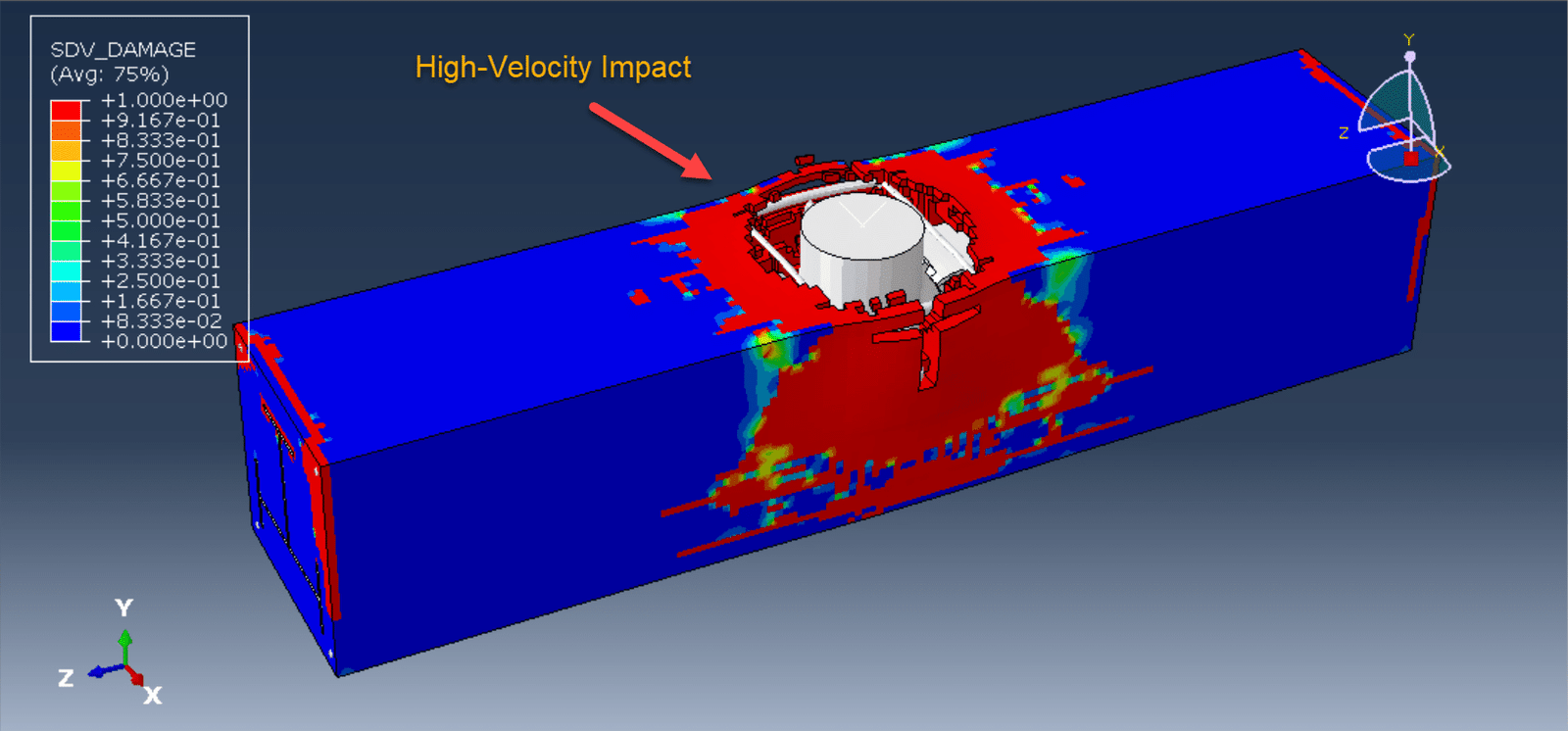
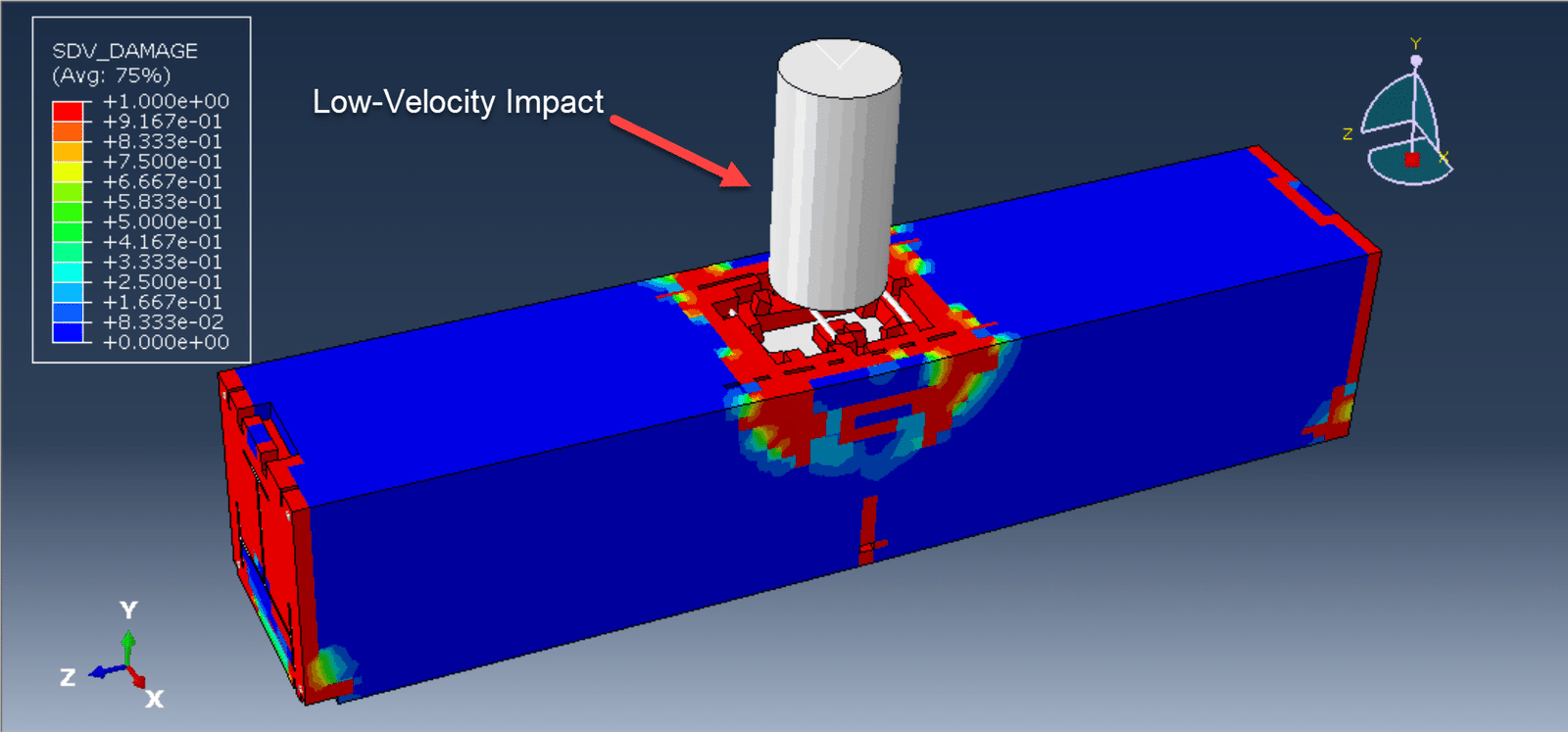
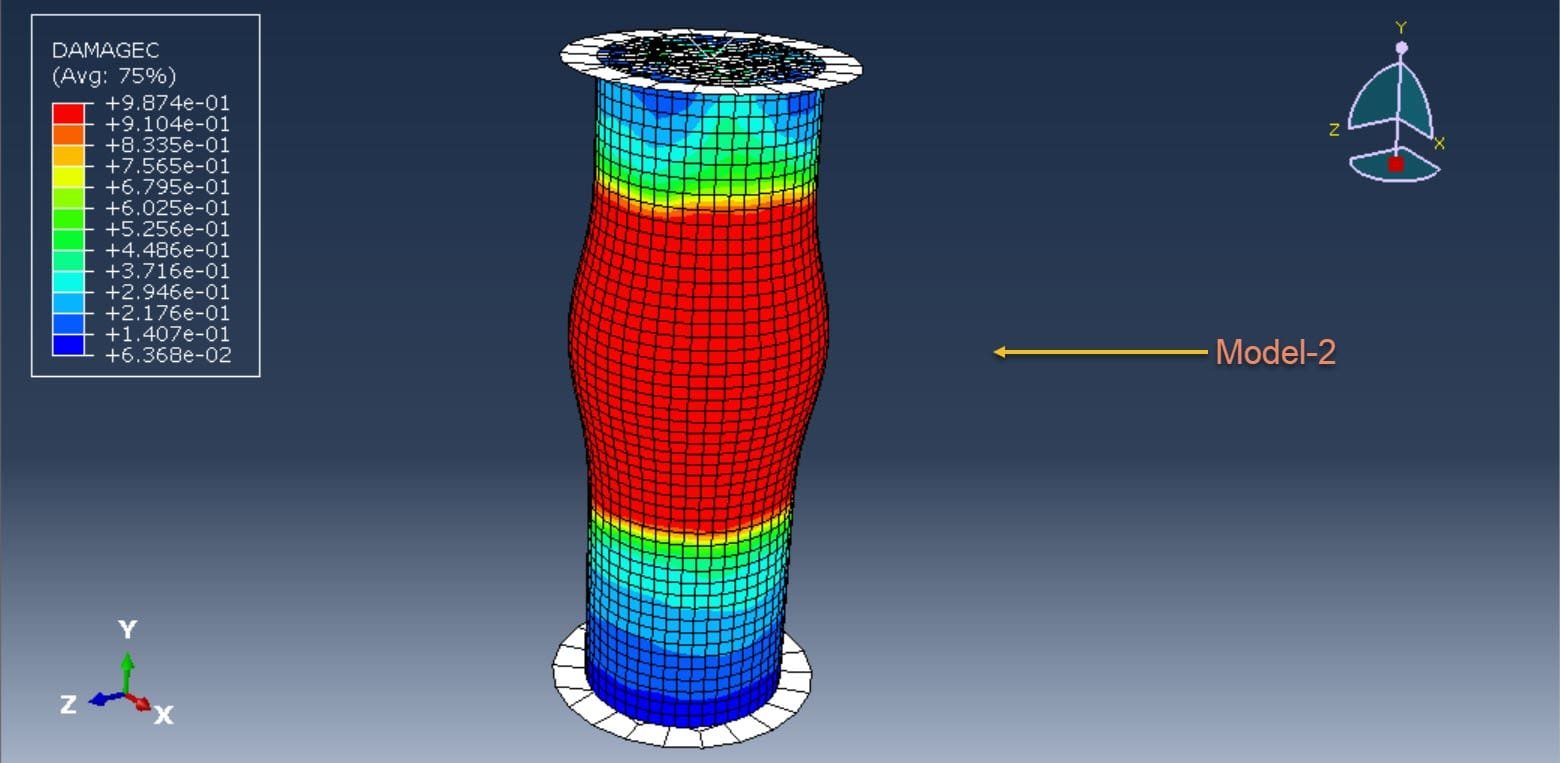
Overview of Restarting an Abaqus Analysis
Abaqus allows you to continue a previously halted analysis by initiating a restart. This process depends on having its files from the prior analysis. These files must be specified before the initial run through the step module under “output” and “restart requests”.
In the new analysis setup, reference the step from the previous job that will serve as the starting point. This can proceed as initially defined or incorporate additional steps, but it cannot include new geometry or constraints. To execute this, select ‘restart’ as the job type. Note that the output for the new steps will be in a separate .odb file from the original analysis.
Practical Applications of Restarting
Restarting is useful for:
- Examining a model under varying loads with a common preloading step.
- Addressing convergence issues by modifying specific steps without repeating earlier ones.
- Resuming interrupted analyses (e.g., due to power outages) from the last saved increment.
How to Set Up Restart Files
