Introduction to the Four-Point Bending Test of an RC Slab with PET Foam Core
The four-point bending test is a widely used experimental method to evaluate the flexural behavior of composite structural elements, such as reinforced concrete (RC) slabs with a PET (polyethylene terephthalate) foam core. This test helps determine key mechanical properties, including flexural strength, stiffness, ductility, and failure modes, under controlled loading conditions.
Purpose of the Test
Assess the structural performance of the PET foam-cored RC slab under bending.
Study the load-deflection response and crack propagation.
Evaluate the composite action between the concrete, reinforcement, and PET foam core.
Compare experimental results with theoretical or numerical models.
Test Setup
1. Specimen Preparation:
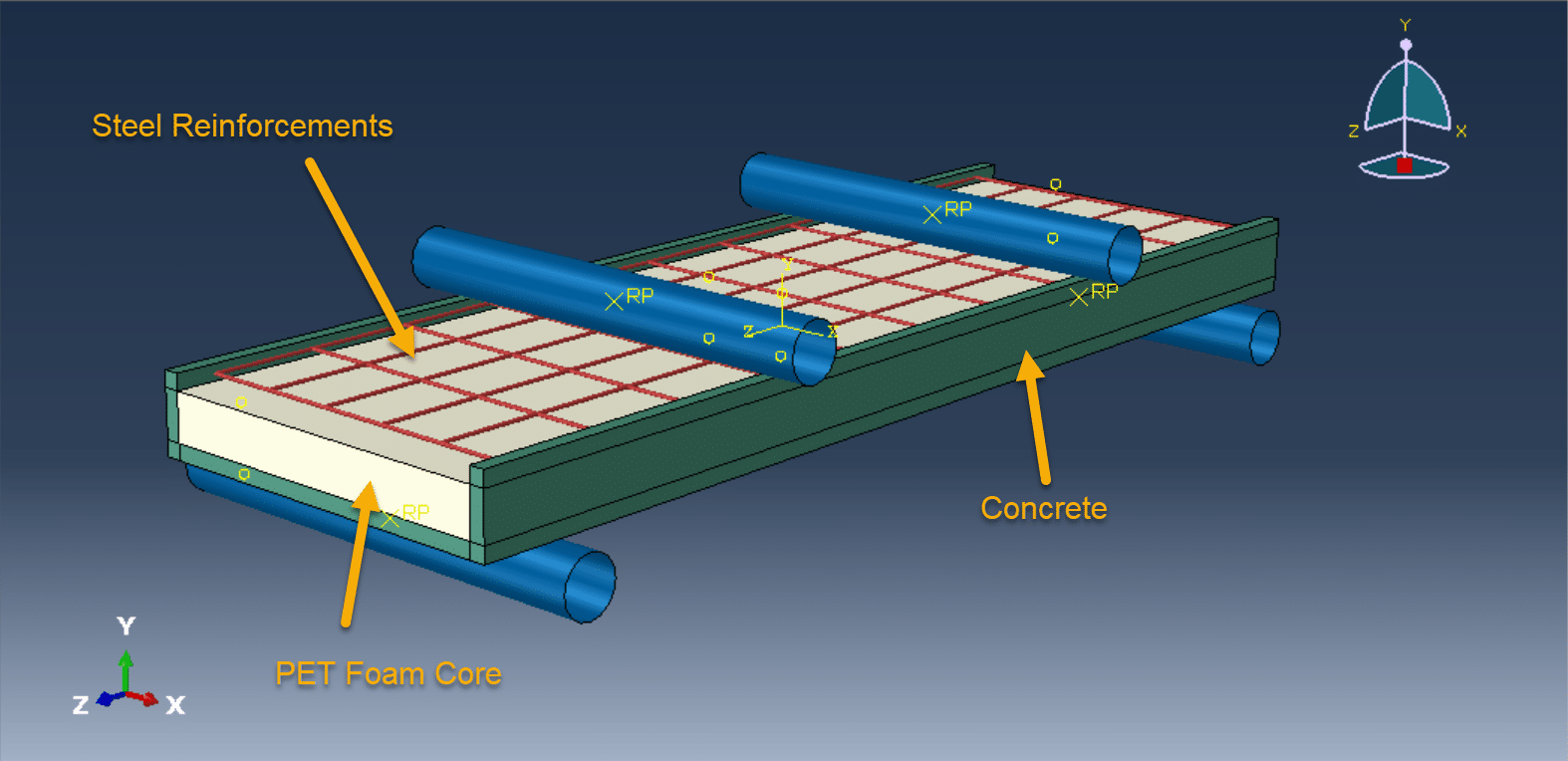
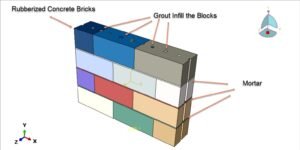
The RC slab consists of concrete layers (top and bottom) with a lightweight PET foam core in between, often reinforced with steel bars or mesh.
