undefined




Papers abstract:
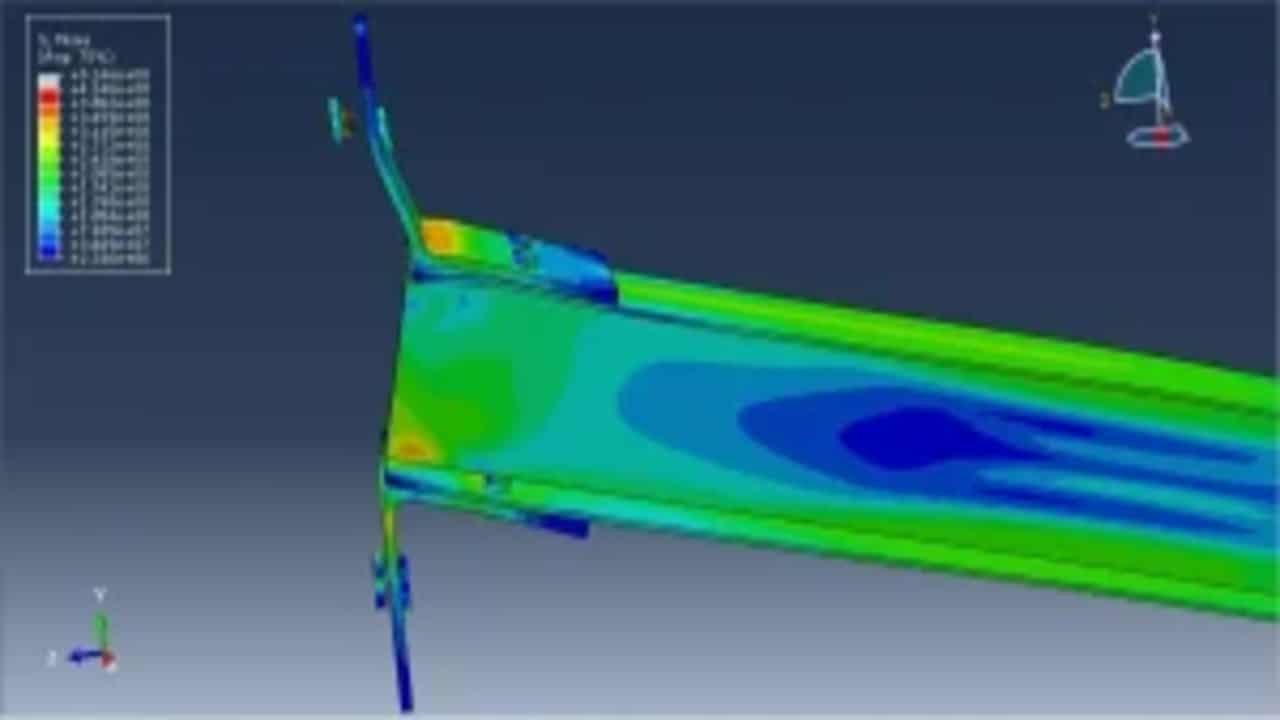
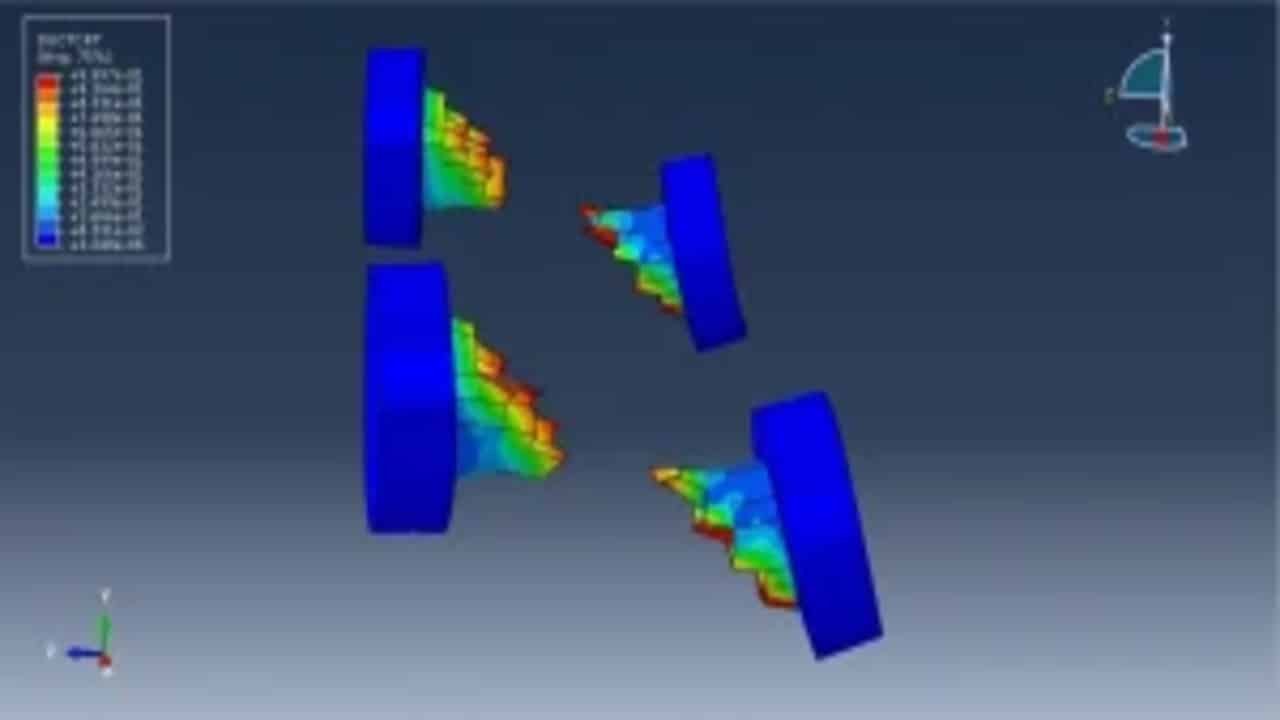
Most of the studies in the area of stainless-steel structures concentrated on the structural performance of separate members, while the response of stainless-steel connections (especially beam-to-column ones) still has not been well-researched. Some numerical investigations were conducted on these connections, however, in addition to their very limited number, they were all undertaken depending on computationally-demanding three-dimensional (3D) solid models. This paper presents for the first time a simplified finite element model able to simulate the behavior of stainless-steel beam-to-column bolted joints, whilst in the companion paper the suggested model is employed to carry out the first exhaustive parametric study on end-plate connections produced from stainless steel. The proposed model has been constructed using 3D shell elements, taking into account the complex interactions between connection components, as well as the geometric and material nonlinearities (including the considerable strain-hardening of austenitic stainless-steel grades). The model was then verified against full-scale tests on stainless steel beam-to-column connections, and very good agreement between the experimental and numerical results (i.e., initial stiffness; ultimate moment capacity; overall moment-rotation response; and failure patterns) was achieved. With regard to computational time, the developed shell model demonstrated apparent superiority, consuming less than 20% of the CPU time of its 3D solid counterpart. Given its efficiency and high accuracy, the suggested model can pave the way for comprehensive systematic studies on beam-to-column connections made of stainless steel.
