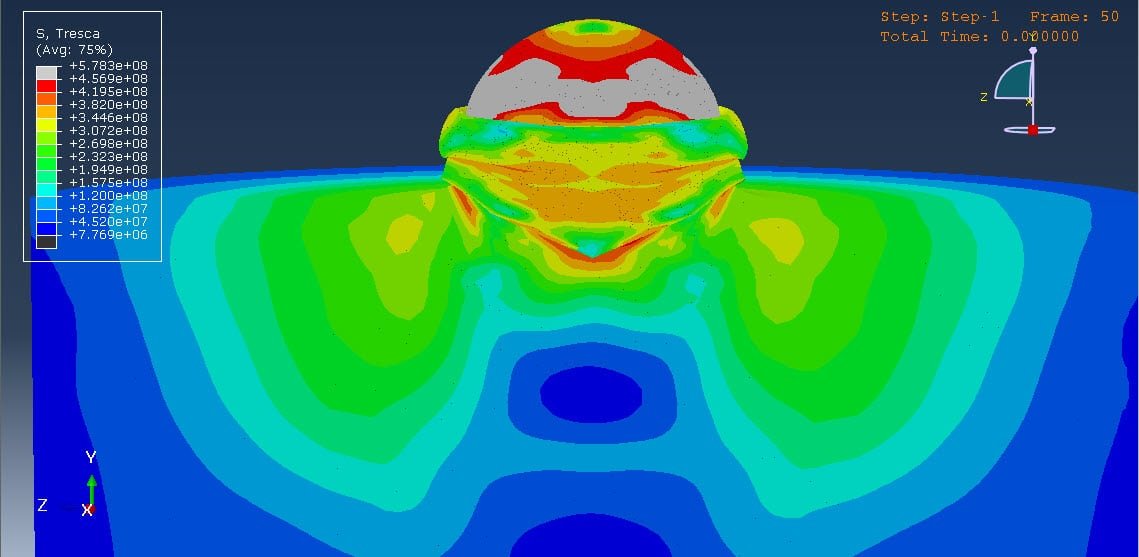
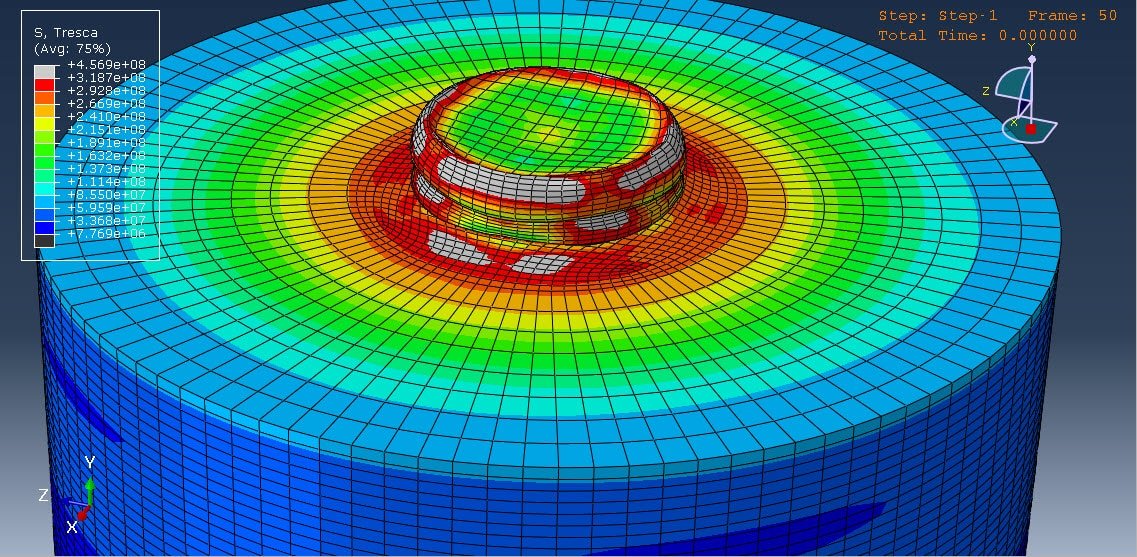
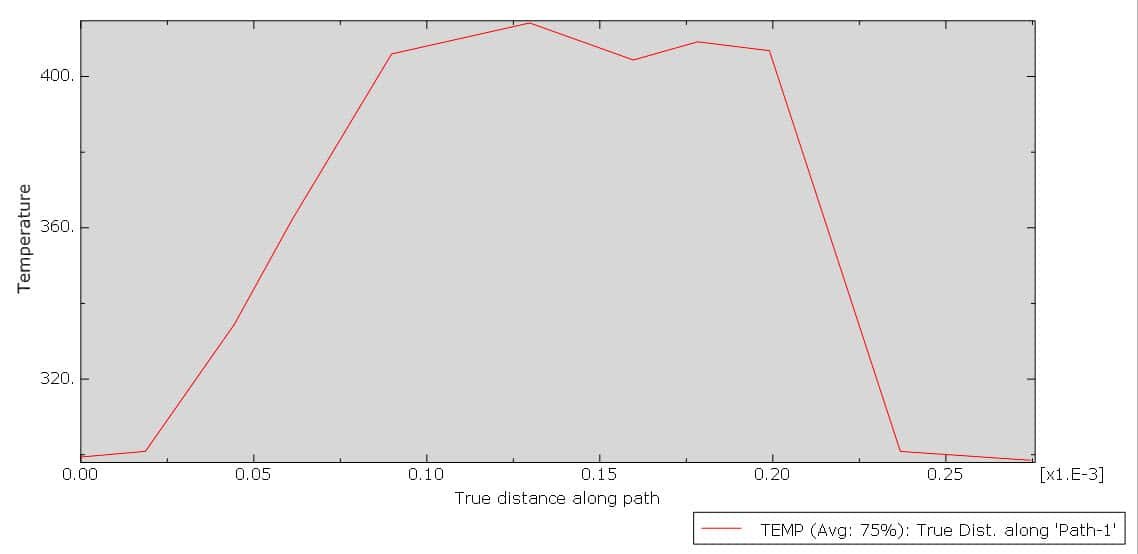
Cold spraying is an advanced coating technique that involves the acceleration of solid powder particles—typically metals like aluminum—to supersonic velocities using a high-pressure gas stream, usually at relatively low temperatures (below the melting point of the material). These particles impact a substrate and bond with it through plastic deformation rather than melting and solidifying, which helps preserve the material’s original properties.
One of the key challenges in optimizing the cold spraying process lies in understanding the impact behavior of multiple particles, especially in materials like aluminum, which is widely used due to its light weight, corrosion resistance, and high thermal/electrical conductivity.
The multi-particle impact analysis focuses on how groups of particles behave when they strike the substrate together, which better reflects real-world conditions than single-particle impact studies. This approach provides deeper insights into the formation of coatings, the quality of the adhesion, and the mechanisms of deformation and bonding at both the micro and macro levels.
The analysis of aluminum multi-particle impact in the cold spraying process provides a crucial understanding for optimizing coating performance. By studying the collective behavior of particles during impact, researchers and engineers can better predict coating quality, improve adhesion strength, and reduce porosity. This knowledge is essential for applications in aerospace, electronics, and automotive industries, where aluminum coatings are valued for their lightweight and functional properties.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
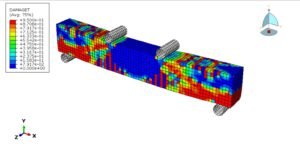
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
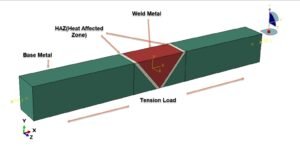
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?