Intro
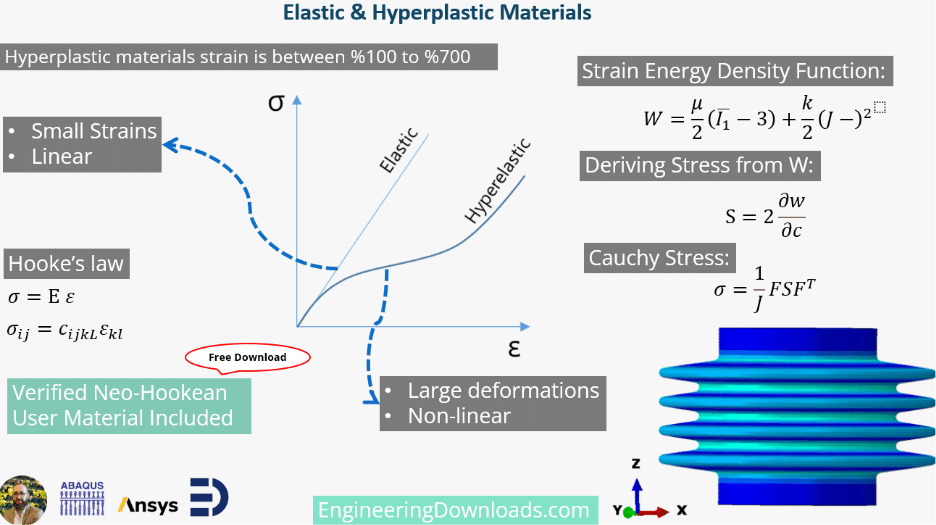
When designing materials for engineering applications, understanding their stress-strain behavior is critical. Two fundamental categories dominate this space: linear elastic and hyperelastic materials. Here’s what you need to know and why it matters.
Linear Elastic Materials: Simplicity at Small Strains
Linear elastic materials follow Hooke’s Law, where stress is directly proportional to strain. Think of a spring: pull it slightly, and it snaps back predictably. Key traits:
- Small deformations (typically <1%).
- Linear stress-strain curves (easy to model!).
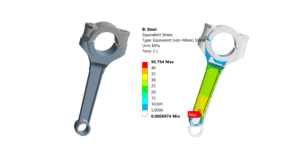
- Applications: Metals, ceramics, and rigid structures.
Hyperelastic Materials: Mastering Large Deformations
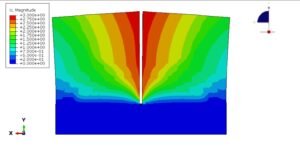
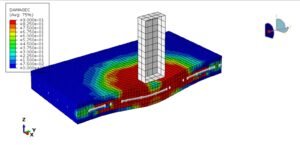
Hyperelastic materials (like rubber, silicone, or biological tissues) thrive under large strains (100%-700%). Their behavior is nonlinear and modeled using strain energy density functions (e.g., Neo-Hookean, Mooney-Rivlin). Highlights:
- Extreme flexibility without permanent deformation.
- Complex mechanics requiring advanced constitutive models.
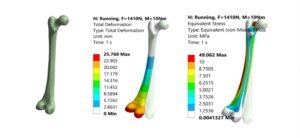
- Applications: Tires, seals, soft robotics, and medical implants.
Why Choose Hyperelastic Models?
For simulations involving elastomers or polymers, linear elasticity falls short. Hyperelasticity captures:
- Geometric nonlinearities.
- Volume changes (compressibility/incompressibility).
- Real-world material responses under finite strains.
Ready to Simulate? Grab our free, verified UMAT for Neo-Hookean hyperelasticity on EngineeringDownloads.com perfect for Abaqus users!
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re working with metals or rubbers, picking the right material model ensures accurate simulations. Hyperelasticity unlocks possibilities for innovative designs, from stretchable electronics to life-like prosthetics.
Are you interested in sharing your thoughts with the ED global audience? Just let us know: