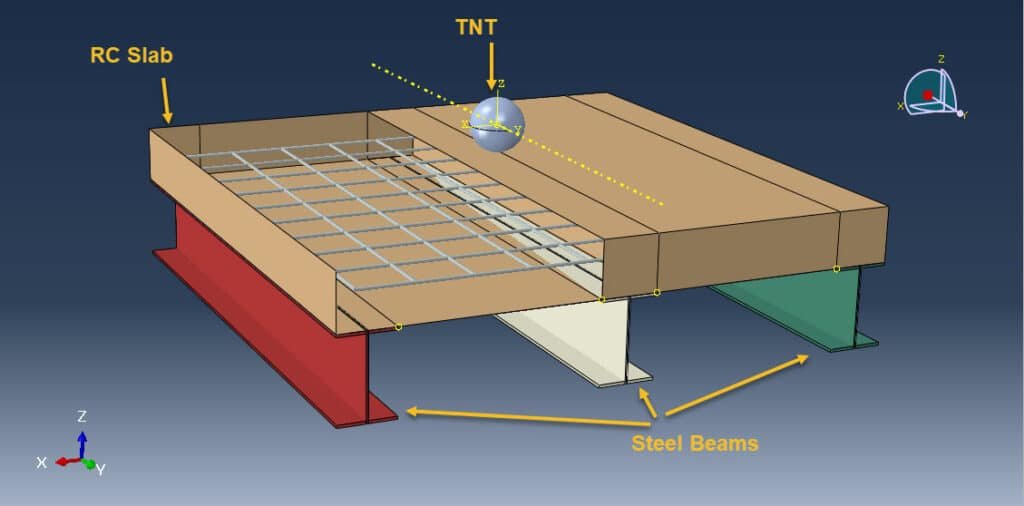
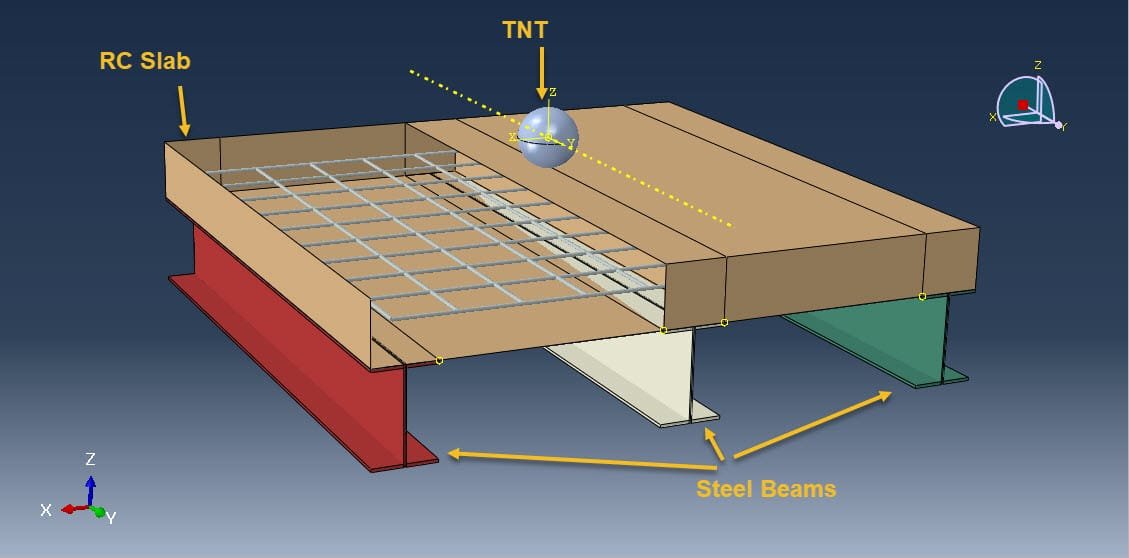


In recent years, there has been a rise in bombing terrorist attacks and accidental explosions worldwide. Recently, a new type of building Concrete slab-steel beam, has been proposed. The Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) method is a numerical approach that combines the Eulerian and Lagrangian finite element methods to address fluid-structure problems. By leveraging the strengths of both methods, the CEL method effectively models the motion and interaction of objects within a flow field
To model steel parts’ behavior, the Johnson-Cook hardening and damage models are used. The Johnson-Holmquist brittle model is considered to define concrete behavior under severe loads. The JWL equation of state is used to define the TNT explosive material.
Concrete sandwich plates are advanced structural elements composed of two outer concrete face sheets bonded to a lighter, often energy-absorbing, core material. These composite systems are increasingly employed in military, nuclear, and critical infrastructure applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced blast resistance.
Close-range blast loading—typically caused by explosions near a structure—can induce highly dynamic, nonlinear, and potentially catastrophic failure modes in concrete-based structures. Accurately predicting and analyzing these responses is essential for the design of blast-resistant materials and systems.
