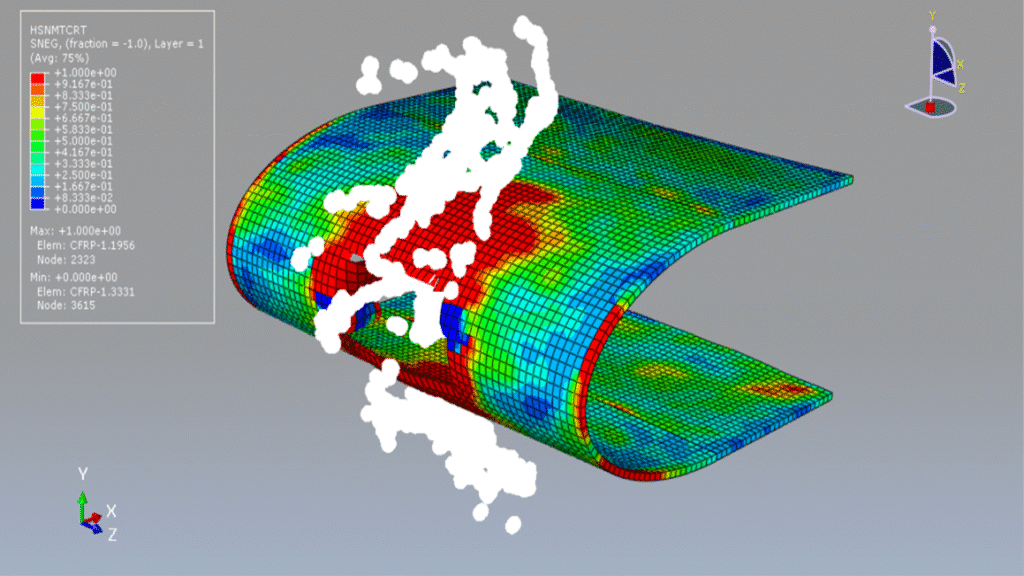
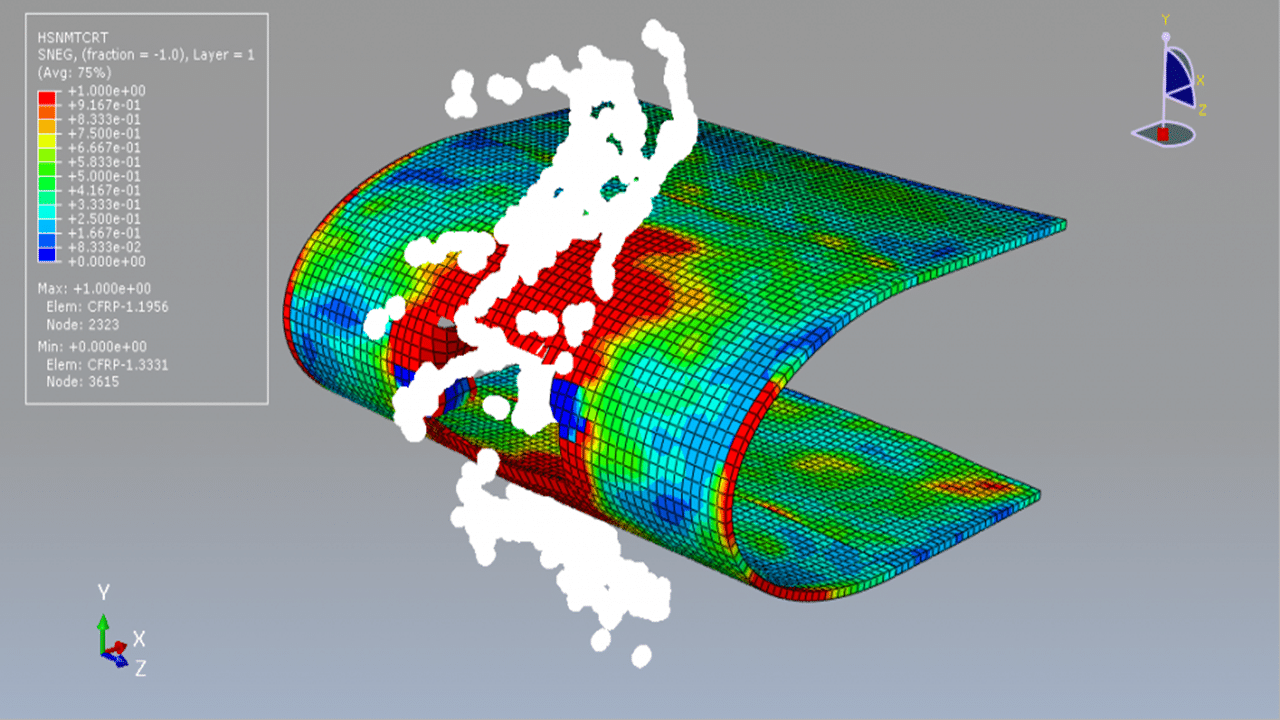
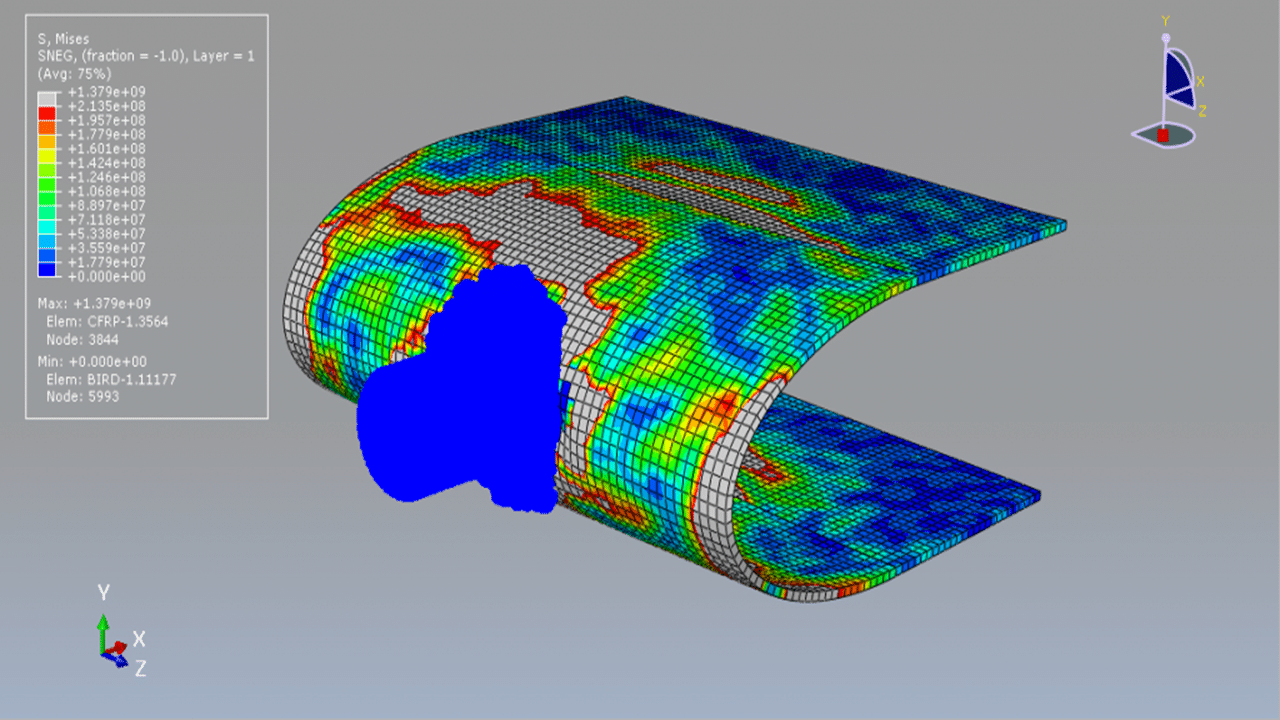
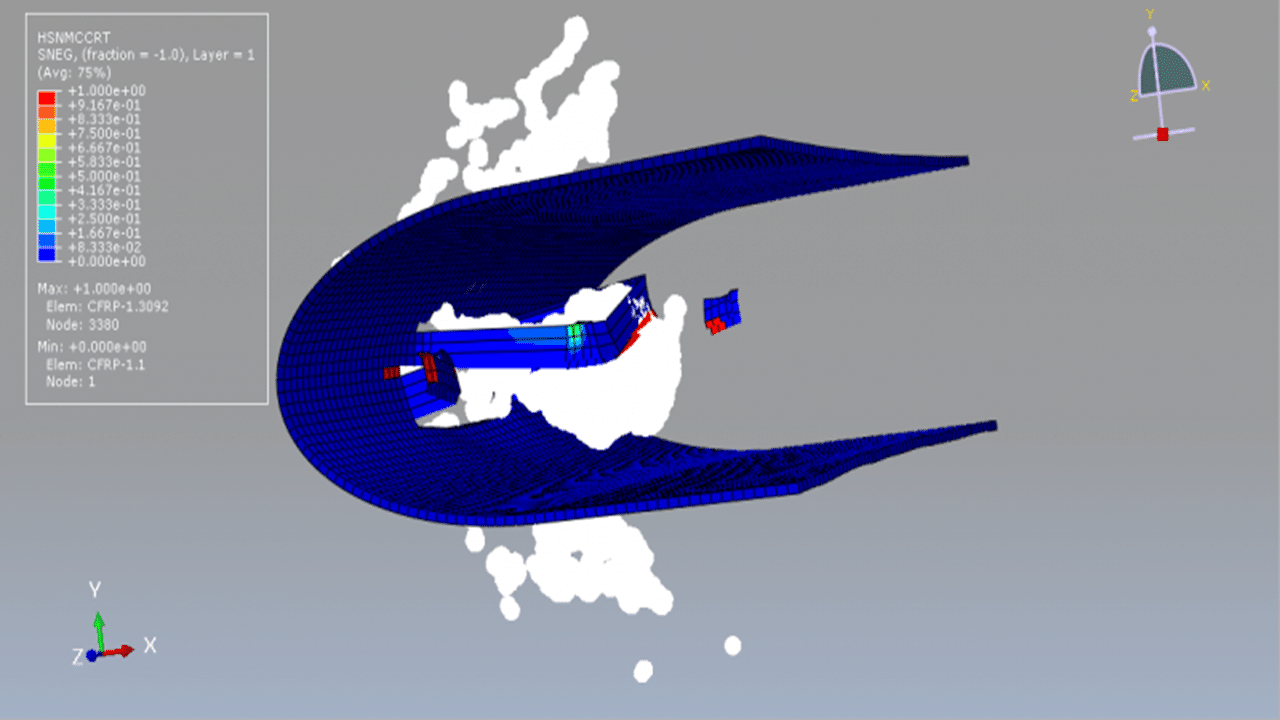
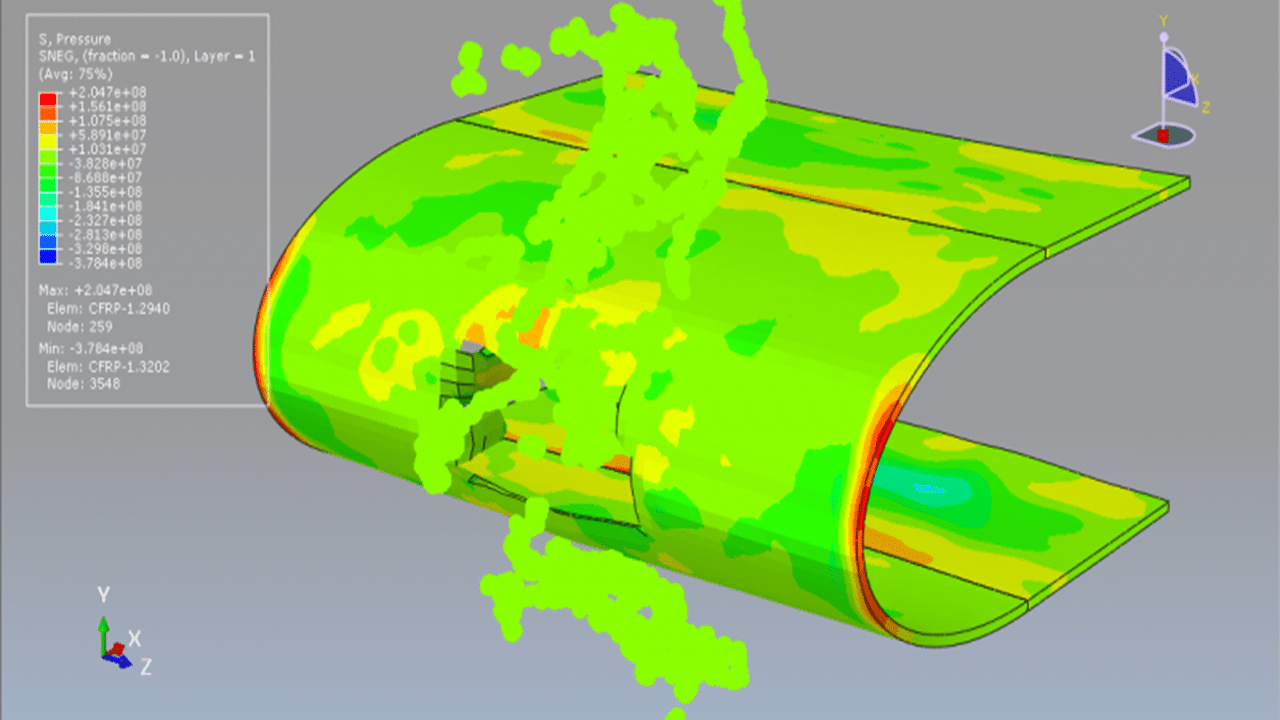
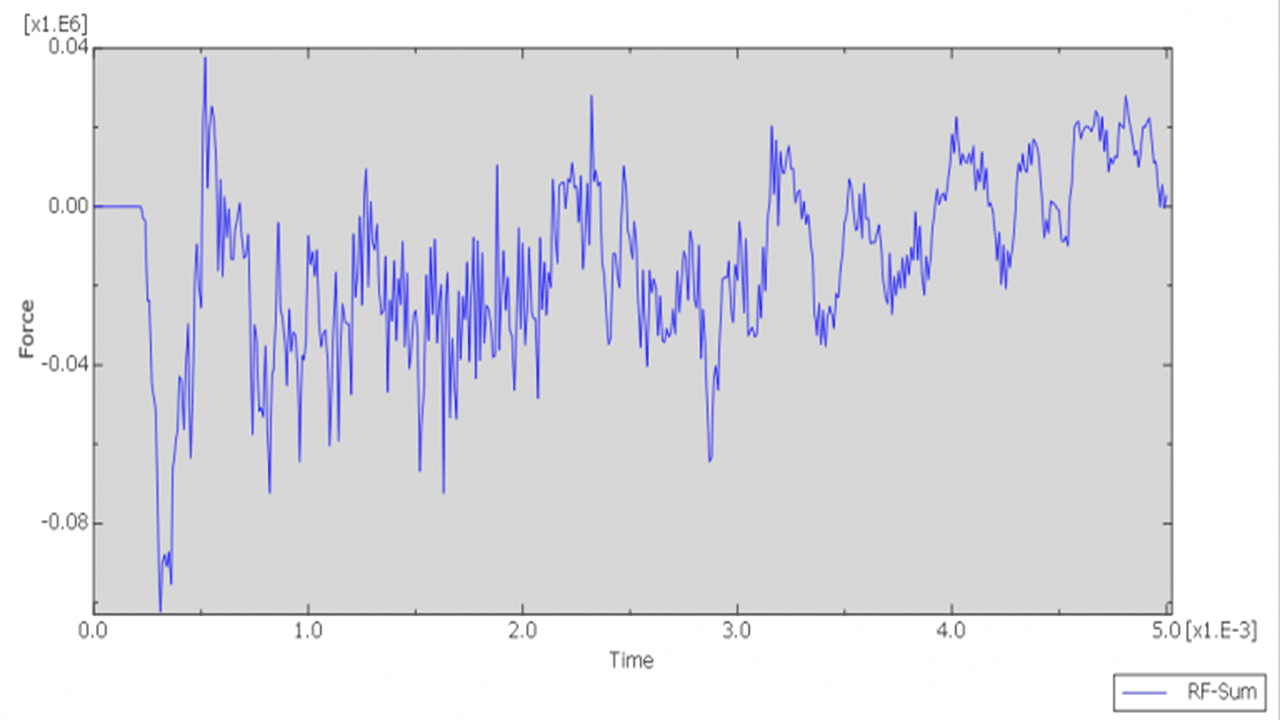
In this tutorial, the simulation of a bird strike impact on a composite blade using the SPH (Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics) method in Abaqus is investigated. The bird is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part, while the composite blade, composed of eight layers, is modeled as a three-dimensional shell part.
A bird strike refers to a collision between a bird and an aircraft during flight or during take-off or landing. These events are common and pose a significant threat to aircraft safety. Smaller aircraft may suffer serious structural damage, while jet-engine aircraft are particularly vulnerable to engine thrust loss due to bird ingestion. Bird strikes can occur at any phase of flight but are most frequent during take-off, initial climb, approach, and landing, when aircraft operate at altitudes where bird activity is highest. Most incidents also occur during daylight hours, when birds are most active.
The Us–Up equation of state is used to model the behavior of the bird material under high-speed impact. For the composite blade, a lamina elastic model is used along with the Hashin damage criterion to capture various failure mechanisms such as fiber tension, fiber compression, matrix tension, and matrix compression.
A dynamic explicit step is used for the analysis, and a general contact algorithm is defined to handle all interactions between components. Initial velocity is applied to the bird model, while appropriate boundary conditions are assigned to the blade. A fine mesh is required for all parts to ensure accurate results.

Abaqus
€97,00 €54,00
Engineering files
€60,00 €50,00
Abaqus
€146,00 €89,00
Abaqus
€85,00 €47,00

Abaqus
€78,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?