PET foam is chosen for its lightweight, thermal insulation, and energy absorption properties.
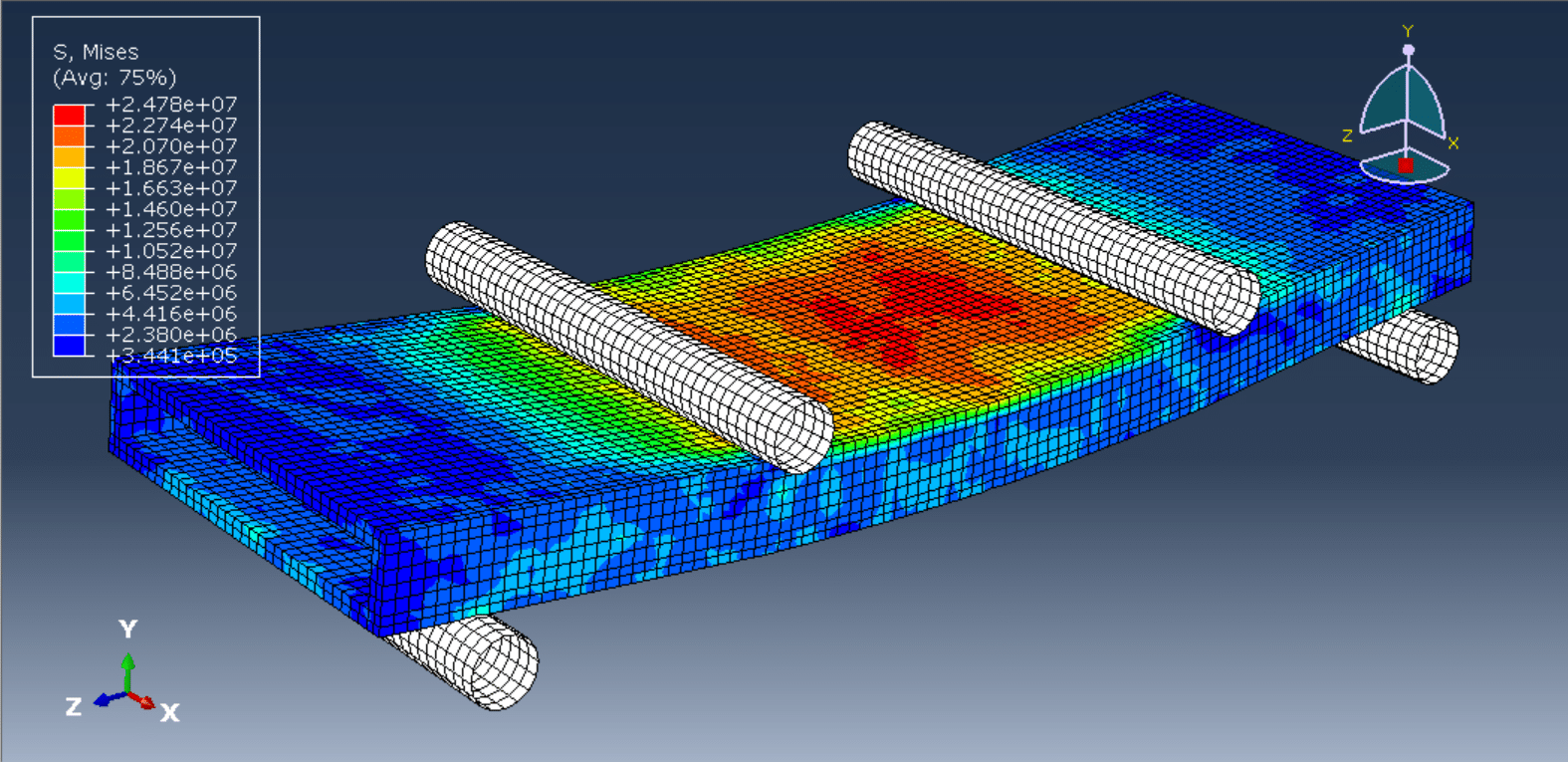
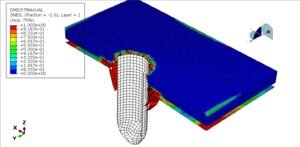
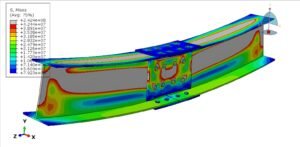
2. Loading Configuration (Four-Point Bending):
The slab is simply supported at two ends.
Two symmetrically placed load points apply a bending moment over a constant moment region (pure bending zone).