Product Overview:
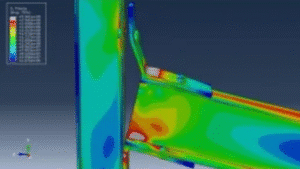
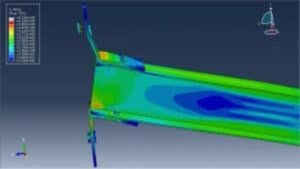
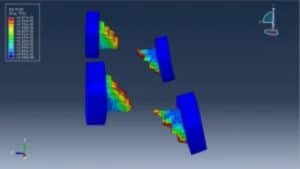
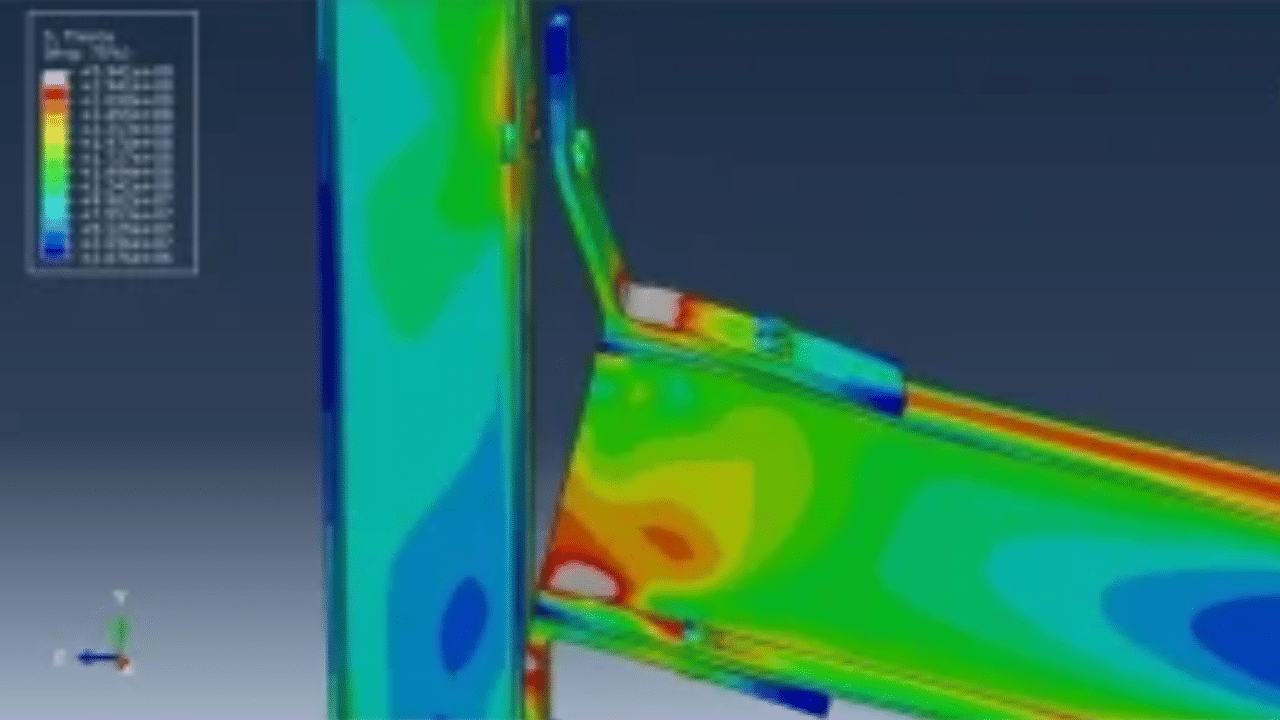
This tutorial explores the simulation of dynamic failure behavior of steel beam-to-column bolted connections in AbStainless steel jointsaqus. While most studies model stainless steel connections using shell elements, this model employs full 3D solid parts with nonlinear behavior and failure tracking. The simulation targets the critical zones—especially bolt failure zones—under dynamic loading. Key simulation steps include:
In this tutorial, dynamic failure of steel beam-to-column bolted joints is simulated, according to data from the work of Mohammed M. Eladly.
We connect engineers through:

Want to receive push notifications for all major on-site activities?