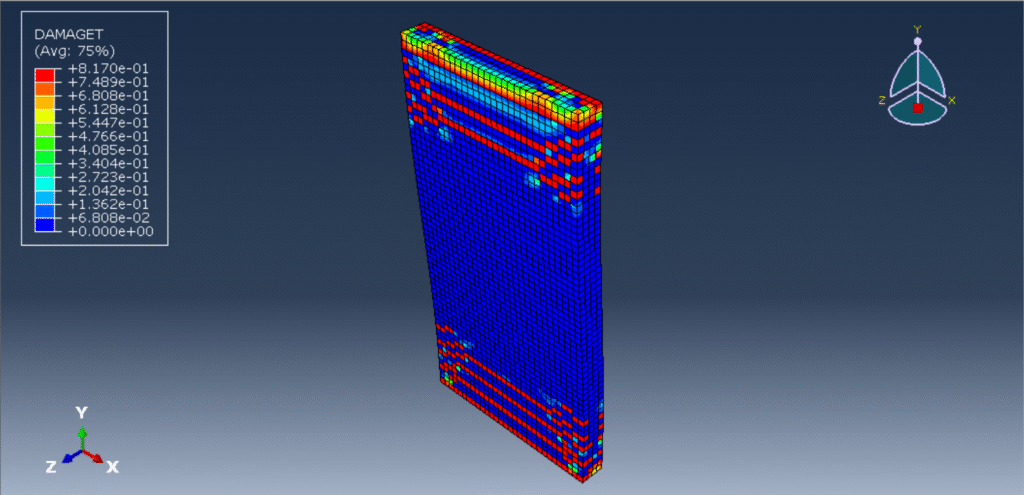
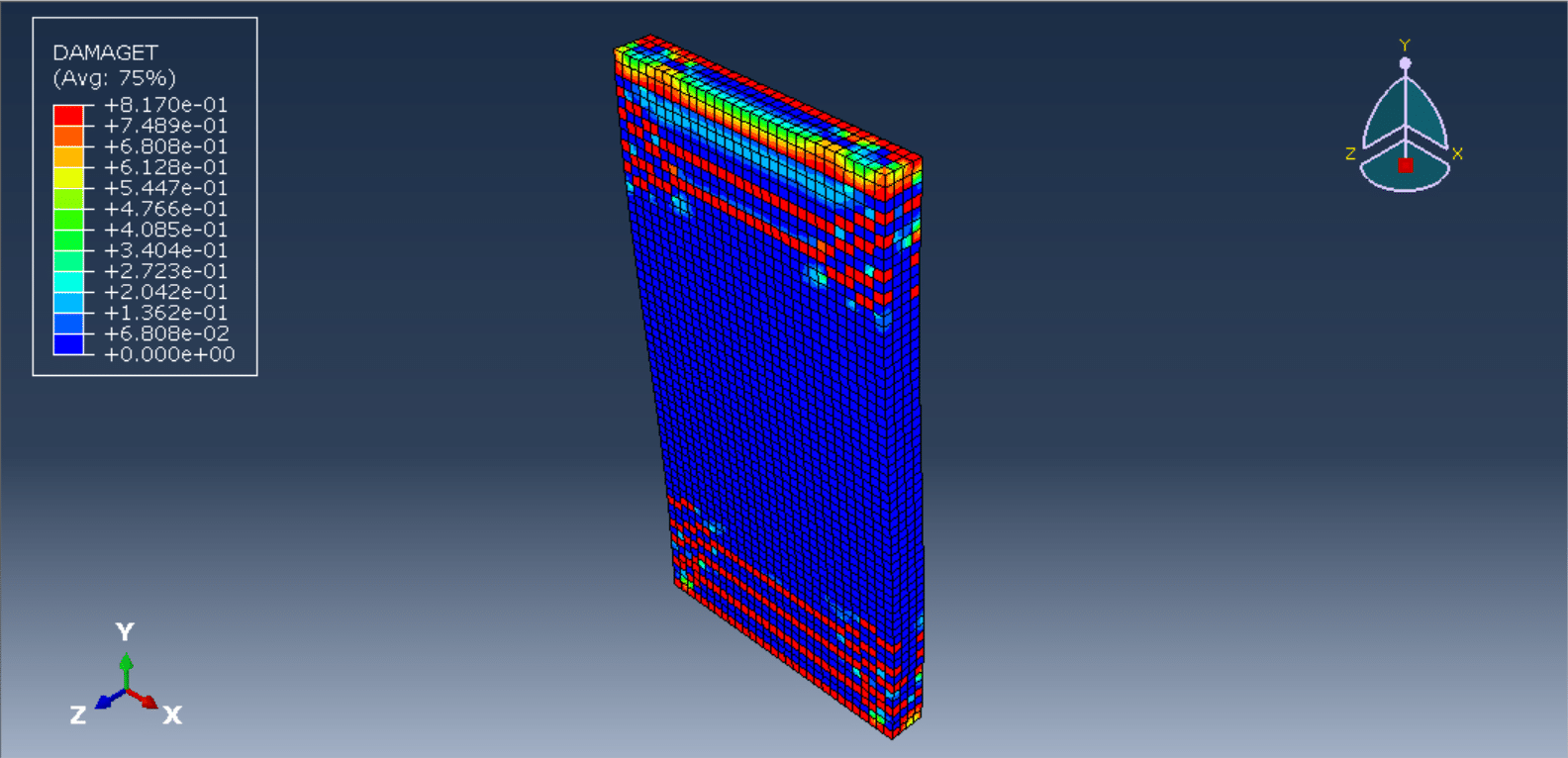
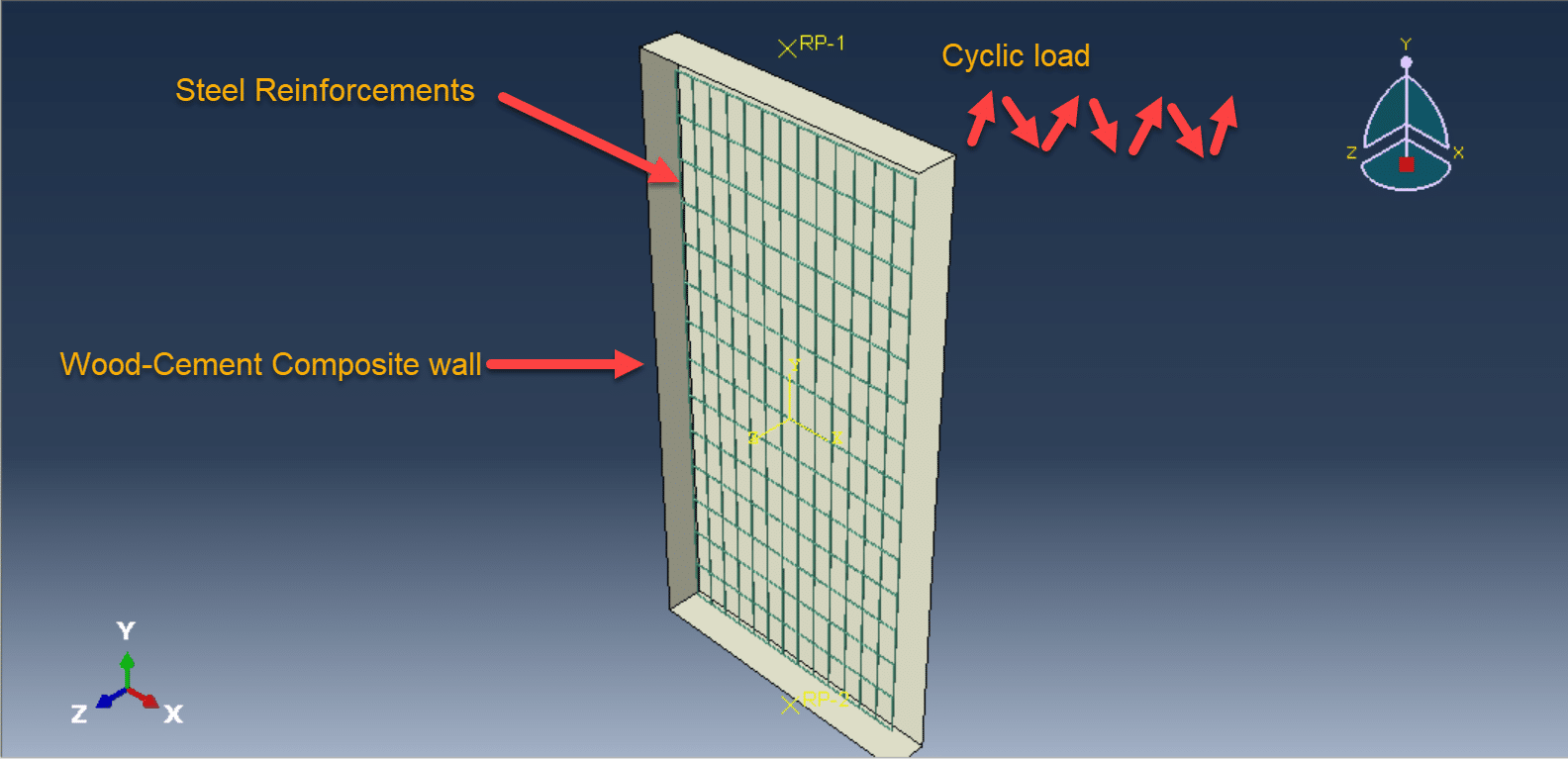
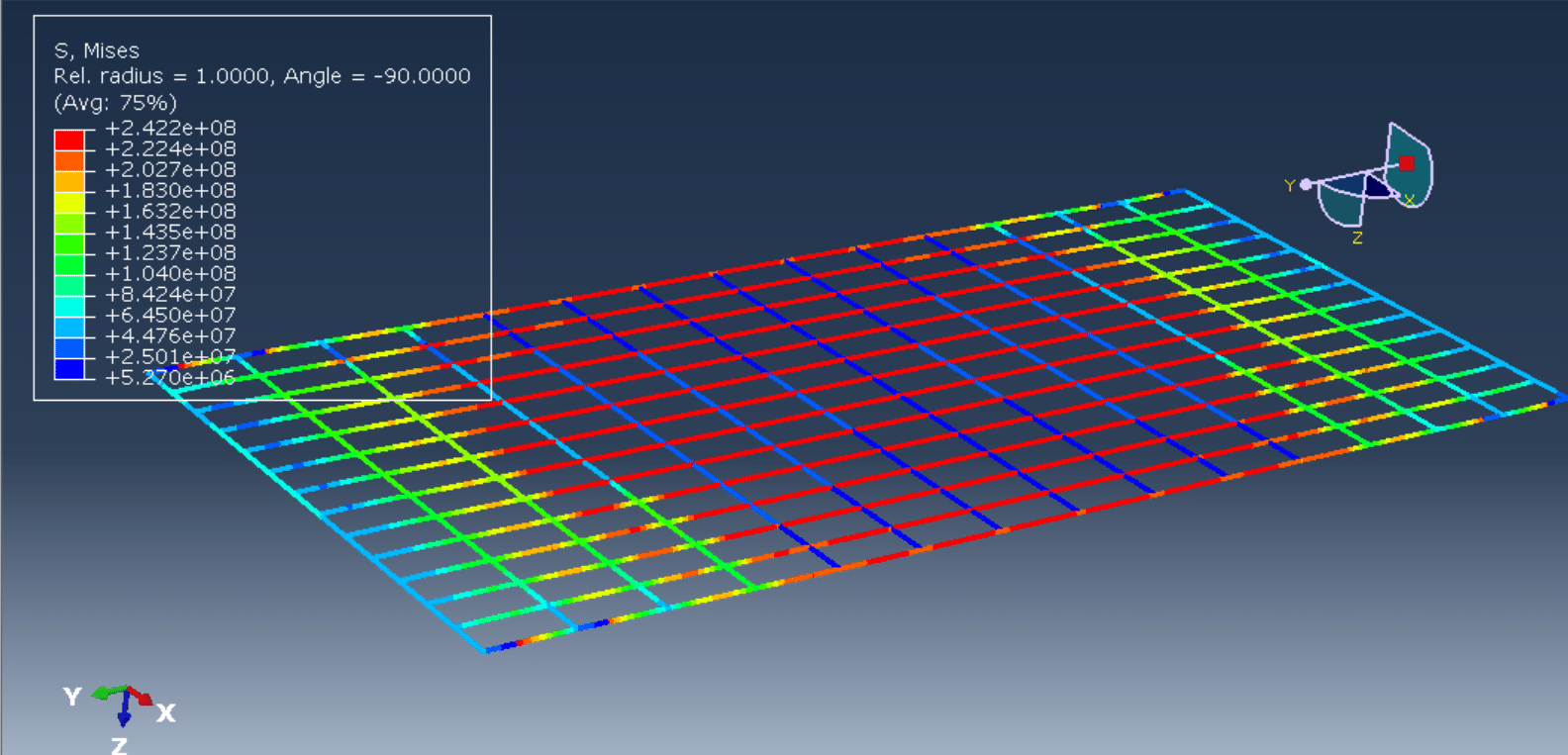
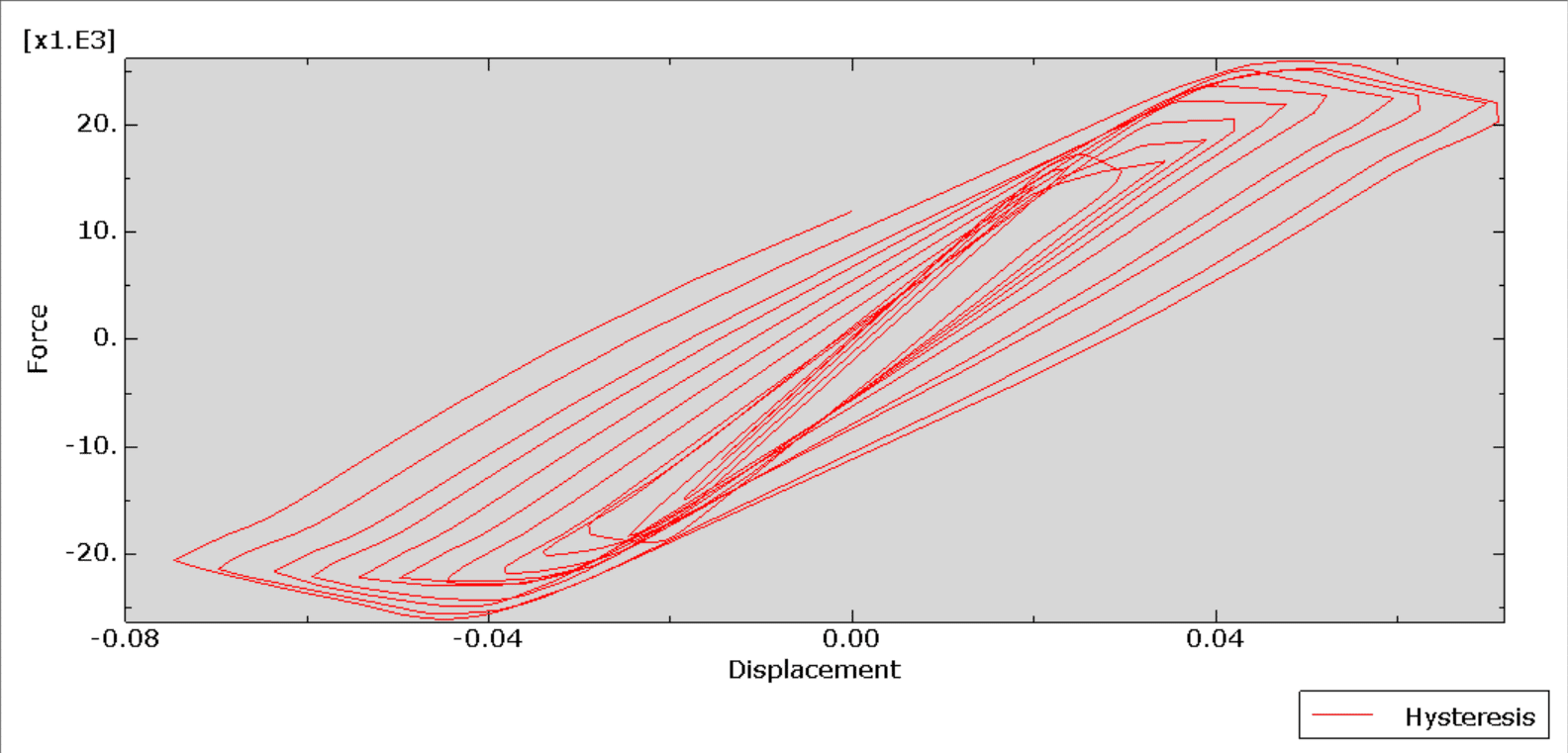
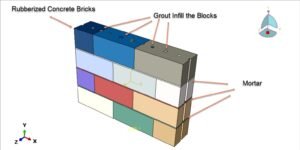
The cyclic loading analysis of a reinforced wood-cement wall is a critical aspect of evaluating the wall’s structural performance, especially under dynamic or seismic loads. Wood-cement