undefined




Papers abstract:
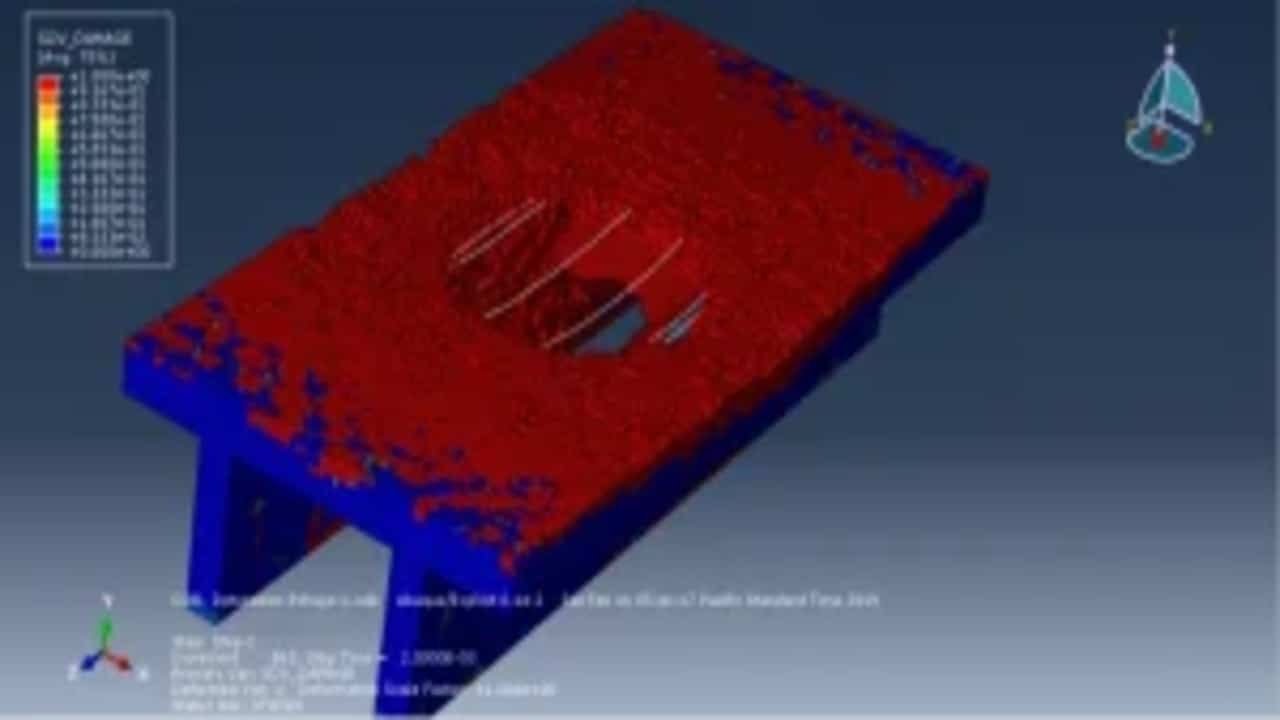
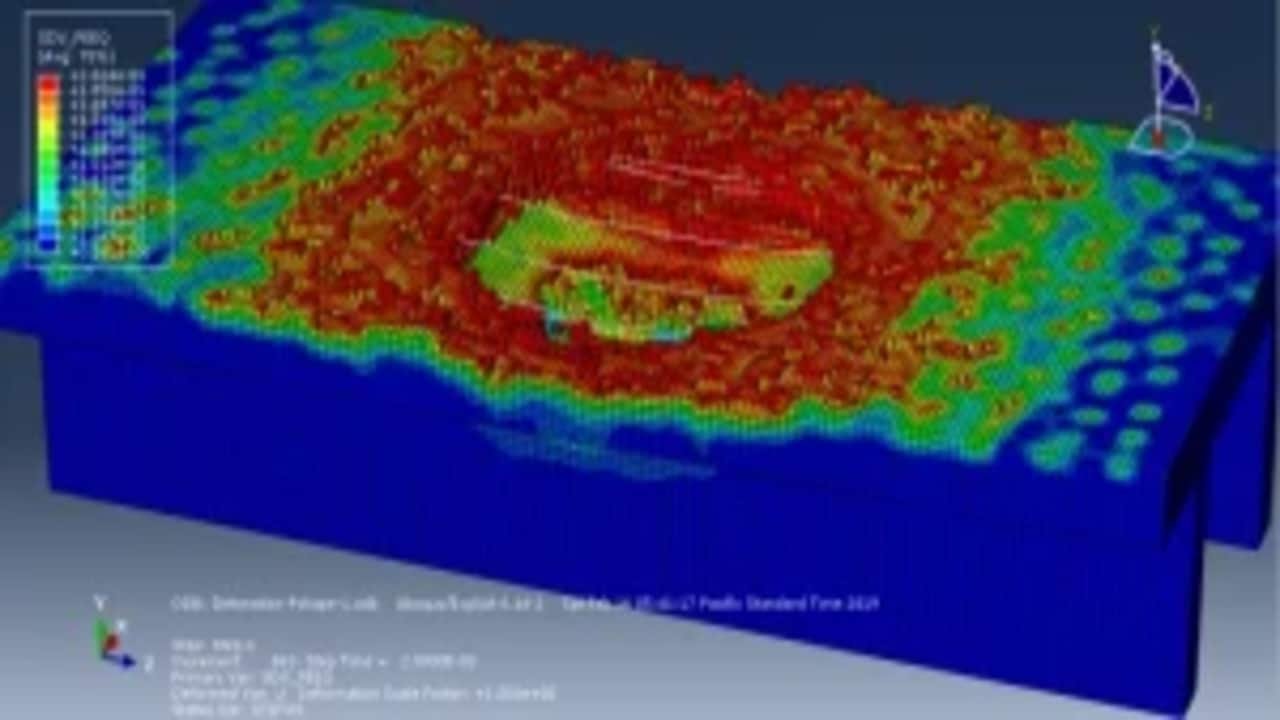
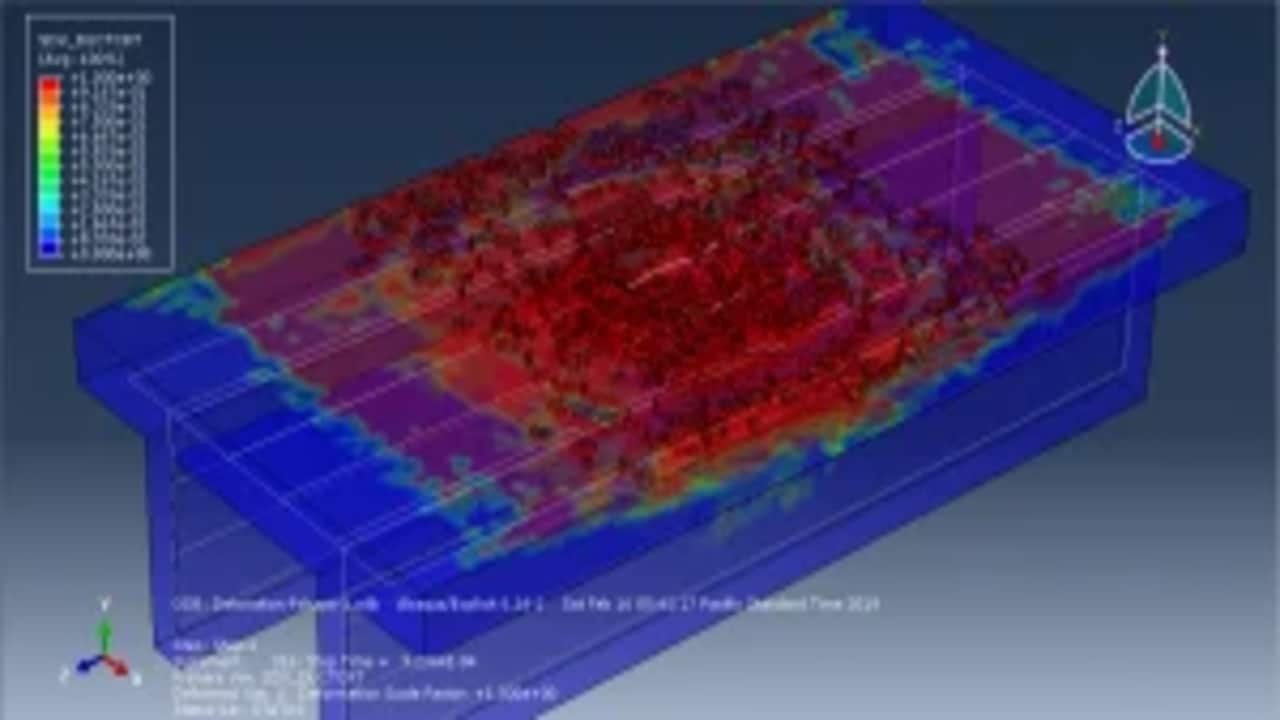
This paper presents the results of an experimental investigation on explosive breaching of p-section concrete beams. Twenty-three p-section concrete beams with a 100 cm length were tested. TNT charges were placed at three positions: contact detonation in the center, contact detonation above the web and close-in detonation in the center. The external and internal breach parameters of the panels were evaluated by measuring the diameter of the ejection crater, spalling crater and breach hole created by the charge detonation. The experimental results were compared to predict values obtained by the analytical models proposed by McVay, Morishita and Remennikov. A modified breach with crater limit line and breach without crater limit line were put forward based on the experimental results. The maximum cross-sectional destruction area ratio (MCDAR) values were used to evaluate the damage degree. The maximum value of MCDAR reached 0.331 corresponding to the C5 experimental condition, of which explosion occurred above the web.
