
Papers abstract:
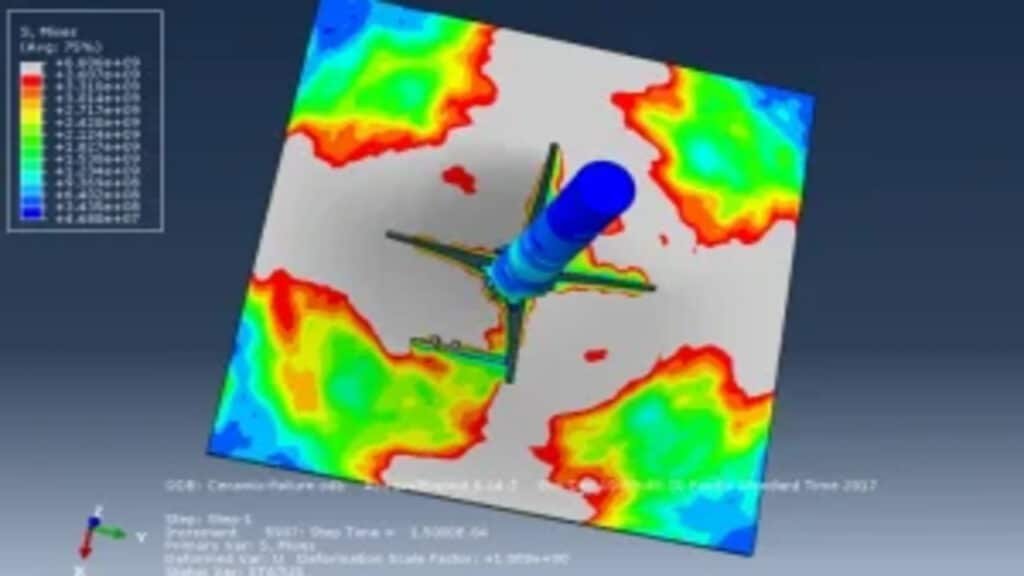
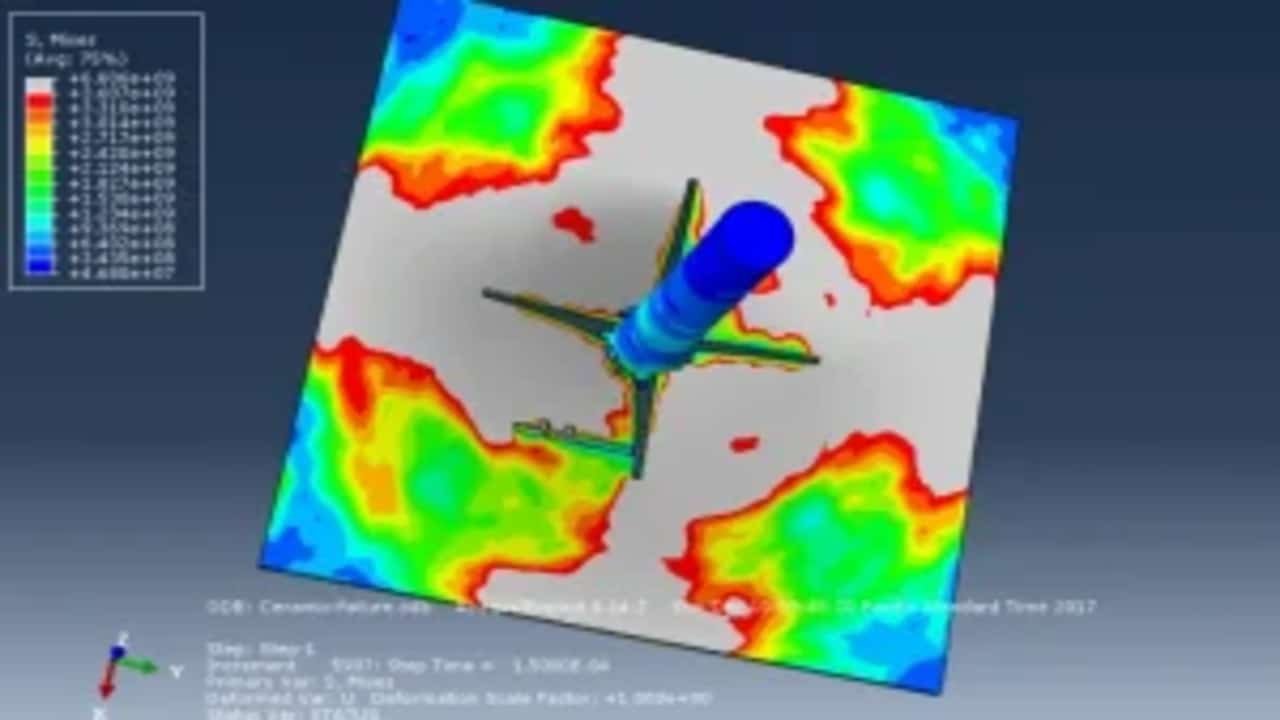
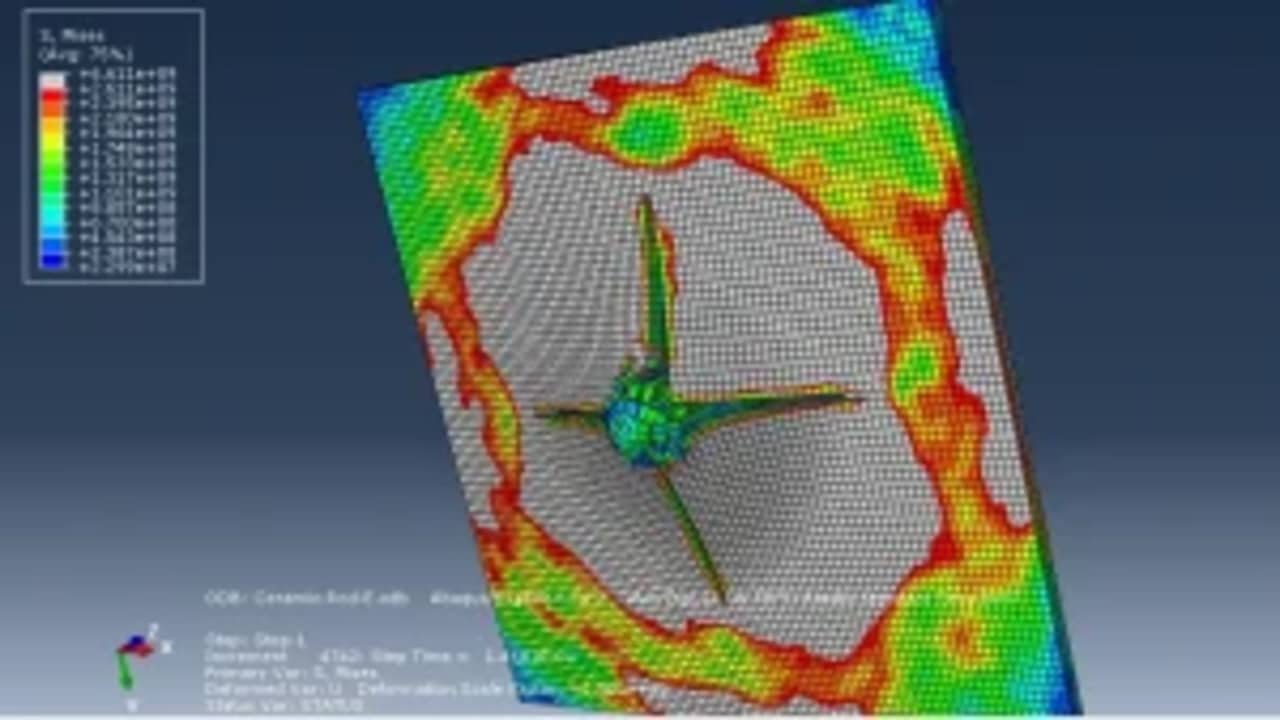
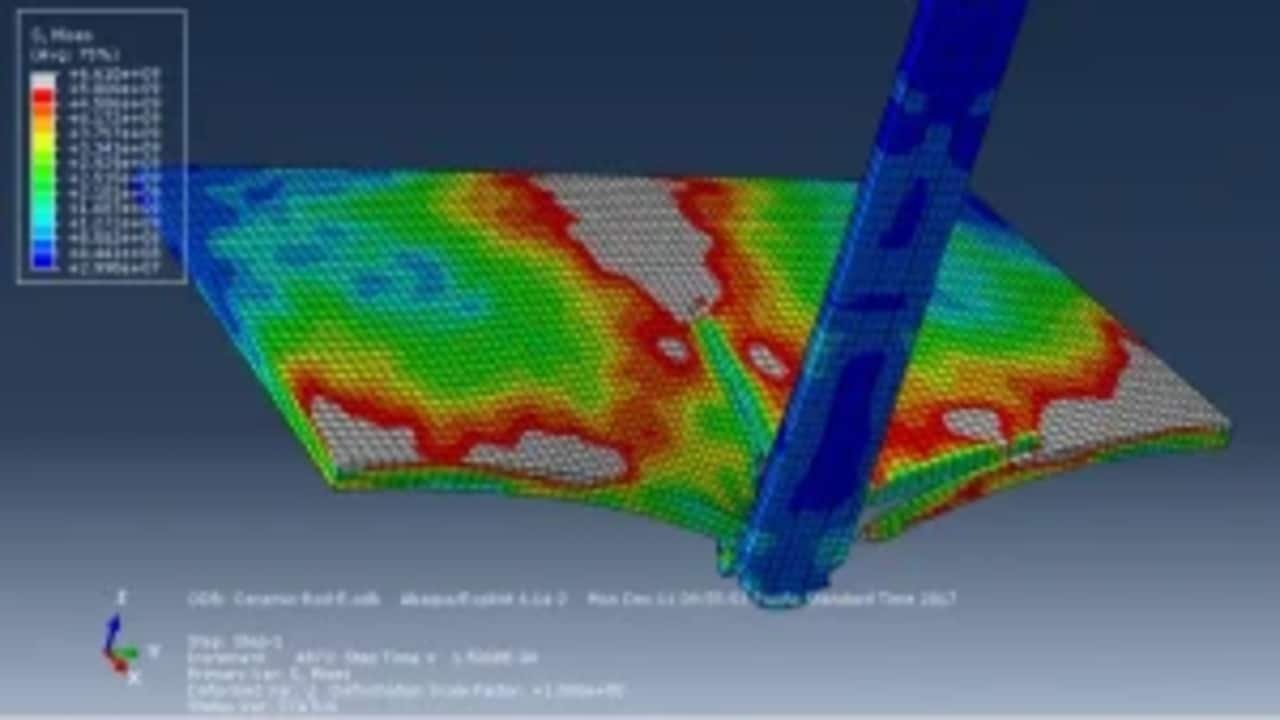
In order to simulate foreign object damage (FOD) phenomenon in aircraft high-pressure compressor blades made of a nickel-based super-alloy, Johnson–Cook (J–C) plasticity model was used. For prediction of material’s plastic behavior at temperature of 400 °C (working temperature of the blades) in the range of strain rates associated with the FOD phenomenon (in order of 106 s21), material parameters of A, B, C, n and m for the J–C plasticity model had to be determined experimentally. Parameters of A, B and