Packages & Tutorials
Engineering Files & Tools
Software
Ready-to-use Models (FEA/CFD)

Excel Sheets & Hand Calculations




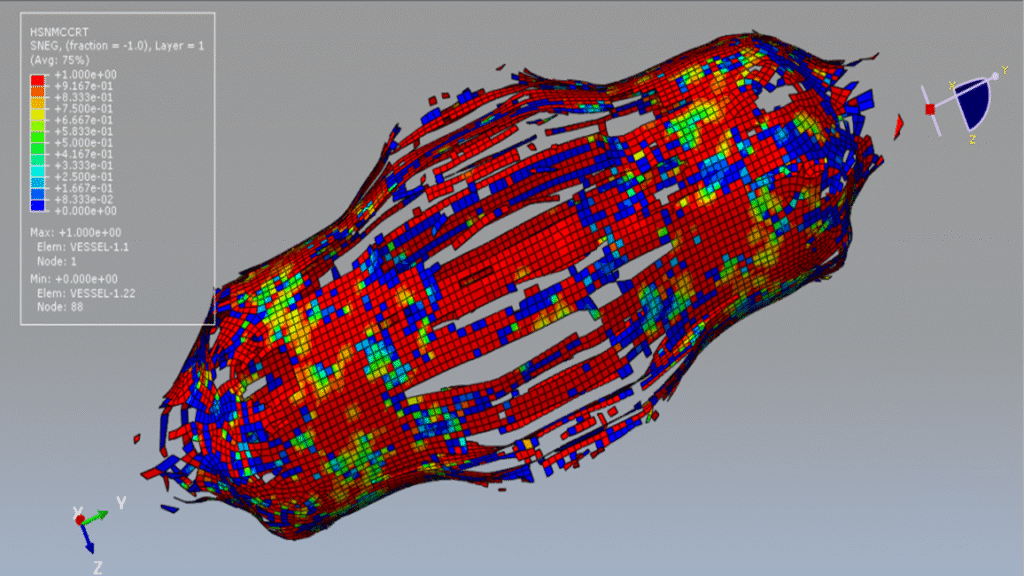
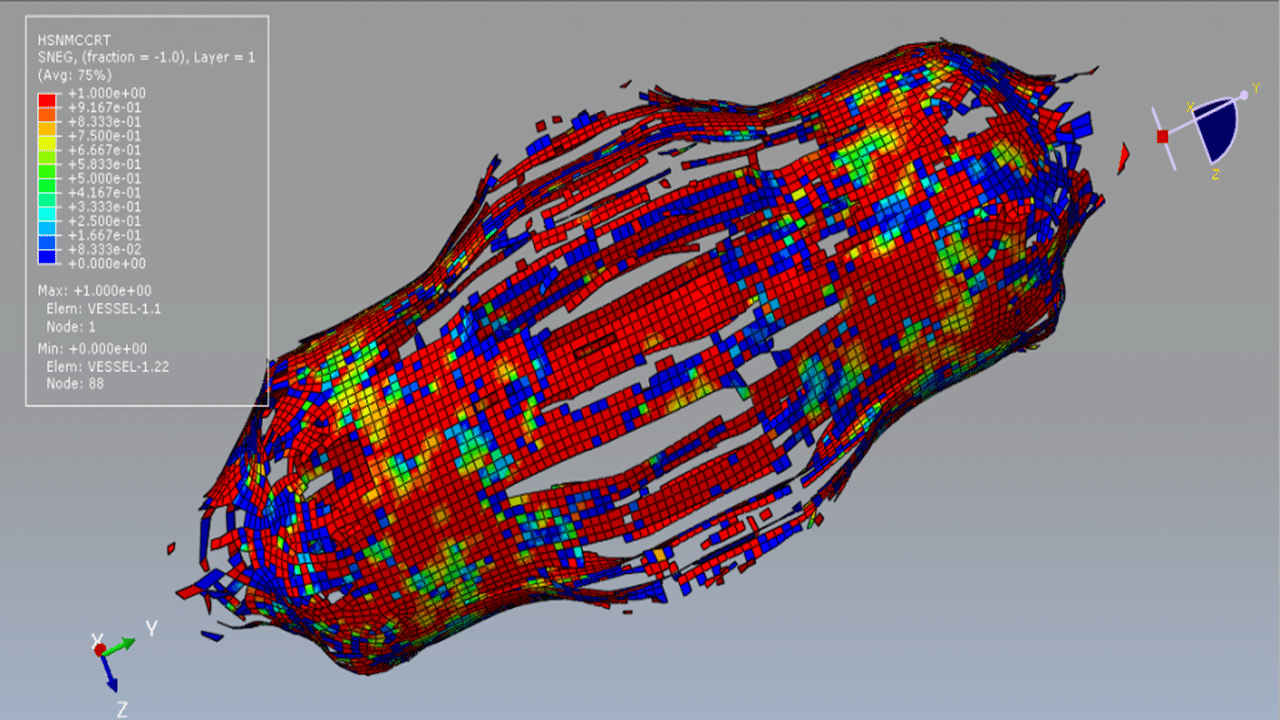
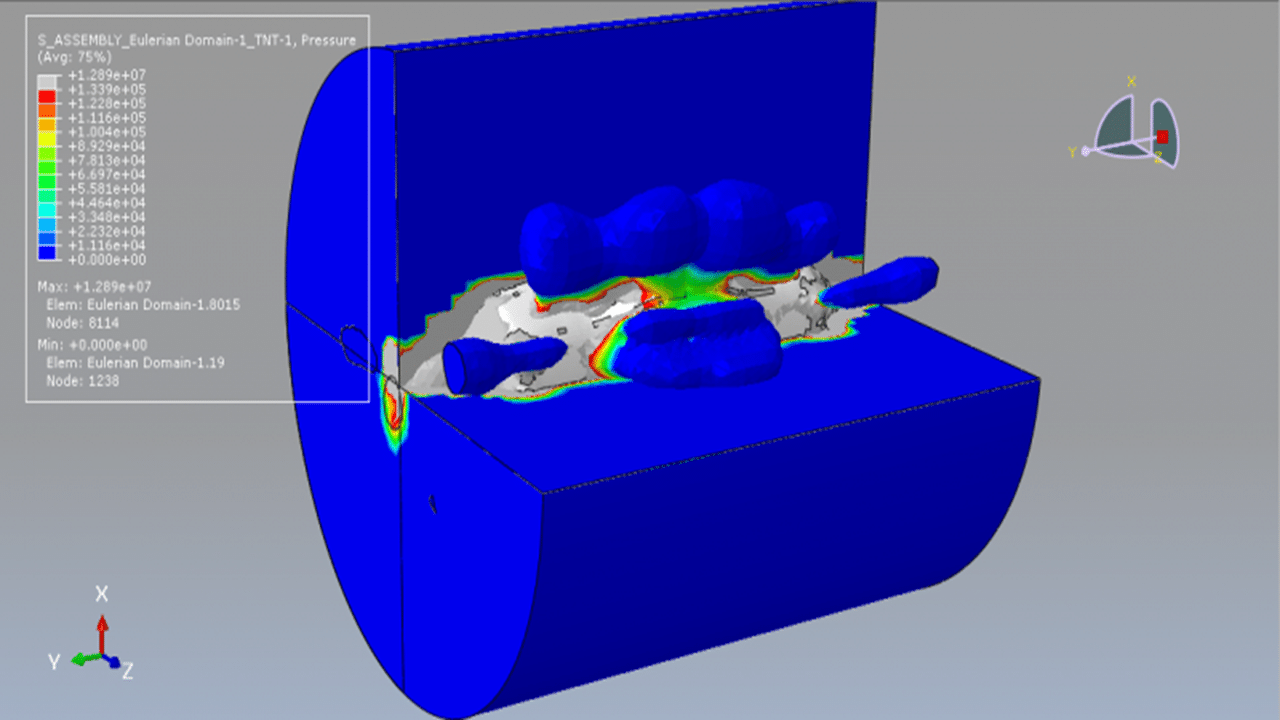
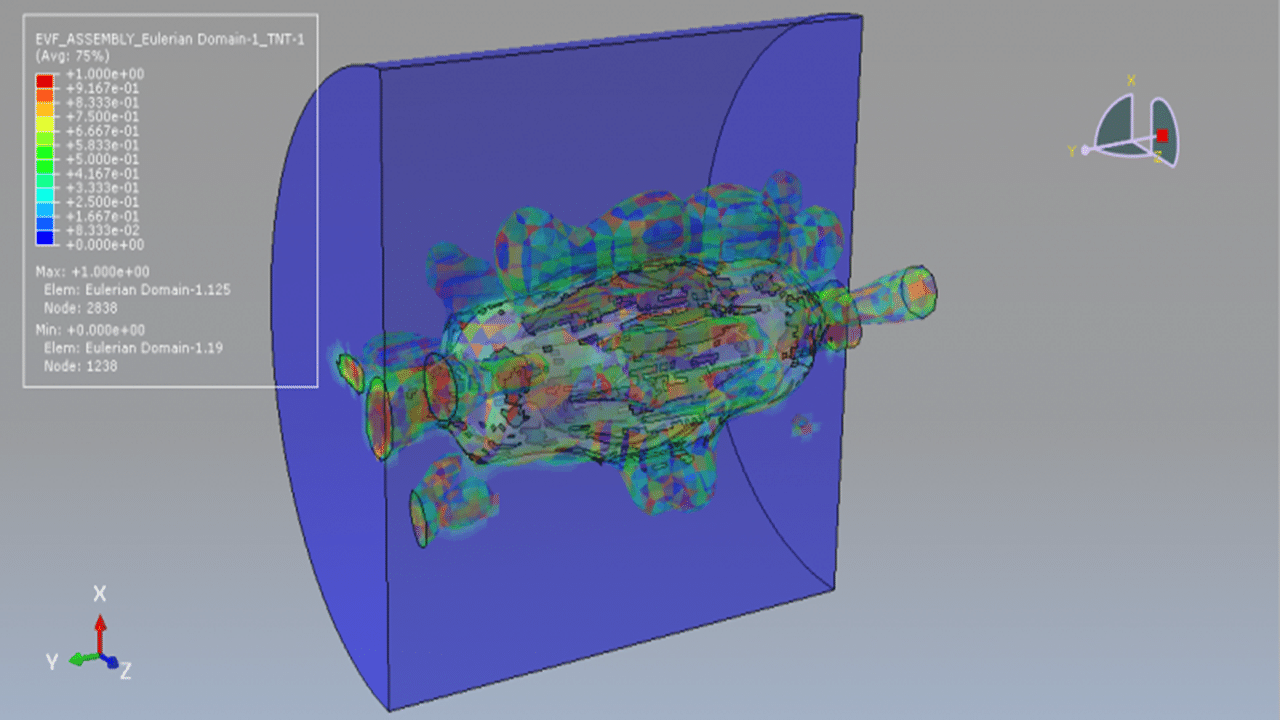


In this tutorial, the simulation of a CEL explosion inside a CFRP composite vessel in Abaqus is investigated. The CFRP vessel is modeled as a three-dimensional shell part with sixteen layers, each with different fiber orientations. The TNT charge is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part, while the surrounding environment is defined as an Eulerian part to capture the fluid-structure interaction during the explosion.
Composite pressure vessels are widely used for storing compressed natural gas in vehicles, and similar technologies are being developed for hydrogen gas storage. These vessels typically consist of fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites. Among these, carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP) are preferred for their high strength-to-weight ratio, although their cost remains a barrier for large-scale applications. In this tutorial, CFRP is selected as the vessel material.
Damage initiation in the composite vessel is modeled based on Hashin’s failure criteria, which capture four main failure mechanisms: fiber tension, fiber compression, matrix tension, and matrix compression. The vessel uses an elastic lamina material model with Hashin damage to simulate progressive failure under blast loading.
To model the explosive behavior of TNT, the Jones-Wilkins-Lee (JWL) equation of state is used. This model represents the pressure generated from chemical energy release during detonation. The programmed burn implementation is used, where detonation is initiated based on geometry and wave speed, rather than being triggered by shock at a material point.
A dynamic explicit step in Abaqus is selected as it is well-suited for high-speed, transient events such as explosions. General contact with specified contact properties is defined across all parts in the model. The volume fraction method is used to define the amount and spatial placement of TNT within the Eulerian domain. A refined mesh is required for all components to achieve accurate and stable results.


Dynamic
€1,00 €0,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?