Introduction to OpenSees
OpenSees (Open System for Earthquake Engineering Simulation) is an open-source software platform developed by the Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center (PEER). It is specifically designed for the finite element analysis (FEA) of structural and geotechnical systems, with an emphasis on nonlinear and dynamic behavior under seismic loads. OpenSees is widely used in both academia and industry for research, performance-based design, and advanced structural assessments.
Key Capabilities for Structural Analysis
Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis
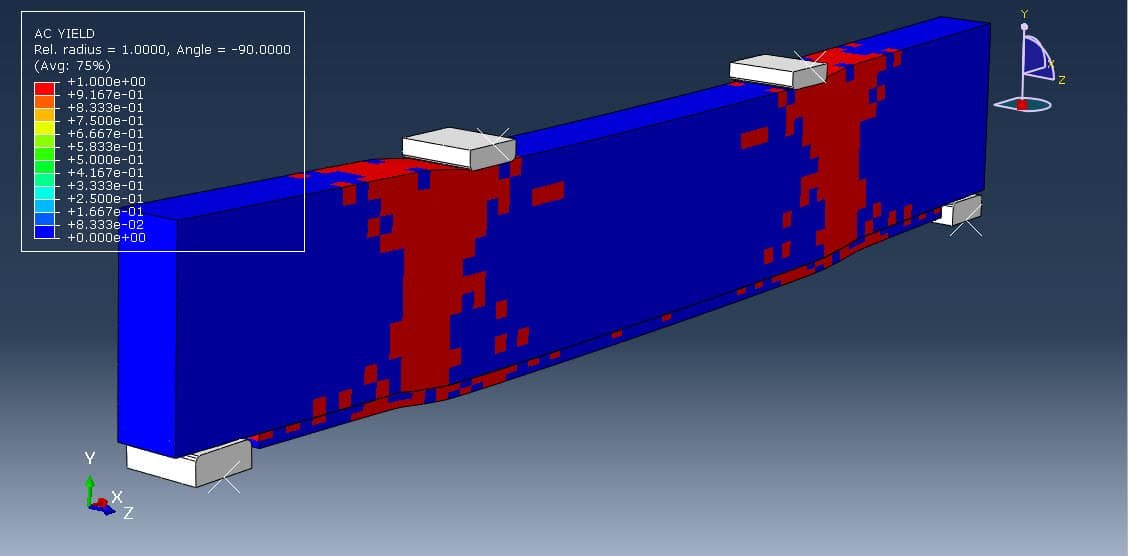
OpenSees excels at modeling nonlinear behavior of structures, which is critical for realistic simulation of structural response under extreme events like earthquakes.
