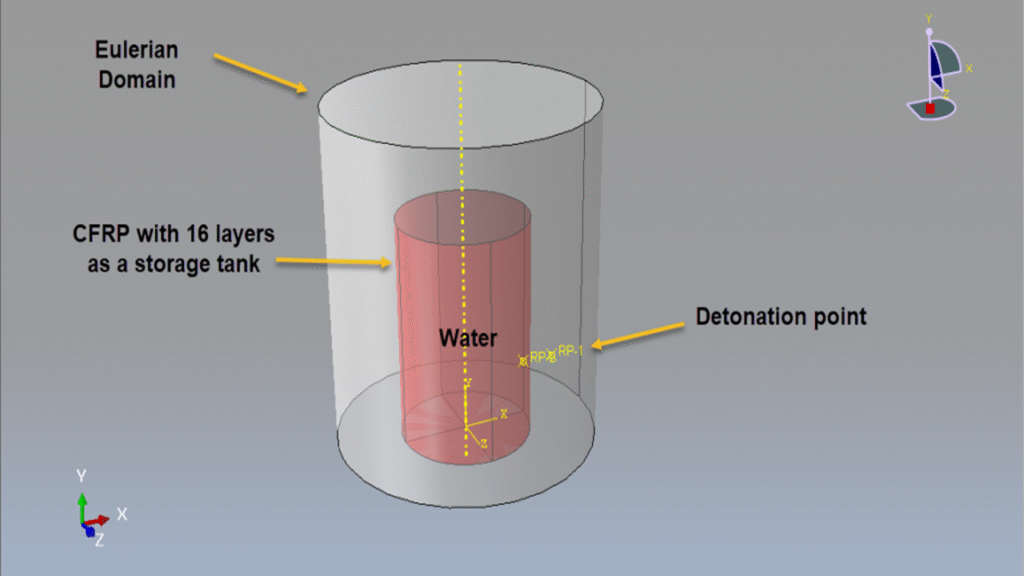
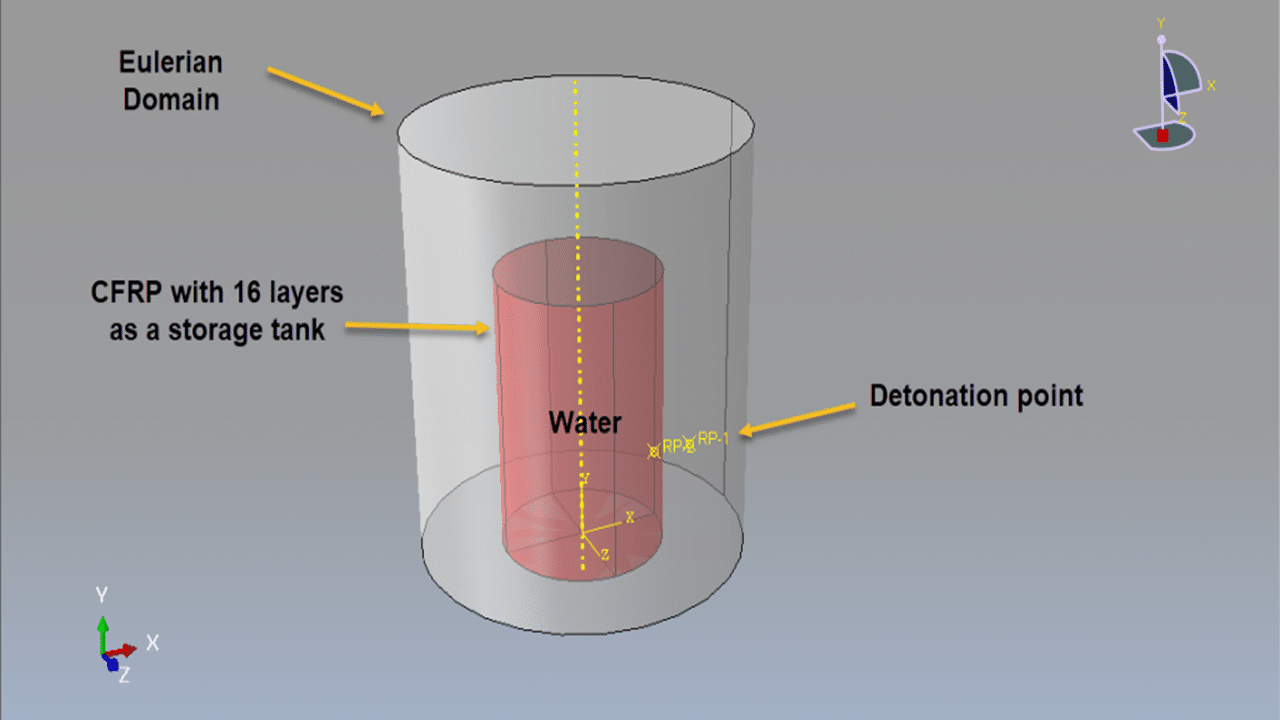
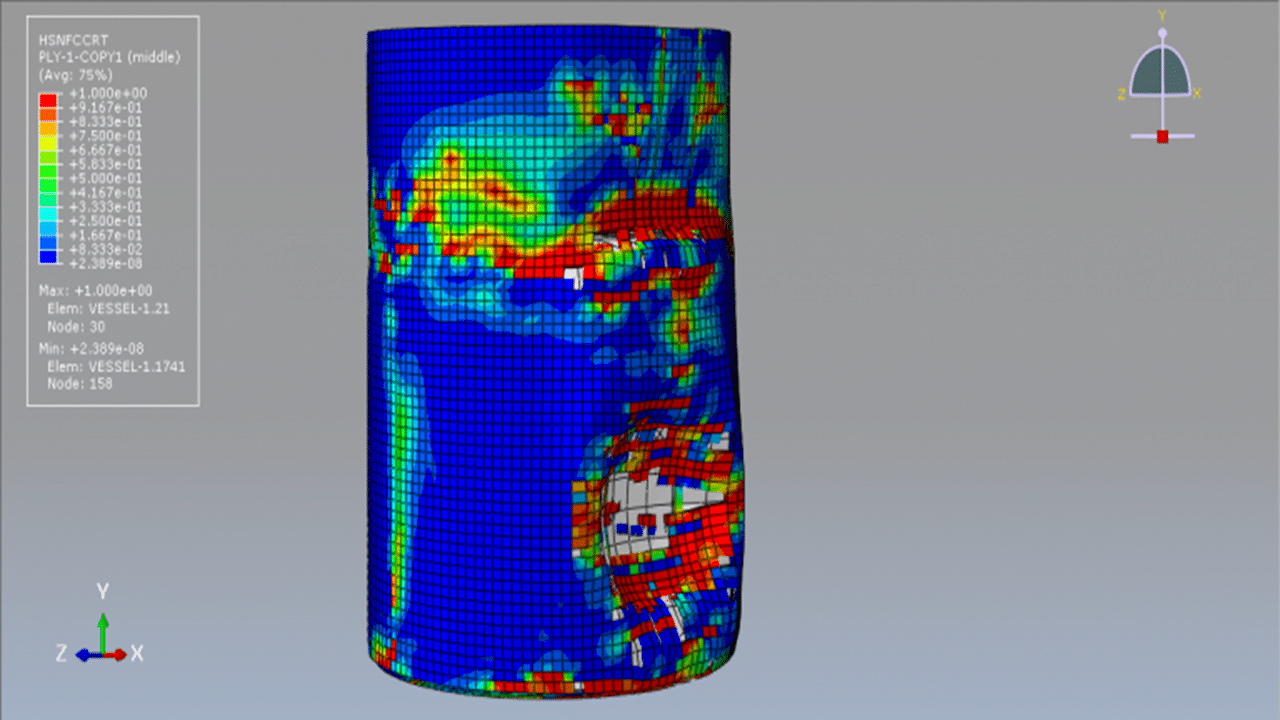
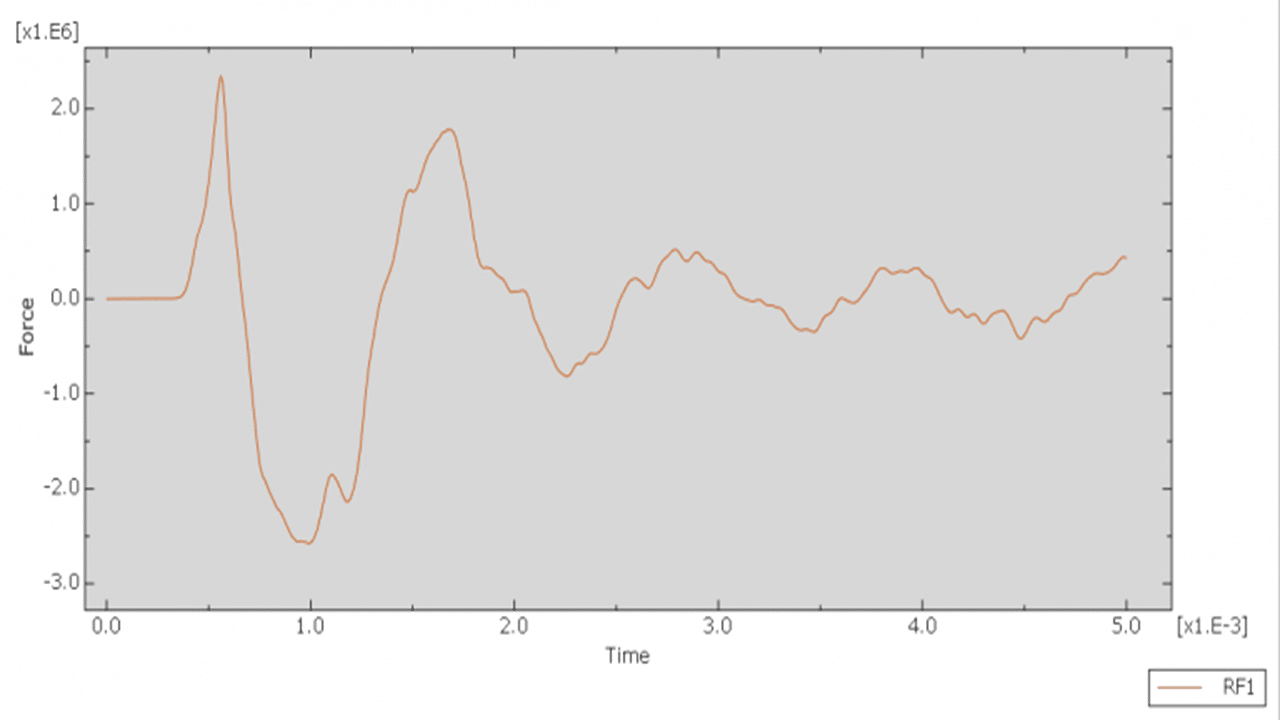
In this tutorial, the simulation of a CFRP water storage tank under a close-range air blast explosion in Abaqus is investigated. The CFRP tank is modeled as a three-dimensional shell part. The water is modeled as a solid part and is used as a reference volume in the load section to define its amount and position inside the domain. The region surrounding the tank and water is modeled as an Eulerian part.
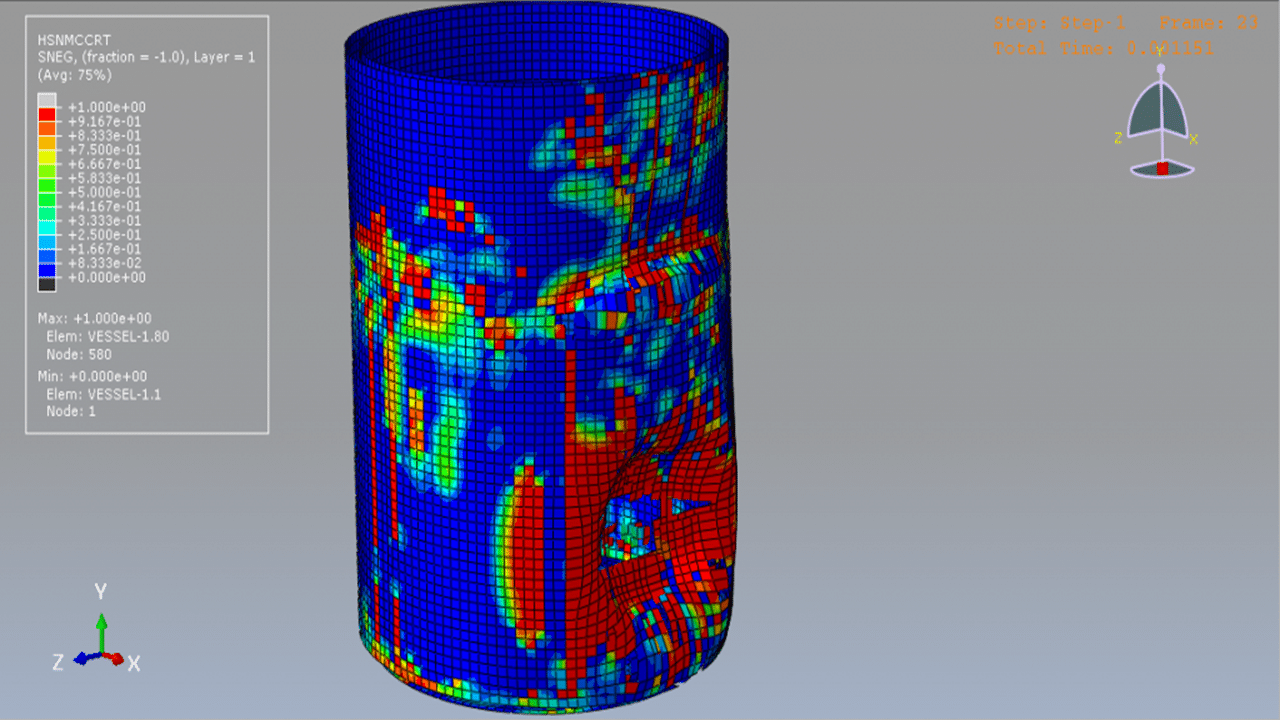
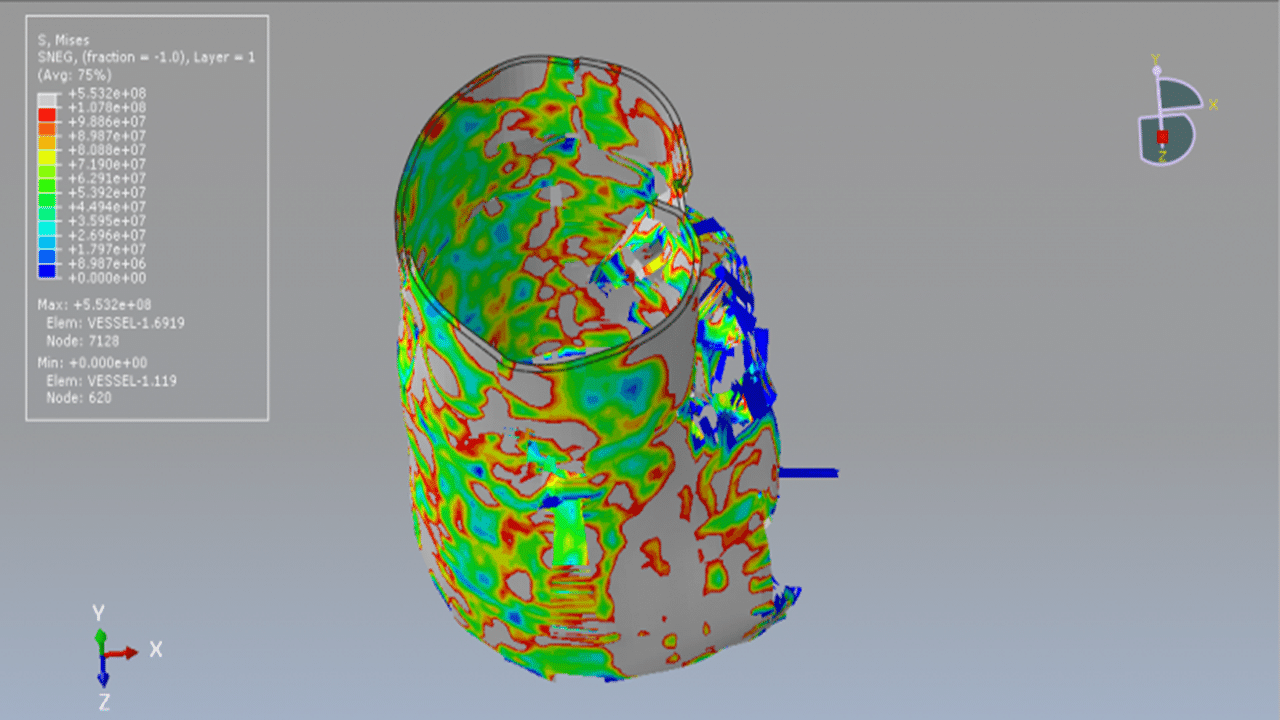
