
Paper title: Accurate simulation of delamination growth under mixed-mode loading using cohesive elements: Definition of interlaminar strengths and elastic stiffness
DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2010.01.012
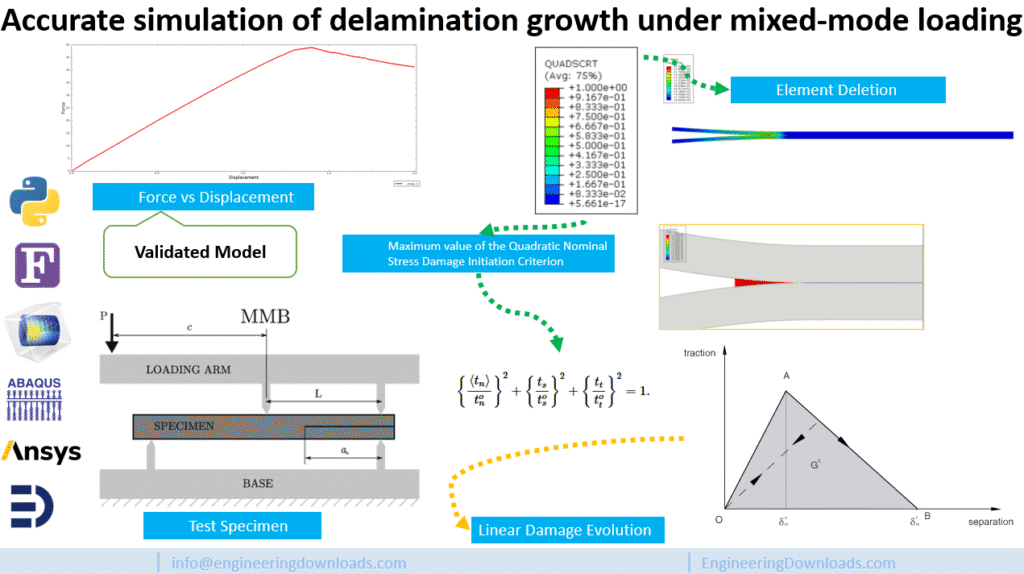
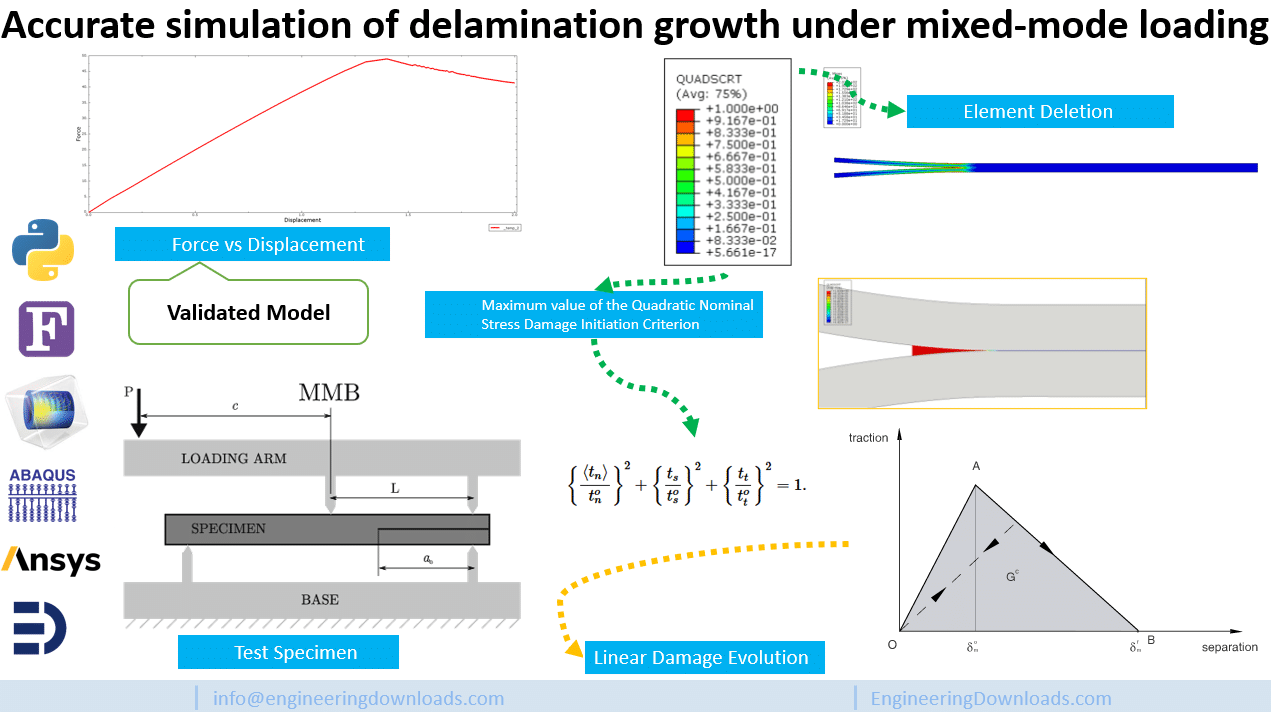
This paper proposes a cohesive-element methodology to predict delamination growth under mixed-mode loading with high accuracy. The authors show that as damage evolves, the local mode mix can shift, which—if not handled carefully—leads to wrong energy dissipation and incorrect load–displacement predictions, even when the global mode mix looks constant. To fix this, they establish consistent relations between interlaminar strengths and penalty stiffness so that the model dissipates the correct energy as the crack advances. The approach is verified across different mode ratios by comparison with LEFM-based analytical solutions.
This product provides my Abaqus replication of one validated scenario from Turon et al. (2010). It’s a clean, ready-to-run example of cohesive-zone modeling (CZM) for delamination growth in composites under mixed-mode loading.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?