Product Overview:
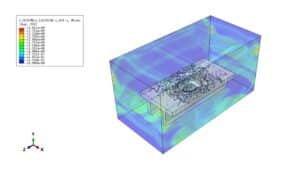
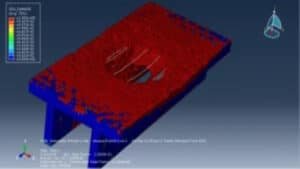
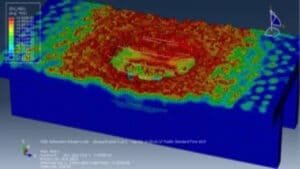
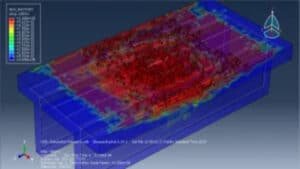
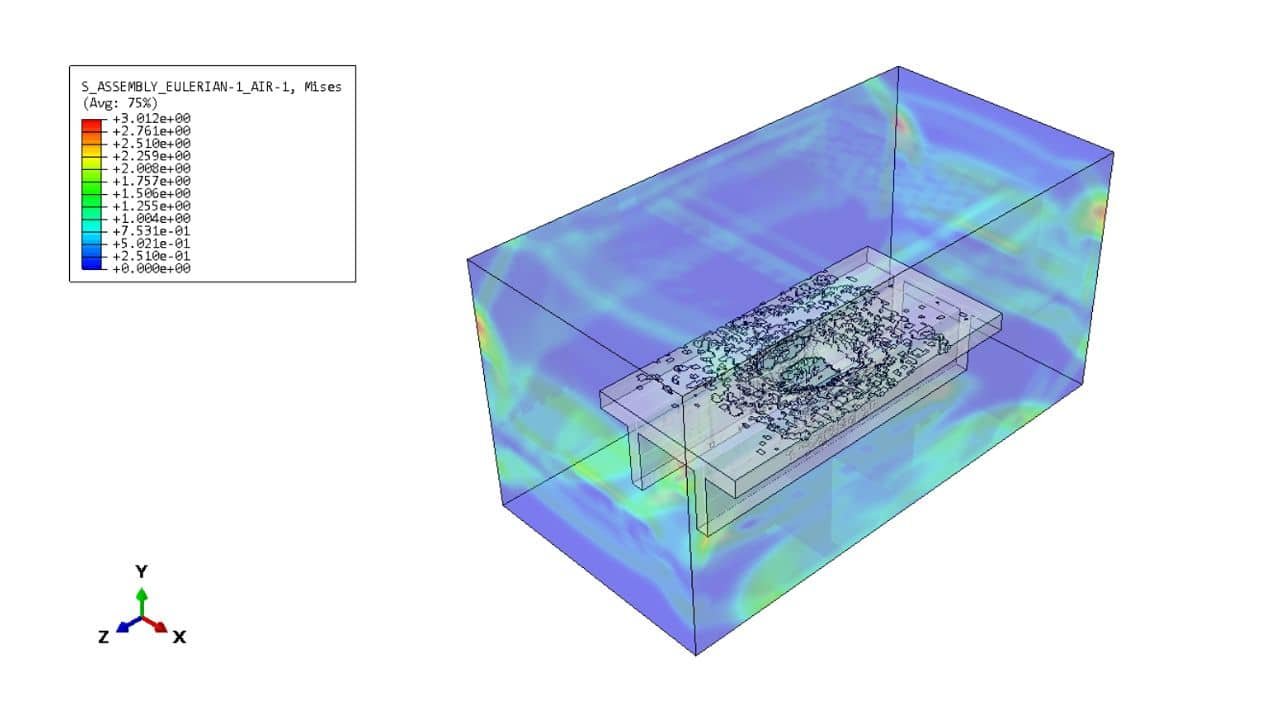
The study investigates the explosive breaching behavior of P-section concrete beams when subjected to contact explosions and close-in explosions. The goal is to assess structural damage under different explosive placements and improve predictive breach models. The tutorial demonstrates how to simulate a coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) explosion on a P-section concrete beam using Abaqus. Key simulation steps include:
In this tutorial, blast effects on reinforced concrete beams are simulated, according to data from the work of Zhen Li et al.
We connect engineers through:

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?