This setup ensures a uniform stress distribution between the loading points, reducing shear effects.
3. Instrumentation:
Load cells measure applied force.
Linear Variable Differential Transformers (LVDTs) record mid-span deflection.
Strain gauges monitor concrete and reinforcement strains.
Digital Image Correlation (DIC) or crack detection methods may be used for failure analysis.
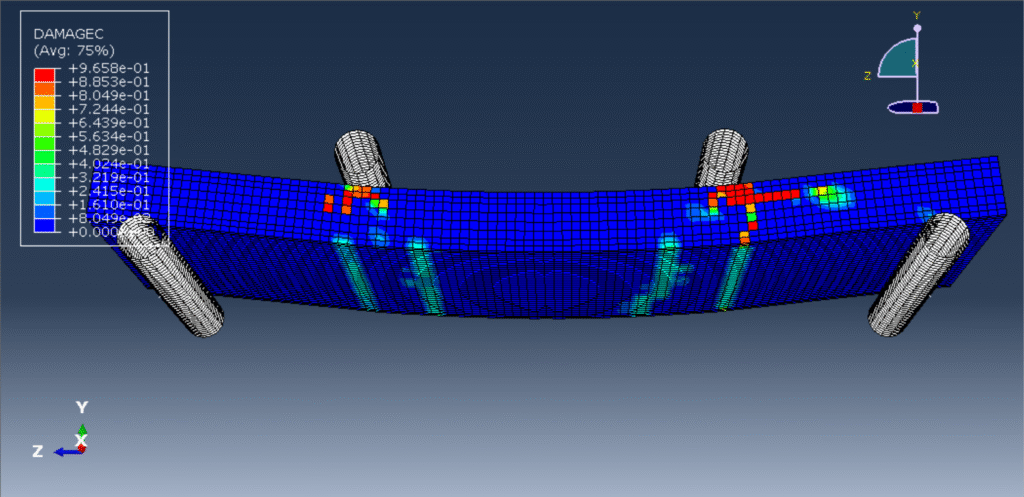
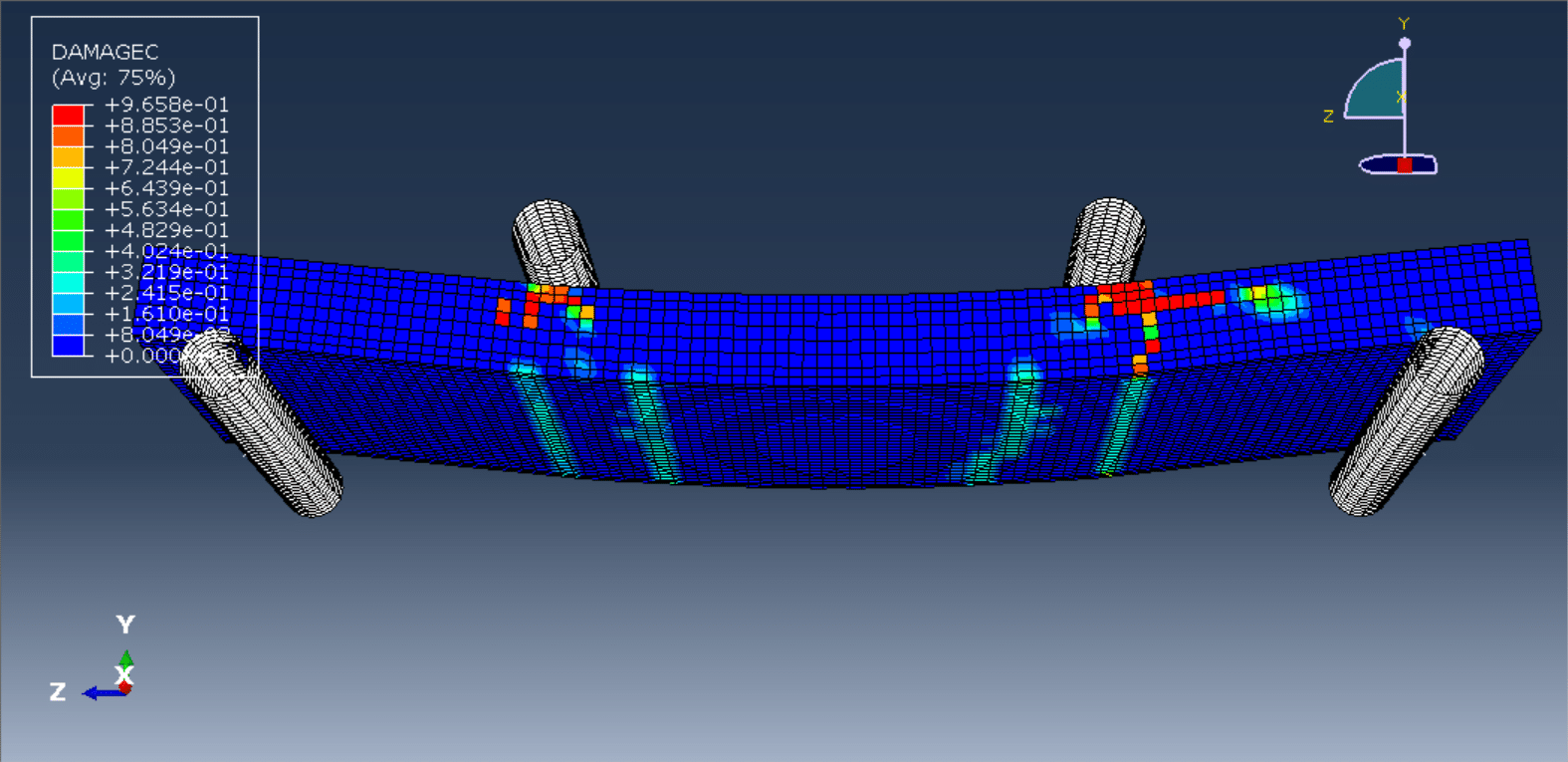