It supports both static (pushover) and dynamic (time-history, response spectrum) analyses.
Rich Library of Materials and Elements
Offers a vast selection of material models (e.g., concrete, steel, soil) including highly nonlinear and cyclic behaviors, creep, shrinkage, and damage models.
Supports a variety of finite elements: beams, trusses, shells, solids, and advanced types like fiber-section elements for detailed cross-section modeling.
Soil-Structure Interaction
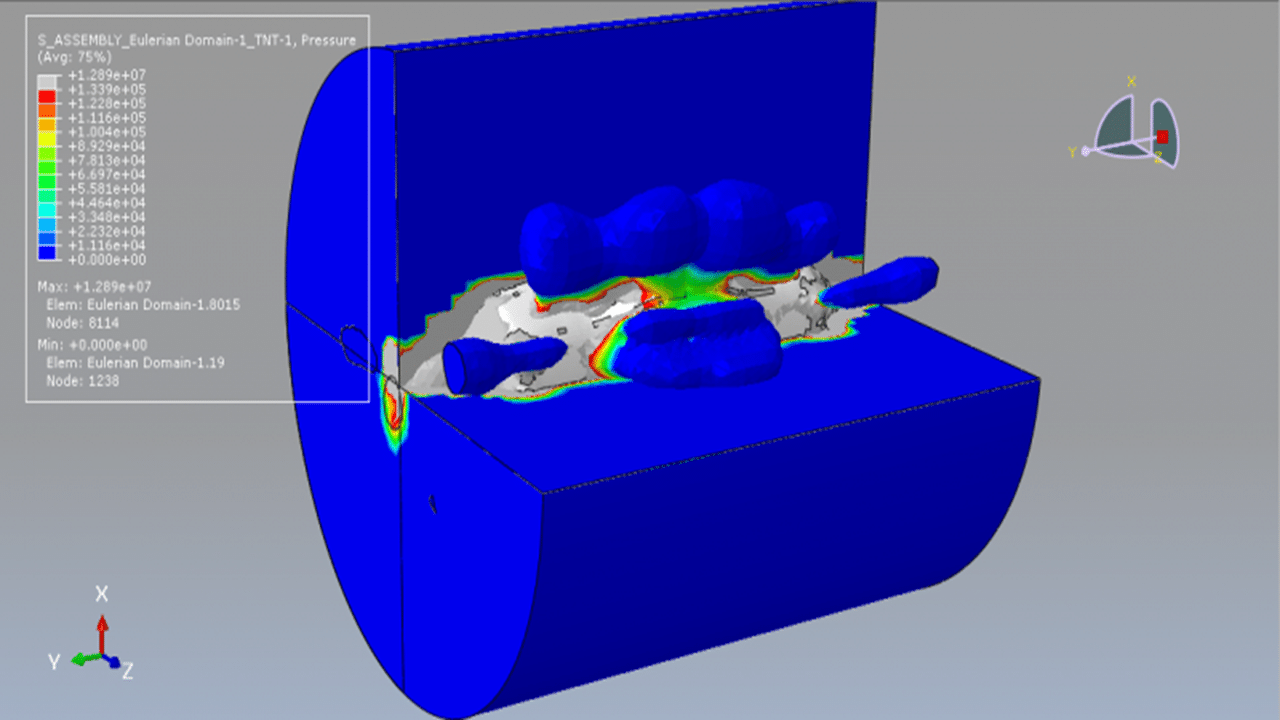
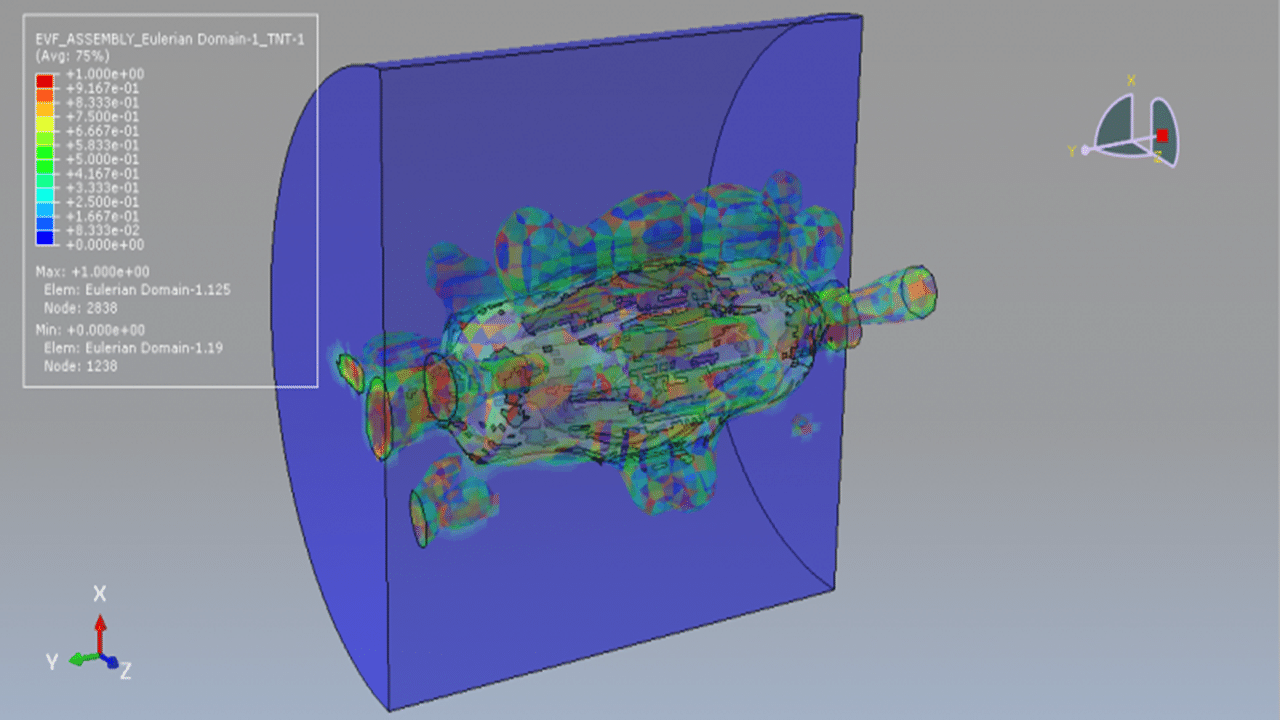
Capable of simulating coupled soil-structure systems, enabling assessment of foundation and ground effects on structural performance.
