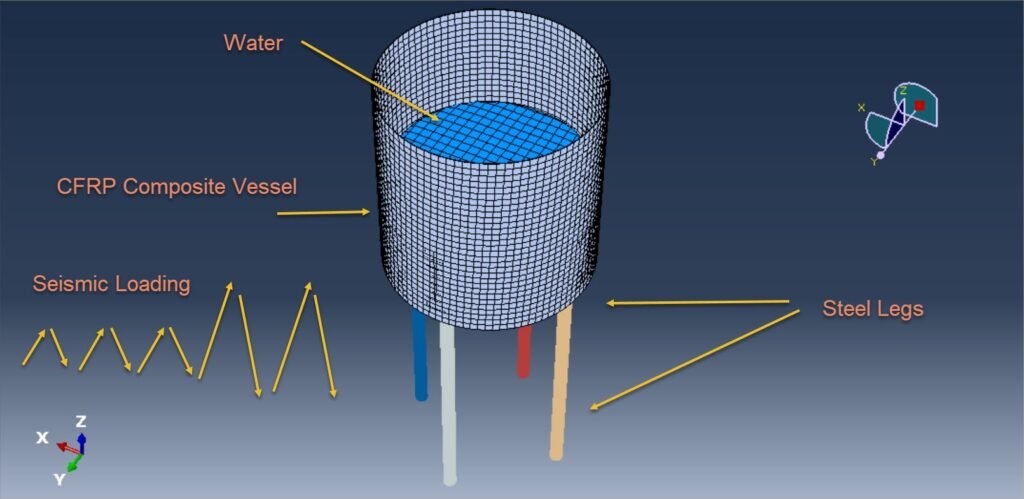
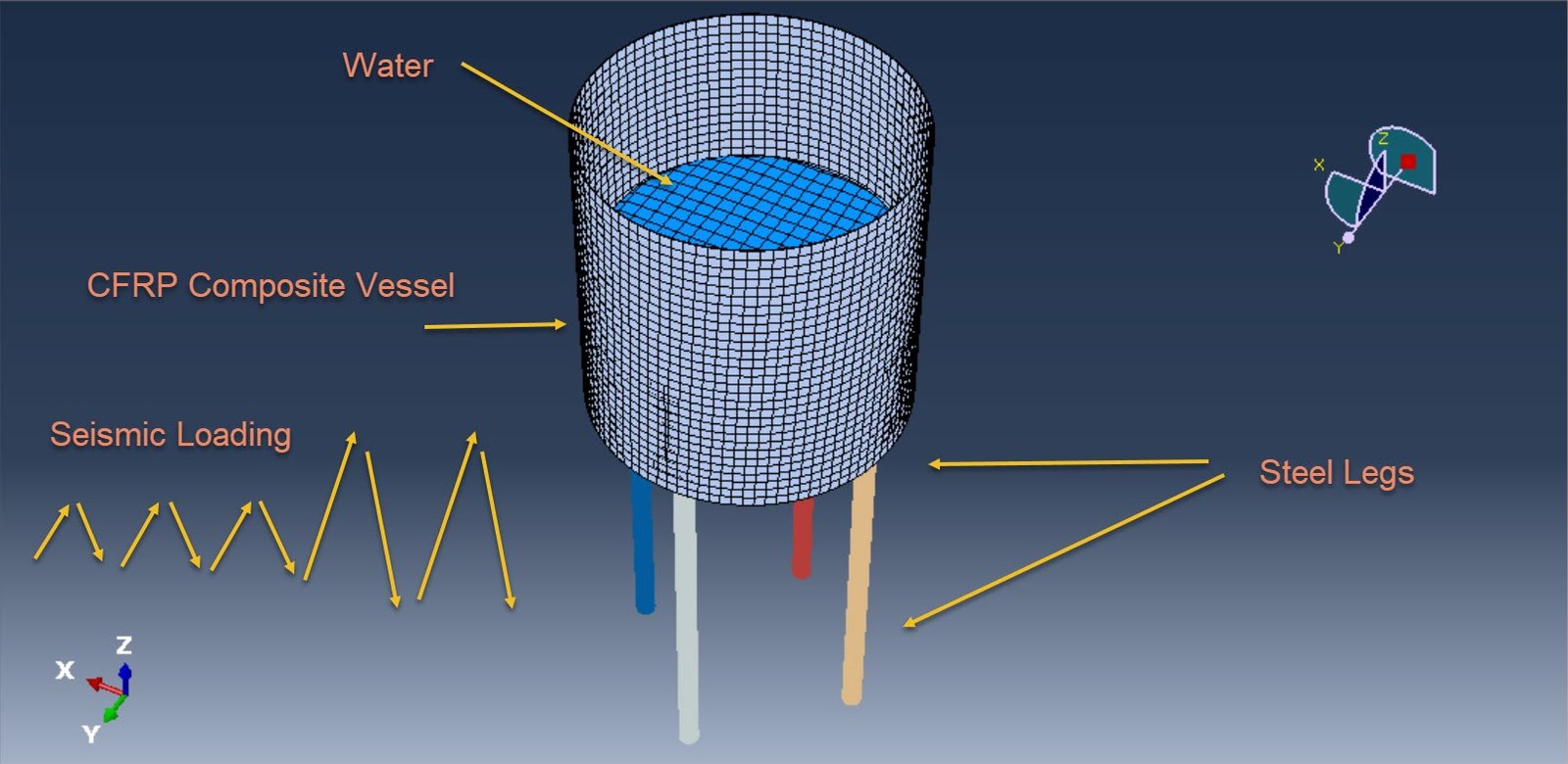


The accurate prediction of fluid-structure interaction (FSI) phenomena, such as liquid sloshing, is crucial in the design and safety analysis of lightweight composite tanks used in aerospace and marine applications. Sloshing refers to the oscillatory motion of a liquid inside a container, often induced by external excitations such as acceleration, vibration, or impact. This motion can lead to dynamic loads on the tank walls, affecting the structural integrity and potentially causing failure under extreme conditions.