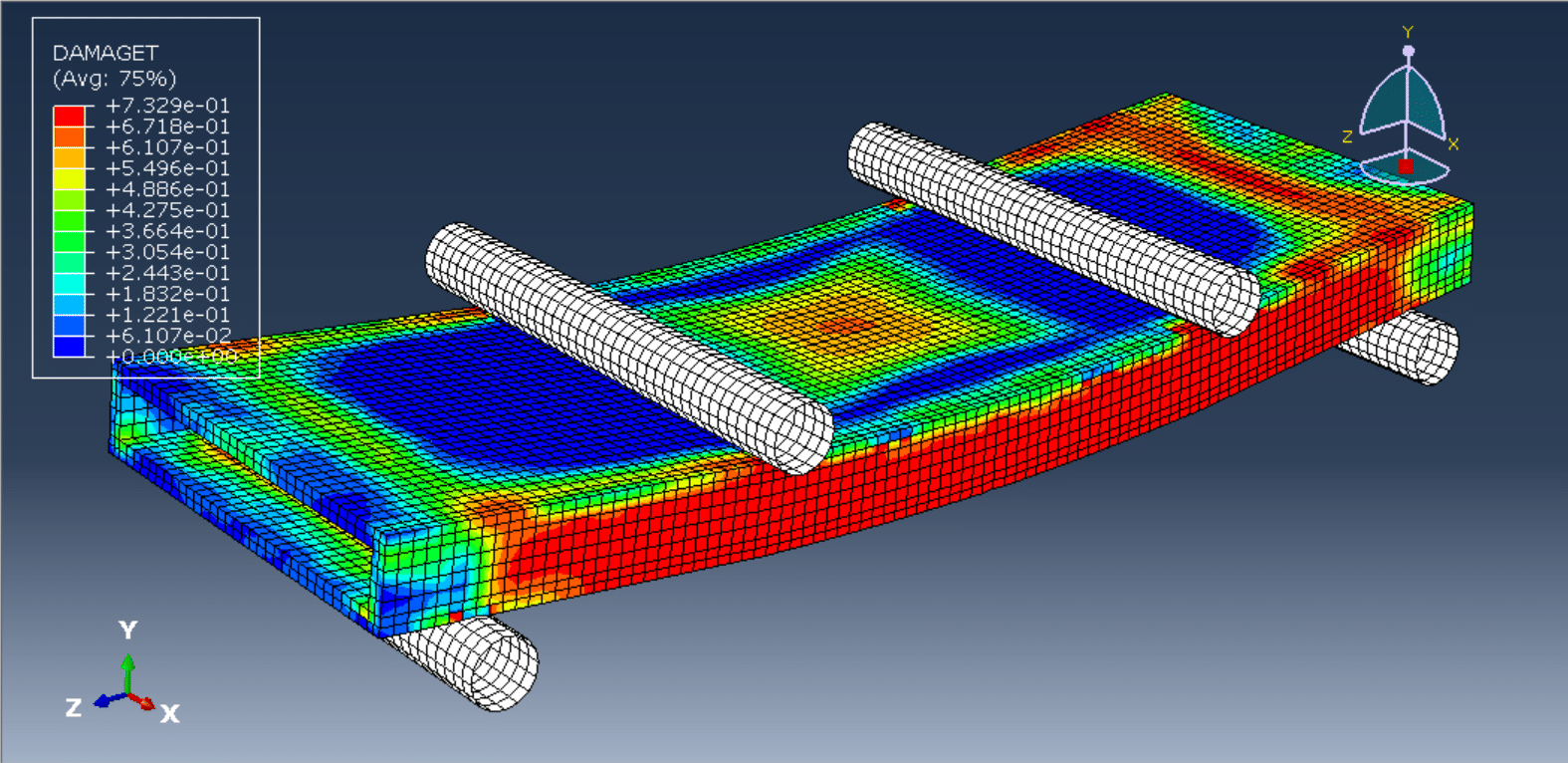
Key Observations & Results
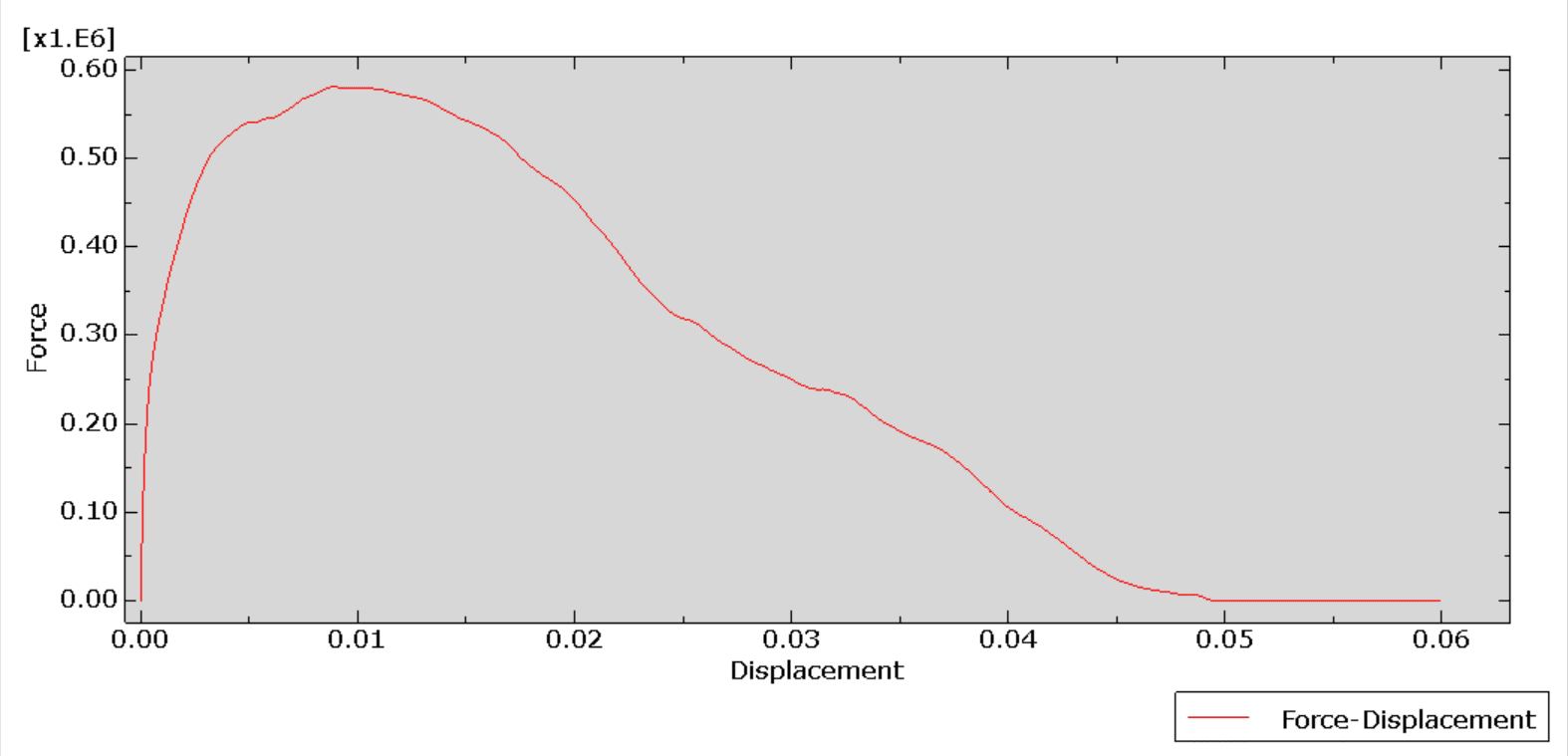
Load-Deflection Curve: Shows elastic behavior, cracking initiation, yielding of reinforcement, and ultimate failure.
Failure Modes:
Flexural cracking in the tension zone.
Delamination (if PET foam-concrete bonding is weak).
Shear failure (if shear resistance is insufficient).
Composite Efficiency: The PET foam core should enhance stiffness without compromising strength.
Advantages of PET Foam Core
Lightweight, reducing the self-weight of the slab.
Thermal and acoustic insulation properties.
Energy absorption under dynamic loads (e.g., impact).
Applications
Prefabricated construction (lightweight panels).
Bridge decks, flooring systems, and insulated walls.
Sustainable construction (PET foam can be recycled).
Conclusion
The four-point bending test provides valuable insights into the structural efficiency of PET foam-cored RC slabs, helping optimize design for lightweight, high-performance applications. Further studies may explore long-term durability, fire resistance, and cyclic loading behavior.

Abaqus
€81,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€299,00 €249,00

Uncategorized
€95,00 €80,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?