composites, often referred to as cement-bonded particleboards or wood-cement panels, combine the sustainability and flexibility of wood with the durability and compressive strength of cement. When reinforced with materials such as steel bars, fiberglass mesh, or additional wood reinforcements, these walls offer improved strength and ductility, making them suitable for use in load-bearing and non-load-bearing structures in seismic-prone areas.
Cyclic loading, which involves repeated application of loads that vary in magnitude and direction (often simulating earthquake forces), is essential for understanding how such composite walls will perform under real-world dynamic conditions. Unlike monotonic loading, cyclic loading subjects the material to repeated stress reversals, which can lead to fatigue, cracking, and eventual failure.
This type of analysis typically involves subjecting the wall specimens to a controlled cyclic displacement or load pattern while monitoring their structural response, including parameters like load capacity, stiffness degradation, energy dissipation, and failure modes. The analysis helps determine the ductility, resilience, and damage tolerance of the wall system.
Reinforced wood-cement walls under cyclic loading are studied to:
Assess their seismic resistance.
Optimize reinforcement layouts.
Improve connection details.
Enhance construction practices for better safety and performance.
With increasing interest in sustainable and resilient building materials, understanding the cyclic performance of wood-cement composites is vital for advancing the use of eco-friendly alternatives in modern construction, particularly in areas subject to seismic activity.