In recent years, Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) composite materials have gained significant attention due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. These properties make CFRP an ideal candidate for manufacturing modern “airy” (i.e., lightweight and optimized) tanks in spacecraft and high-performance vehicles. However, the anisotropic and often nonlinear behavior of CFRP composites under dynamic loading necessitates sophisticated modeling techniques to capture their interaction with internal fluids accurately.
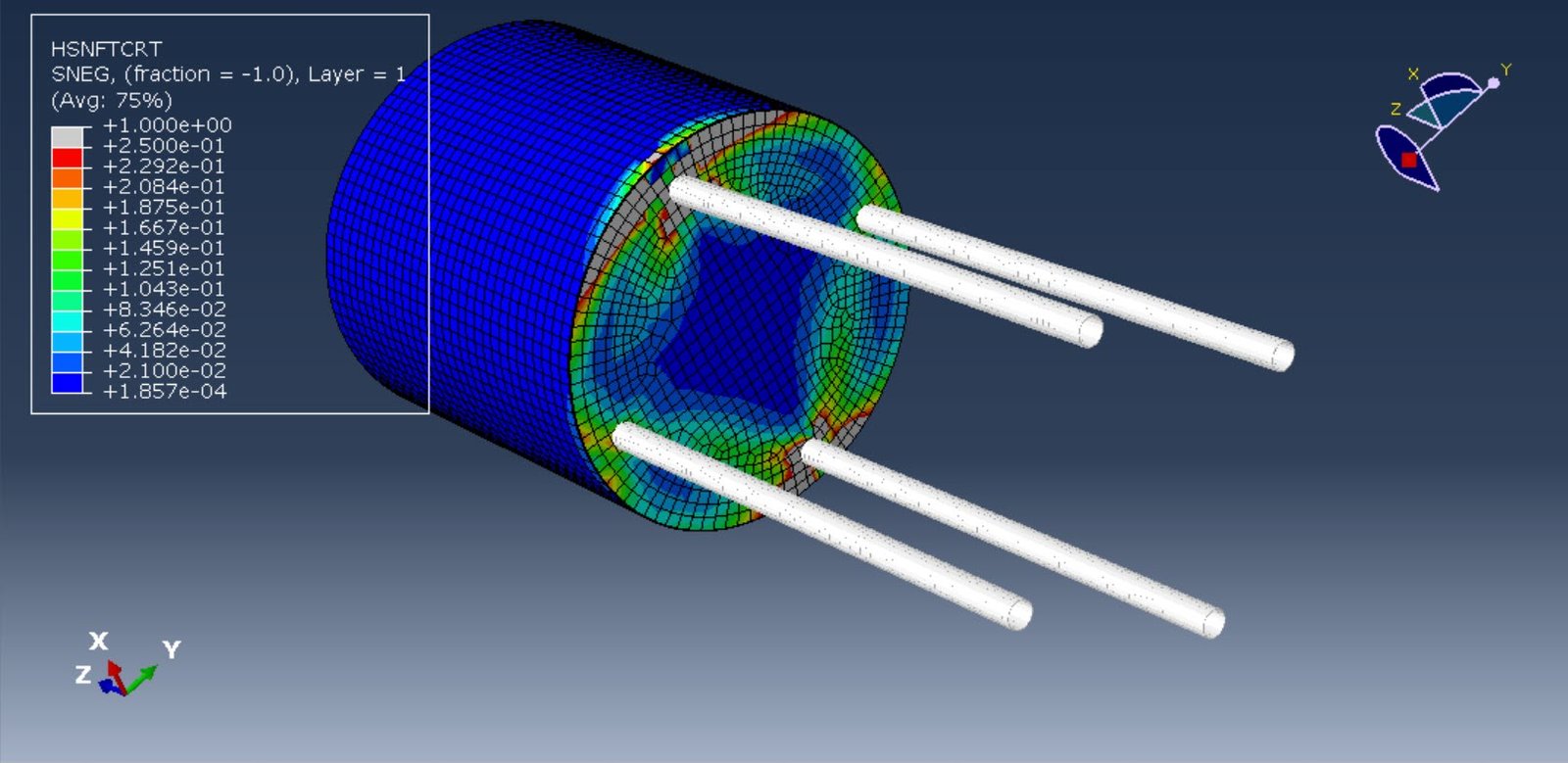
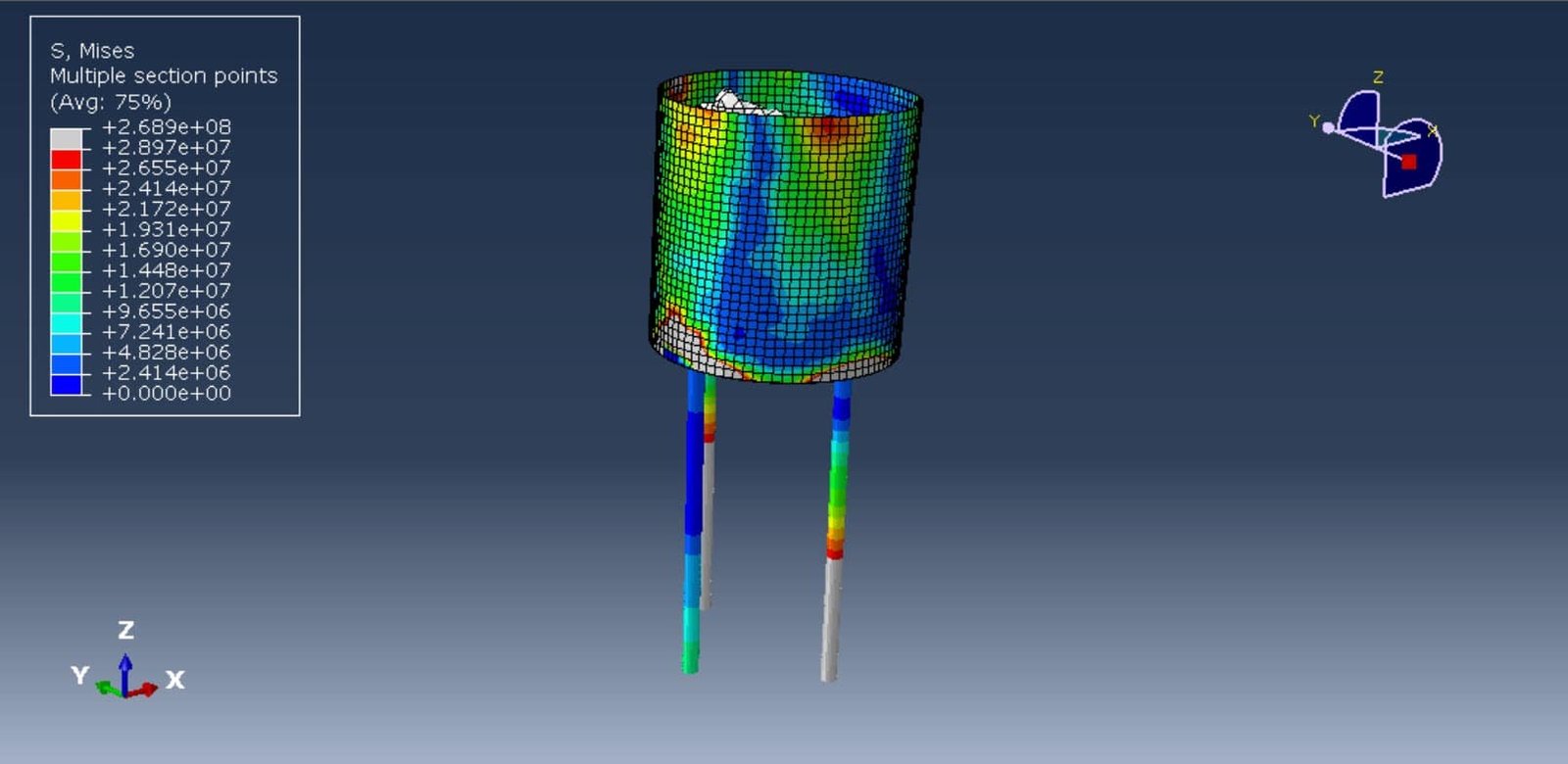
The Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) method offers a robust computational approach for simulating such FSI problems. In CEL, the structure (tank) is typically modeled using a Lagrangian formulation, which tracks the material mesh with the structure, while the fluid (water) is modeled using an Eulerian formulation, which allows for large deformations and free surface flow within a fixed mesh. This hybrid framework enables the simulation of complex sloshing behavior, including fluid impact, wave breaking, and free surface motion, while accounting for the deformation of the composite tank walls.

Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€75,00 €37,00
Abaqus
€76,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?