The blast loading process involves complex physics, including:
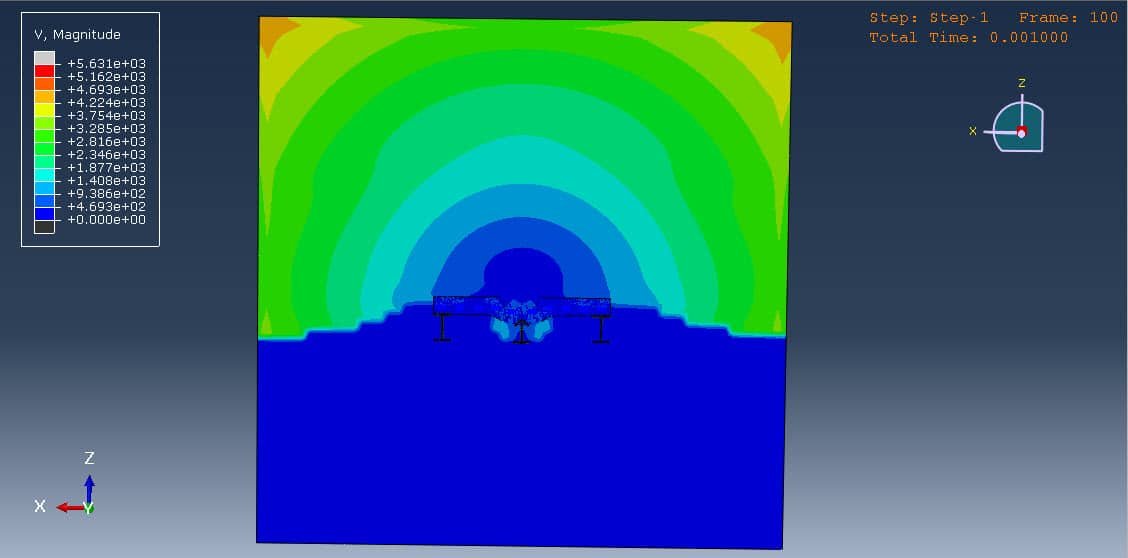
Shock wave propagation through air,
Fluid-structure interaction at the surface of the concrete plate,
High-strain-rate deformation of materials,
Spalling, cracking, and fragmentation of concrete.
Traditional finite element methods (FEM) using pure Lagrangian formulations struggle to capture such phenomena due to severe element distortion and numerical instabilities during large deformations and material separation.
The Coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian (CEL) method is a hybrid numerical modeling approach designed to handle large deformation problems with complex fluid-structure interactions. In this framework:
The air and explosive products are modeled using Eulerian elements, which allow material to flow through a fixed mesh. This avoids mesh distortion during the high-speed expansion of gases.
The concrete sandwich plate is modeled using Lagrangian elements, which follow the motion of the solid structure and allow for detailed tracking of structural deformation and damage.
This coupling enables the simulation to realistically model:
Shock wave propagation from the explosion,
Interaction of pressure waves with the concrete structure,
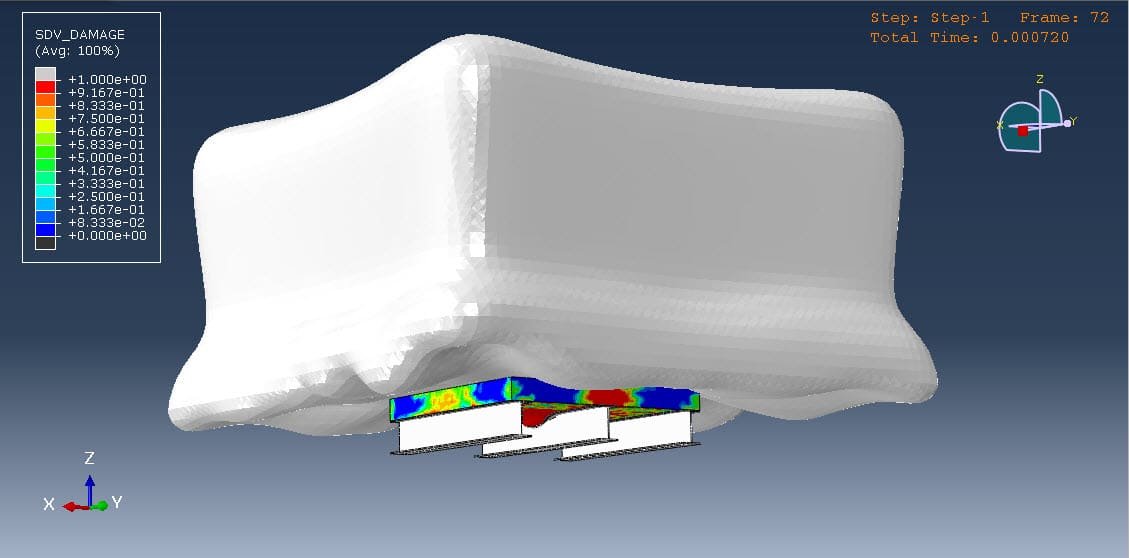
Progressive damage, cracking, and delamination in the sandwich plate.
In CEL-based simulations of concrete sandwich plates subjected to close-range blasts:
Material models for concrete often incorporate strain-rate sensitivity, damage evolution (e.g., Johnson-Holmquist or RHT models), and failure criteria (e.g., Drucker-Prager).
Blast scenarios are typically defined using empirical charge models like CONWEP or high-fidelity detonation modeling, or the CEL method.
Simulations can provide critical insights such as:
Peak displacement and velocity of face sheets,
Damage patterns (e.g., cracking, spalling, delamination),
Energy absorption capacity of materials,
Failure time and potential for catastrophic collapse.
These results are crucial for designing more resilient concrete sandwich structures and optimizing core materials and layer thicknesses for blast mitigation.

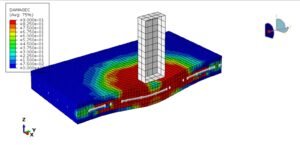
Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
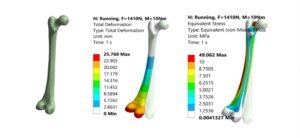
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
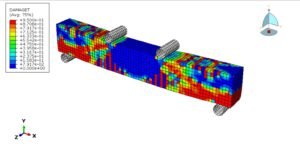
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
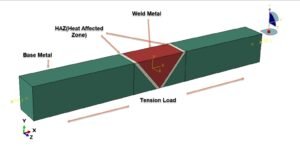
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?