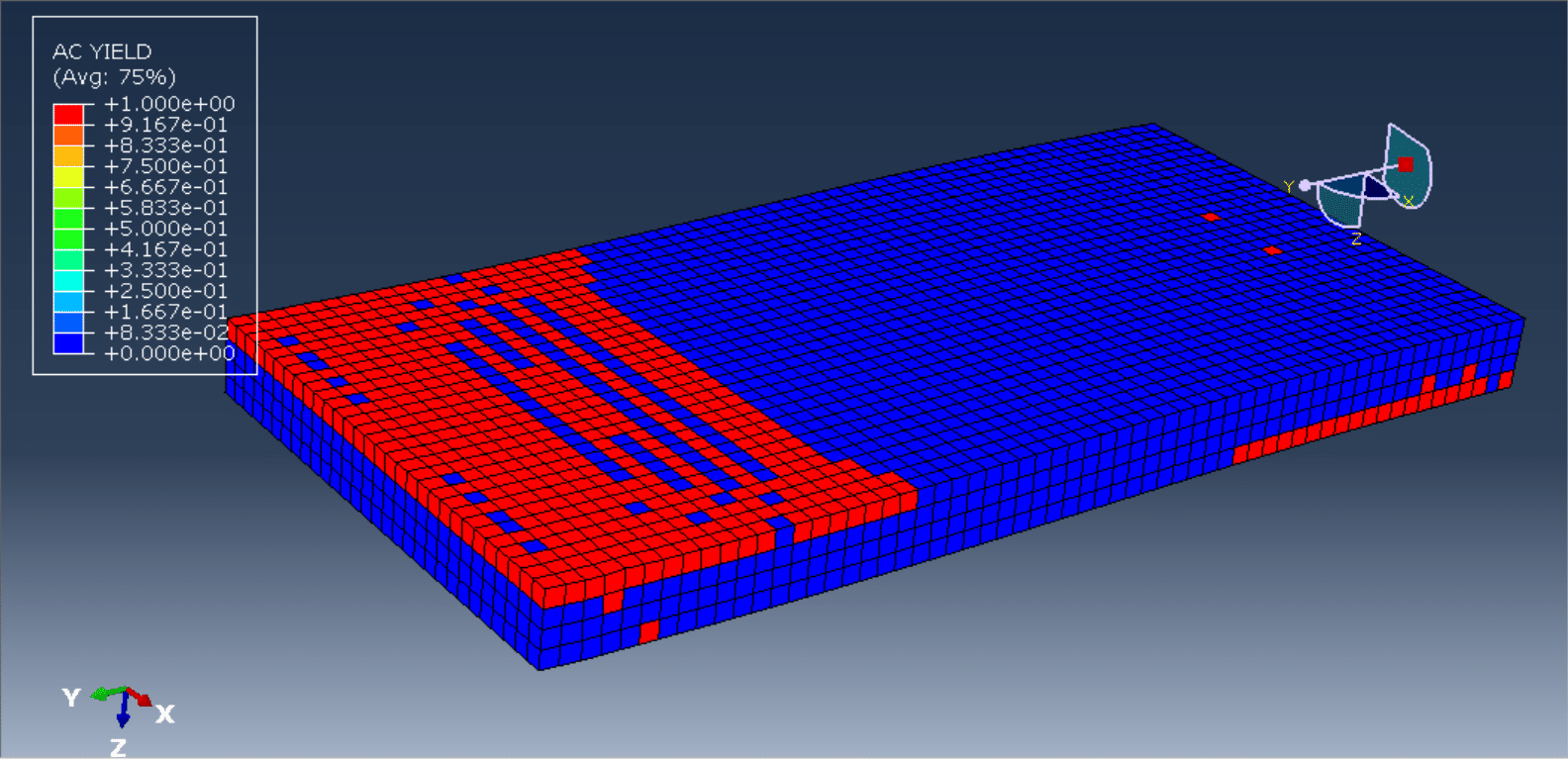
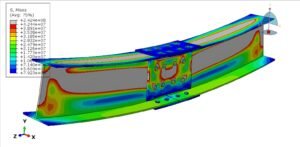
Reinforced wood-cement walls are subjected to quasi-static or dynamic cyclic loading protocols, typically following standards such as ASTM E2126, EN 12512, or FEMA 461. These tests generate load-displacement hysteresis curves, from which structural behavior such as strength degradation, pinching effects, and failure modes (e.g., crushing, shear sliding, reinforcement yielding) can be characterized.
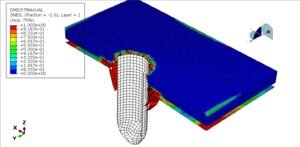
Furthermore, numerical modeling and finite element simulations are often employed in parallel with experimental work to predict performance under various loading scenarios and to inform the design process. The integration of mechanical fasteners, reinforcement detailing, and boundary conditions plays a crucial role in the global response of the wall system.

Abaqus
€81,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€299,00 €249,00

Uncategorized
€95,00 €80,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €38,00
Abaqus
€68,00 €34,00
Abaqus
€77,00 €39,00
Abaqus
€79,00 €39,00
See more

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?