Restart files must be predetermined before the initial analysis, especially for long-running simulations. Abaqus/Standard does not automatically generate these files, and Abaqus/Explicit only does so at the start and end of each step.
To request restart files in the CAE:
- Navigate to the Step module.
- Select “output” and then “restart requests”.
Set the frequency or number of intervals for the output.


Options include:
- Frequency: Every nth increment for writing files.
- Intervals: Equally spaced points in time for file writing.
- Overlay: Limits file size by overwriting old data.
- Time Marks: Writes output at exact time points, which may increase simulation time.
Once the initial job is executed, the .res file will be available for use.
Performing a Restart Analysis
To set up a model:
1- Copy the original model in the .cae file.

2- Right-click the model in the model tree and select “Edit Attributes”.
3- In the Edit Model Attributes dialog box, check “read data from job” and input the previous job’s name and the specific step for restarting.
You can restart from the end of a step or an intermediate increment. For interrupted analyses, restarting from the last saved increment is advisable. For convergence issues, modify and restart from the beginning of the problematic step.

In the new model, add any additional steps required. Remember, previous step settings (geometry, mesh, material properties) cannot be altered. Constraints must be defined in the initial analysis. To finalize, create and run a new job, selecting ‘restart’ as the job type. This ensures results are drawn from the previous analysis.


Final Considerations for Restarting
Before conducting the initial analysis, it is important to decide whether restart files are necessary. Restart files can be crucial for continuing interrupted analyses without starting over from the beginning. Ensure that any modifications you plan to implement can be accommodated within a single analysis, as only changes that fit within this scope are feasible. This means carefully planning and understanding the limitations of the analysis process. Additionally, be aware that the output files from the original and restart analyses will remain separate, which helps in maintaining clarity and organization of the results. By effectively using this function, you can save both time and resources, as it allows for more efficient processing and reduces the need for redundant work.
This approach to restart analysis in Abaqus ensures efficient management of complex simulations, enabling targeted modifications and continuity without redundant computations.