n with values of 1108, 699 MPa and 0.5189, respectively, were obtained from quasi-static tensile tests. Moreover, m was determined to be 1.2861, also through quasi-static tensile tests with a strain rate of 1 s21 at three temperatures of 475, 550 and 625 °C. However, in order to determine C, firstly a steel ball was impacted on the surface of a flat specimen made of a precipitation-hardening alloy, and then, the impact site was 3D scanned to obtain the induced crater profile. Finally, the impact test (ballistic) was simulated using Abaqus, and a C value of 0.0085 was determined by comparing the actual crater profile with the one obtained from the simulation through a trial-and-error approach.
Product Overview:
This tutorial provides a step-by-step Abaqus simulation of cold spray deposition, where steel particles impact an Inconel718 target, replicating high-velocity impact conditions. Key simulation steps include:
In this tutorial, particle-substrate interactions are simulated, according to data from the work of Farahani et al.

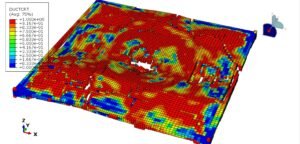
Abaqus
€81,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€299,00 €249,00

Uncategorized
€95,00 €80,00
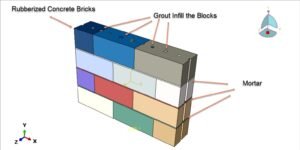
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
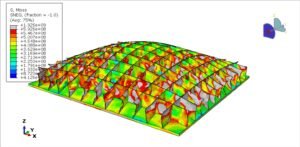
Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?