Scripting and Automation
Models are created using scripting languages (primarily Tcl and Python via OpenSeesPy), allowing for automation, parametric studies, and batch processing.
This scripting flexibility is particularly useful for research and custom analysis workflows.
Customization and Extensibility
As open-source software, OpenSees allows users to develop and implement new materials, elements, and solution algorithms—ideal for cutting-edge research or unique project requirements.
Pros of OpenSees
Highly Flexible & Extensible: Perfect for advanced or non-standard analyses, and for developing new modeling approaches.
Advanced Nonlinear Modeling: Particularly strong in simulating inelastic behavior, degradation, and collapse mechanisms.
Cost-Effective: Completely free and open-source—no licensing fees.
Scriptable & Automatable: Enables large-scale studies and easy integration with other tools (e.g., MATLAB, Python).
Strong for Research: Widely recognized and accepted in academic publications, especially for earthquake engineering and performance-based design.
Cons of OpenSees
Steep Learning Curve: Requires familiarity with scripting (Tcl or Python) and a solid understanding of finite element principles.
Lack of Native GUI: Most modeling is done via scripts; visualization and pre/post-processing often require external tools or third-party add-ons.
Fragmented Documentation: While there are many resources, they can be scattered and sometimes technical, making it challenging for beginners.
Community-Based Support: Support is primarily through user forums and community contributions, rather than dedicated professional support.
Computational Demands: Large or highly nonlinear models can be computationally intensive and may require careful tuning of analysis parameters.
Expanded Perspective and Real-World Applications
OpenSees is especially valuable for:
Seismic performance assessment of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure.
Nonlinear pushover and time-history analyses for collapse prediction.
Soil-structure interaction studies and geotechnical modeling.
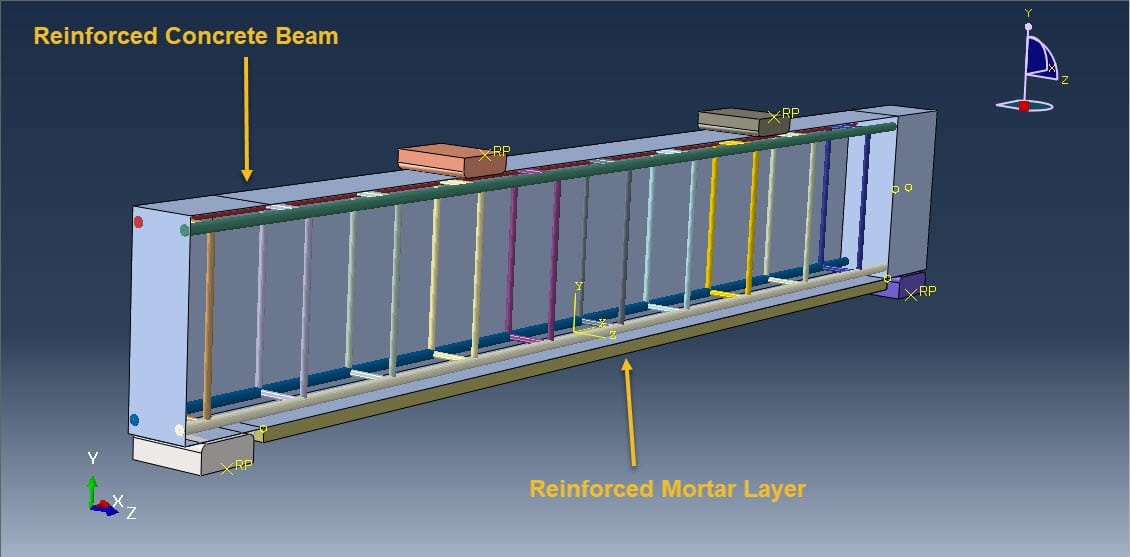
Developing and testing new materials or structural systems (e.g., innovative retrofitting techniques, like CFRP-strengthened RC beams).
Academic research in advanced structural mechanics and earthquake engineering.
However, for routine design tasks or when a GUI-driven, out-of-the-box solution is needed, commercial software (such as SAP2000, ETABS, or Abaqus) may be more efficient.
Conclusion
If your work involves detailed nonlinear modeling, research, or the need for custom analysis routines, OpenSees is a powerful and versatile tool—especially for earthquake engineering and performance-based assessment. Its scripting nature means a higher learning curve, but the flexibility and capability it offers are unmatched in the open-source FEA world.