Damage initiation refers to the onset of material degradation at a given point. In Abaqus, the damage initiation criteria for fiber-reinforced composites are based on Hashin’s theory, which includes four failure modes: fiber tension, fiber compression, matrix tension, and matrix compression. The CFRP tank is modeled with sixteen layers, using the lamina elasticity model combined with the Hashin damage model.
To represent water behavior, the Us–Up model is applied by defining the sound velocity of the fluid. A dynamic explicit step with a specified time duration is used, and the mass scaling technique can also be applied. The general contact algorithm with defined contact properties is used for all interacting domains. The CONWEP air blast method is used to simulate an explosion near the tank with a specific amount of TNT. Proper boundary conditions are assigned to the model components.
The volume fraction method is used to define the amount and location of water within the Eulerian domain. A sufficiently fine mesh should be used to ensure accurate results and clear visualization.

Acoustic
€100,00 Original price was: €100,00.€99,99Current price is: €99,99.
Abaqus
€150,00 Original price was: €150,00.€120,00Current price is: €120,00.
Abaqus
€49,00 Original price was: €49,00.€29,00Current price is: €29,00.
Abaqus
€46,00 Original price was: €46,00.€26,00Current price is: €26,00.

Abaqus
€50,00 Original price was: €50,00.€30,00Current price is: €30,00.
Abaqus
€46,00 Original price was: €46,00.€27,00Current price is: €27,00.
Abaqus
€45,00 Original price was: €45,00.€28,00Current price is: €28,00.
See more
Let’s Learn and Collaborate
Get VIP access to new content.
Sign up for weekly deals and news.
Engineering Downloads is a hub for learning,
collaboration, and sharing engineering models
and resources.
© 2025 Engineering Downloads. All rights reserved.

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?